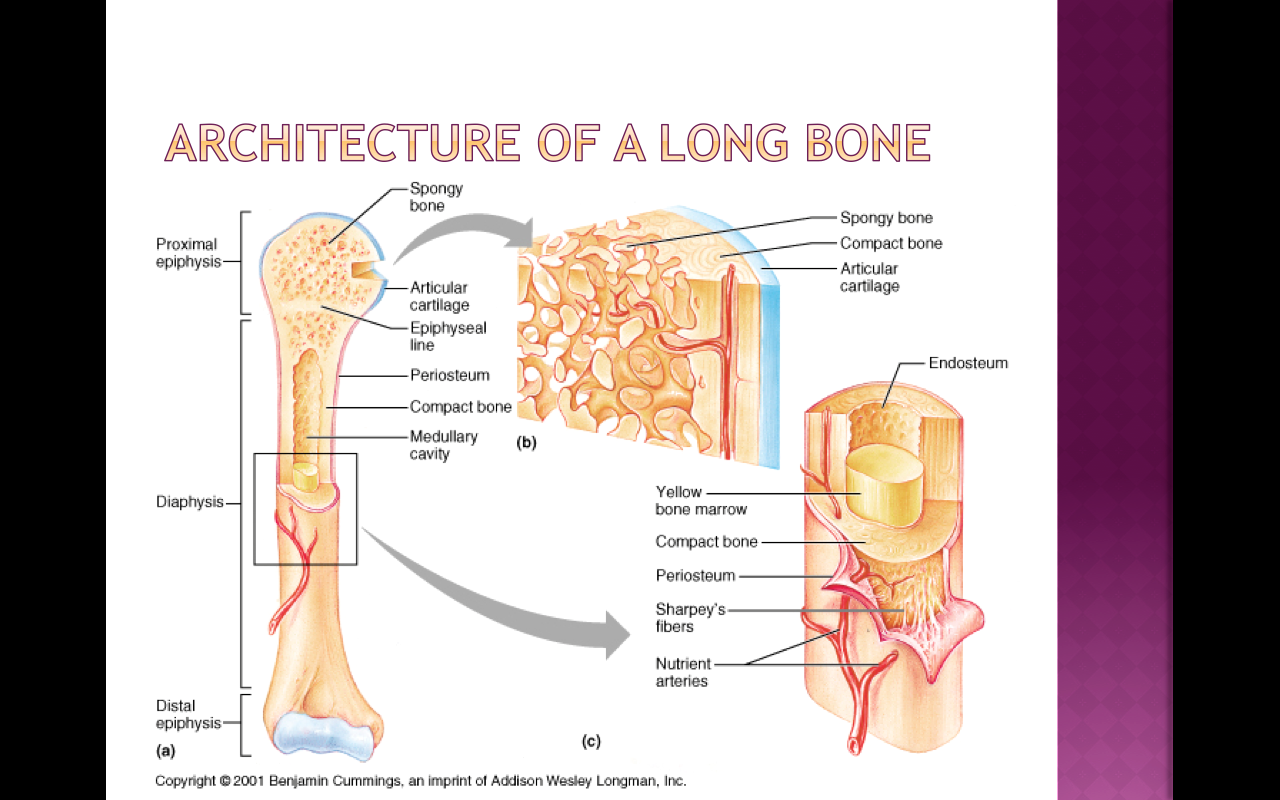
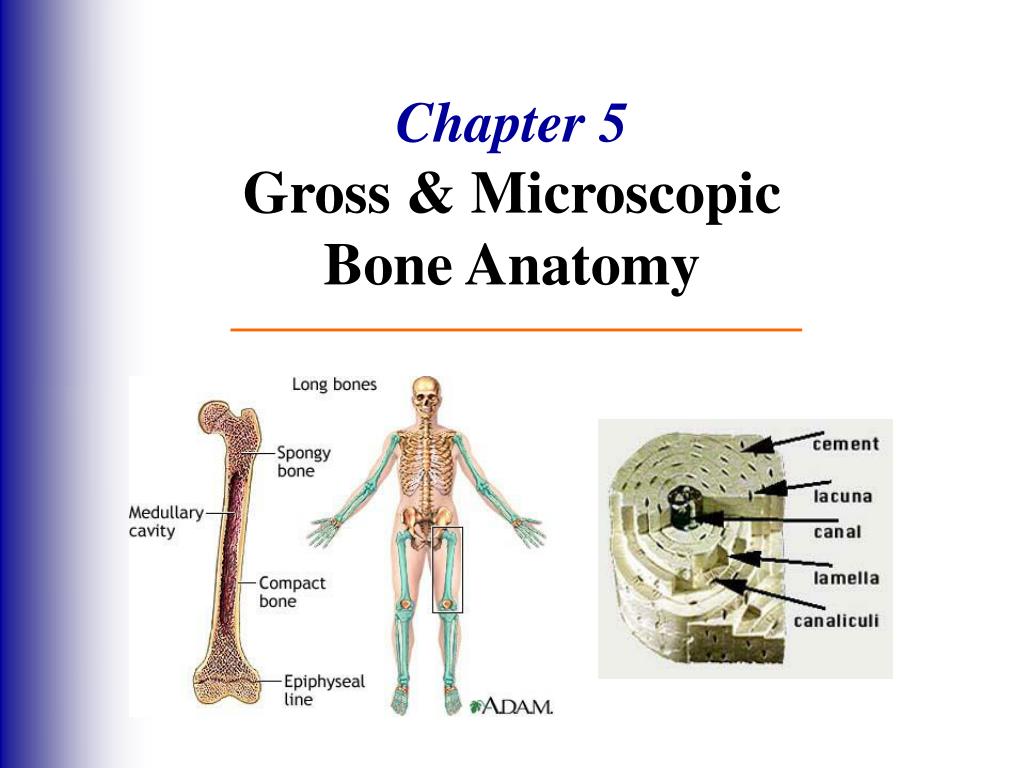
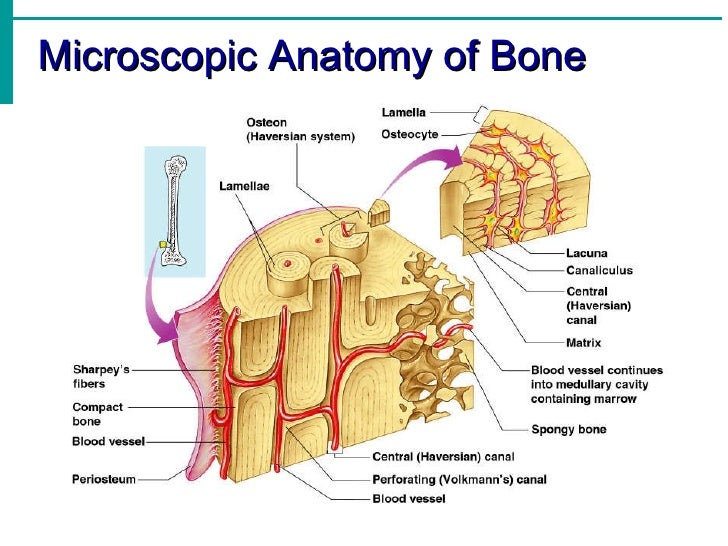
Anatomy of a long bone. Matrix consists of two parts organic and inorganic.
 Module 6 2 Microscopic Structure Of Bone Tissue Arteries
Module 6 2 Microscopic Structure Of Bone Tissue Arteries
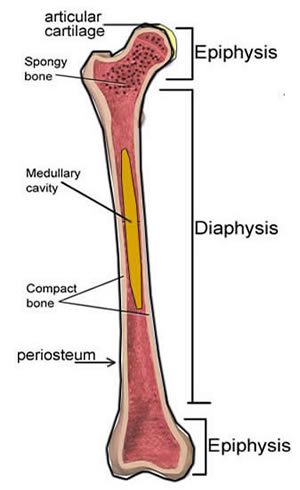
A typical long bone shows the gross anatomical characteristics of bone.
