The upper airway extends from the mouth to the trachea. In the nasal cavity a layer of nasal mucosa acts as a filter and traps pollutants and other harmful substances found in the air.
Anatomy of theanatomy of the upper airwayupper airway dr.
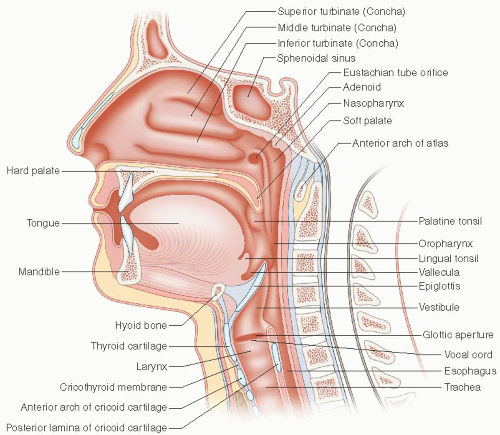
Airway anatomy. Lymph tissue filters bacteria commonly infected. Warm filter and humidify air. Saurabh barde anaest hesiology gmch nagpur.
Nasal cavity and nasopharynx. Components of the upper airwaycomponents of the upper airway nosenose nasopharynxnasopharynx. The upper airway is the a of the abcs as such it takes on special importance in any emergency response.
Next air moves into the pharynx a passage that contains the intersection between the oesophagus and the lary. The nose is a structure of the face made of cartilage bone muscle and skin that supports and protects the anterior portion of the nasal cavity. As the entry point for oxygen any damage to or blockage of the structures in the upper airway can rapidly result in unconsciousness or death.
It includes the mouth the nose the palate the uvula the pharynx and the larynx. This section also describes the functional physiology of this airway. The nose and nasal cavity form the main external opening for the respiratory system and are the first section of the bodys airwaythe respiratory tract through which air moves.