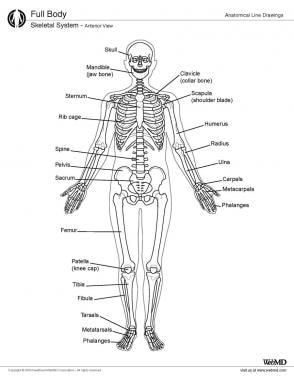
Microscopic bone anatomy. Microscopic anatomy of bone key points. Woven bone is found on the growing ends of an immature skeleton or in adults. 0 0000 a shoutout is a way of letting people know of a game you want them to play.
These either fill the gaps between forming osteons or are remnants of osteons that have been cut through by bone remodeling. Filled with bone ma. Bone matrix is laid down by osteoblasts as collagen also known as osteoid.
Cavity within the shaft of the long bones. In the center of these layers is a canal called the haversian canal or central canal. Bones are composed of bone matrix which has both organic and inorganic components.
Red marrow fills the spaces in the spongy bone. It can be found under the periosteum and in the diaphyses of long bones where it provides support and protection. The wider section at each end of the bone is called the epiphysis plural epiphyses which is filled with spongy bone.
Osteoid is hardened with inorganic salts such as calcium and phosphate and by the chemicals released from the osteoblasts through a process known as mineralization. Just pick an audience or yourself and itll end up in their incoming play queue. It consists of cells and intercellular substance or matrix.
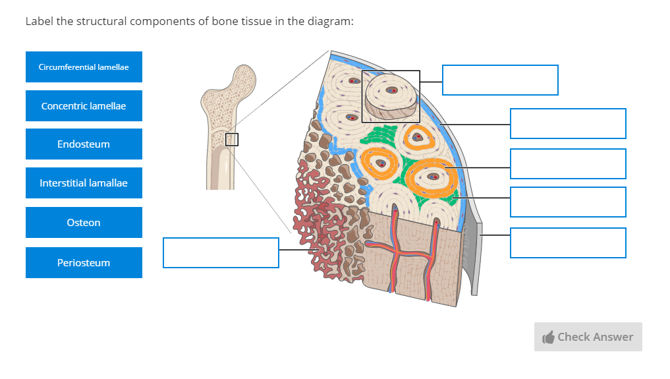
Tough layer of connective tissue surrounding a bone. Each osteon is composed of concentric rings of calcified matrix called lamellae singular lamella. Compact bone is the denser stronger of the two types of bone tissue.
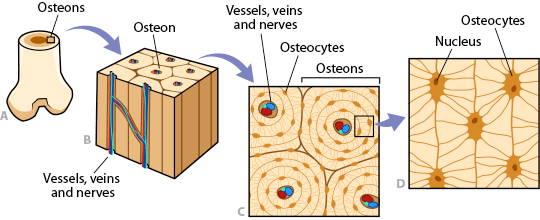
Layer of bone tissue that has many small spaces and is found j. The microscopic structural unit of compact bone is called an osteon or haversian system. Microscopic anatomy of bone.
Bone is a specialised connective tissue. Each of these layers is called a lamellae. Woven bone is characterized by the irregular.
Read this article to learn about the microscopic anatomy of bone. Lying between intact osteons are incomplete lamellae called interstitial lamellae inter stishal figure 66c. Dense hard layers of bone tissue that lie underneath the peri.
Four types of cells are recognised in bone tissue osteoprogenitor cells osteoblasts osteocytes and osteoclasts. The basic microscopic unit of bone is an osteon or haversian system. So each of these osteons looks like of like a cylinder and it has multiple concentric layers of bone or sheets really that wrap around each other to form this osteon.