The upper airway consists of the pharynx and the nasal cavities. The respiratory tract is lined with respiratory mucosa or respiratory epithelium. In humans the respiratory tract is the part of the anatomy of the respiratory system involved with the process of respiration.
However some authors include the larynx and trachea as well. The anatomy of the upper airway can be broken down into the nose mouth and throat. Upper airway anatomy definition.
Formed by union of facial bones nasal floor towards ear not eye lined with mucous membranes cilia tissues are delicate vascular adenoids. Anatomy of the respiratory system nose and nasal cavity. Air is breathed in through the nose or the mouth.
Basic airway anatomy upper airway. The upper airway is a multipurposethe upper airway is a. Managing the airway of a patient with craniofacial disorders poses many challenges to the anesthesiologist.
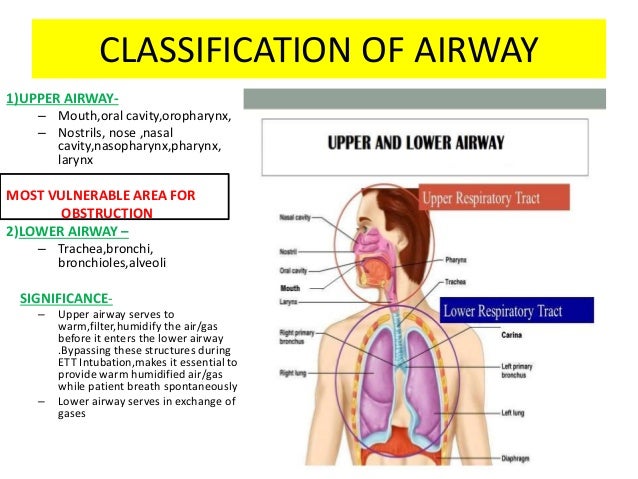 Airway Anatomy Its Assessment And Anaesthetic Implication
Airway Anatomy Its Assessment And Anaesthetic Implication
 Chapter 28 Noninvasive Airway Management Tintinalli S
Chapter 28 Noninvasive Airway Management Tintinalli S
Airway Management Module 2 1 Ceu Continuing Education From
 Regional And Topical Anesthesia For Awake Endotracheal
Regional And Topical Anesthesia For Awake Endotracheal
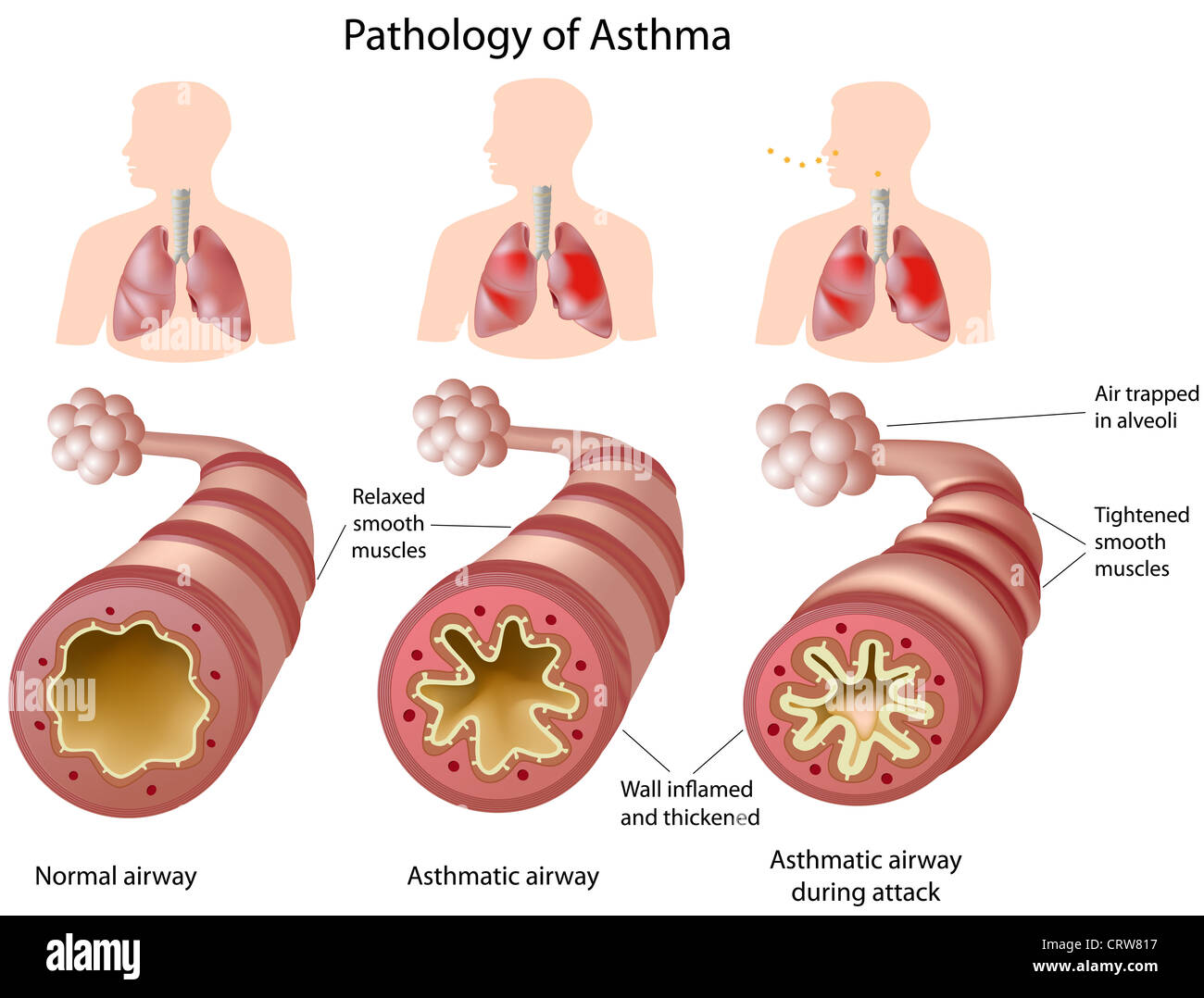 Anatomy Of Asthma Healthy Airways Versus Asthmatic Airways
Anatomy Of Asthma Healthy Airways Versus Asthmatic Airways
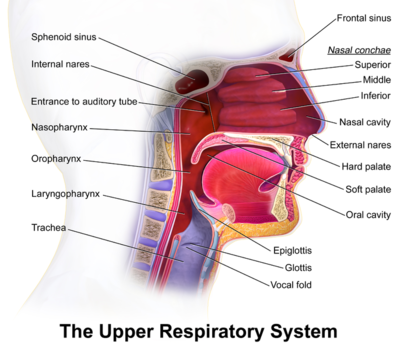 Upper Respiratory Airways Physiopedia