 Microscopic Structure Of Bone The Haversian System Video
Microscopic Structure Of Bone The Haversian System Video
 Chapter 5 Microscopic Bone Anatomy Part Ii Diagram Quizlet
Chapter 5 Microscopic Bone Anatomy Part Ii Diagram Quizlet
 Skeletal System Anatomy In Children And Toddlers Overview
Skeletal System Anatomy In Children And Toddlers Overview
 Ppt Skeletal System Powerpoint Presentation Free Download
Ppt Skeletal System Powerpoint Presentation Free Download
 A P 1 Unit 2 The Skeletal System Intro Macroscopic
A P 1 Unit 2 The Skeletal System Intro Macroscopic
 Microscopic Structure Of Compact Bone Skeletal System
Microscopic Structure Of Compact Bone Skeletal System
 Macroscopic Microscopic Structure Of Skeletal System
Macroscopic Microscopic Structure Of Skeletal System
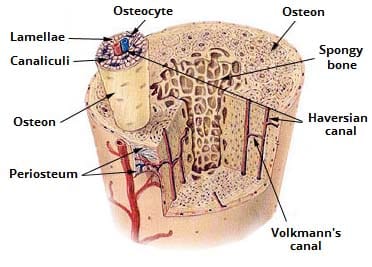 Ultrastructure Of Bone Components Structure Teachmeanatomy
Ultrastructure Of Bone Components Structure Teachmeanatomy
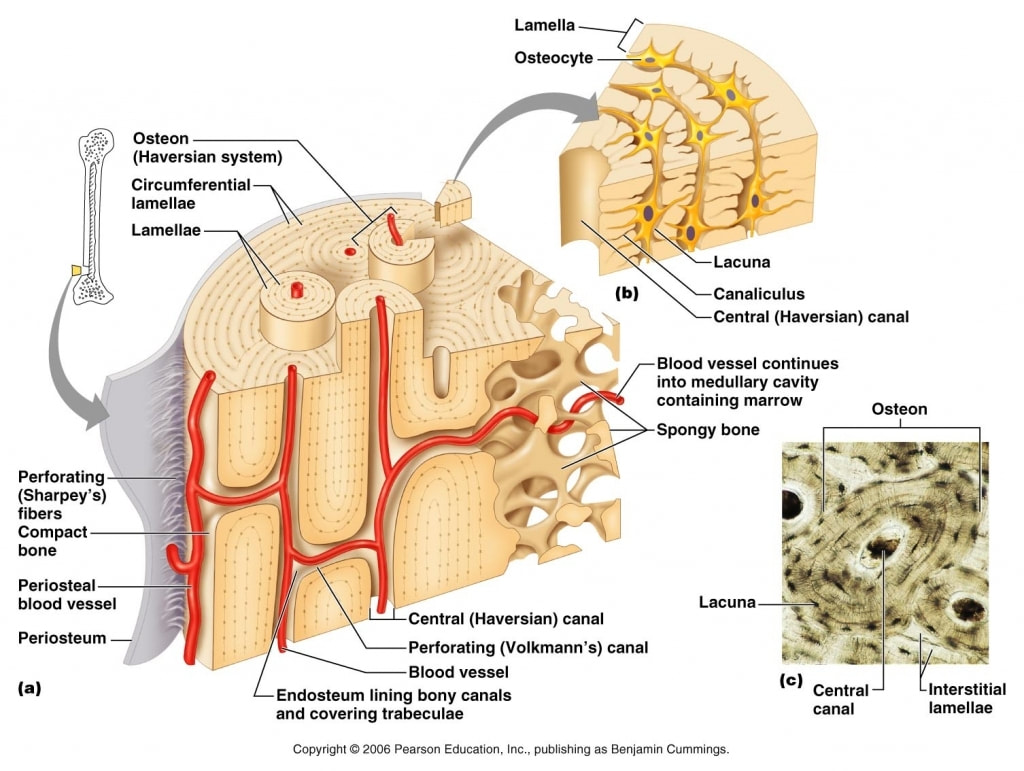 Skeletal System Mrs Merritt S Anatomy Class
Skeletal System Mrs Merritt S Anatomy Class
 Skeleton Human Anatomy Overview Function And Structure
Skeleton Human Anatomy Overview Function And Structure
 Skeletal System Anatomy And Physiology
Skeletal System Anatomy And Physiology