Upper Respiratory Airways Physiopedia
 Airway Anatomy Se Diagram Quizlet
Airway Anatomy Se Diagram Quizlet
Emdocs Net Emergency Medicine Educationtrach Travails
 Applied Functional Anatomy Of The Airway Anesthesia Key
Applied Functional Anatomy Of The Airway Anesthesia Key
 Diagram Of The Upper Respiratory System Airway Anatomy
Diagram Of The Upper Respiratory System Airway Anatomy
 Anatomy 101 Learning About Airway Walls Asthma Net
Anatomy 101 Learning About Airway Walls Asthma Net
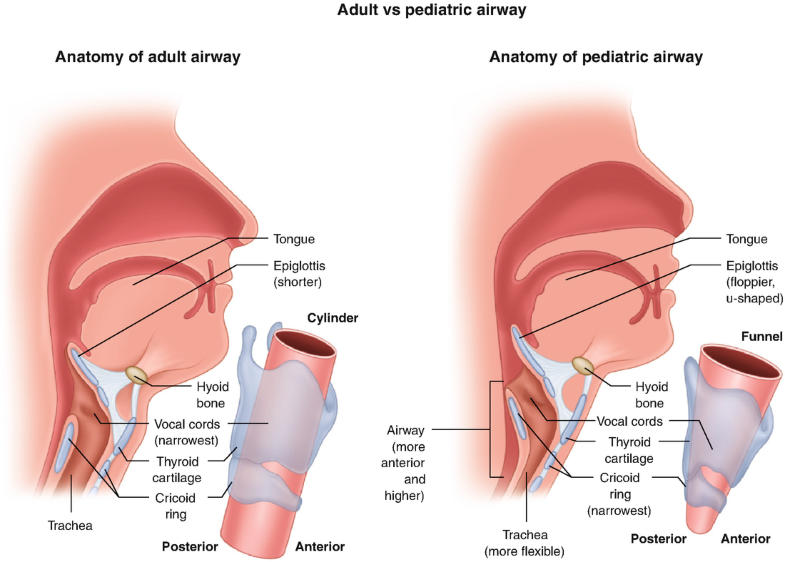 Airway Pediatric Anatomy Infants And Children Springerlink
Airway Pediatric Anatomy Infants And Children Springerlink
 Anatomy Of The Airway Springerlink
Anatomy Of The Airway Springerlink
Airway Anatomy And Physiology Clinical Essentials
 Upper Airway Anatomy Diagram Geoface F373b3e5578e Of
Upper Airway Anatomy Diagram Geoface F373b3e5578e Of
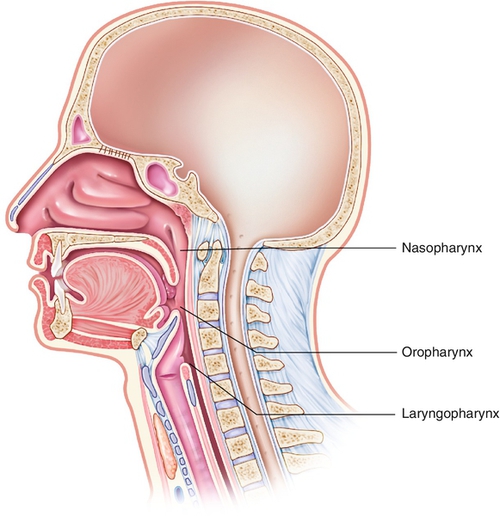 8 Anatomy And Physiology Of Respiration And Airway
8 Anatomy And Physiology Of Respiration And Airway
 Anatomy And Physiology A P Of The Upper Airway First Aid
Anatomy And Physiology A P Of The Upper Airway First Aid
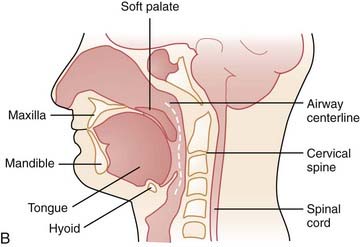 Anatomy And Physiology Of Upper Airway Obstruction Neupsy Key
Anatomy And Physiology Of Upper Airway Obstruction Neupsy Key
 Upper Airway Anatomy Snoring Sleep Apnea Stock Vector
Upper Airway Anatomy Snoring Sleep Apnea Stock Vector
 An Overview Of Airway Anatomy Emt Training Base
An Overview Of Airway Anatomy