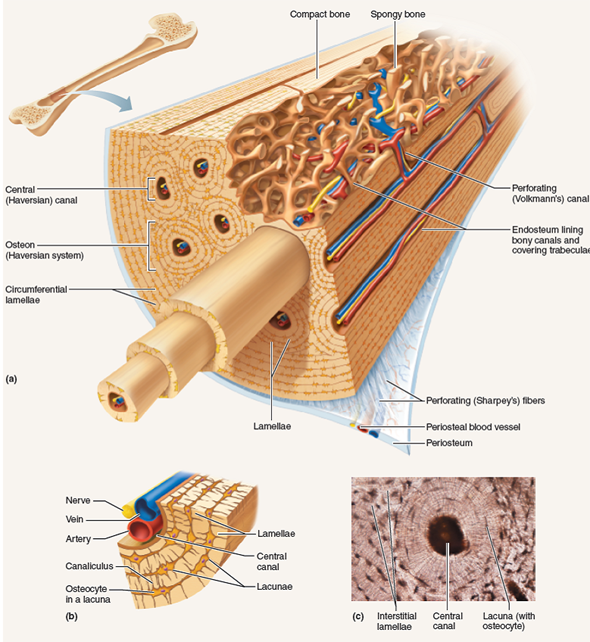 Examining The Microscopic Structure Of Compact Boneif A
Examining The Microscopic Structure Of Compact Boneif A
 Cancellous Bone Anatomy Britannica
Cancellous Bone Anatomy Britannica
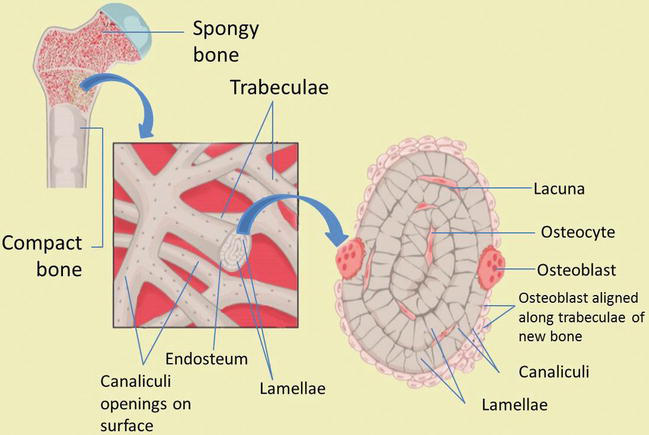 Bone Development And Growth Intechopen
Bone Development And Growth Intechopen
 Introduction To Bone Boundless Anatomy And Physiology
Introduction To Bone Boundless Anatomy And Physiology
 Ppt Chapter 5 Gross Microscopic Bone Anatomy Powerpoint
Ppt Chapter 5 Gross Microscopic Bone Anatomy Powerpoint
Introduction To Bone Boundless Anatomy And Physiology
 Compact Bone Definition Structure Function
Compact Bone Definition Structure Function
 Skeletal System Anatomy In Adults Overview Gross Anatomy
Skeletal System Anatomy In Adults Overview Gross Anatomy
 2 Microscopic Structure Of Compact Bone Download
2 Microscopic Structure Of Compact Bone Download
 Amazon Com Antique Anatomy Print Microscopic Bone Joint Pl
Amazon Com Antique Anatomy Print Microscopic Bone Joint Pl
 Bone And Cartilage Histology Lab Lt Anatomy Collection Adi
Bone And Cartilage Histology Lab Lt Anatomy Collection Adi
Microscopic Structure Of Bones
 Bone Tissue Anatomy Tissue Components
Bone Tissue Anatomy Tissue Components

Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar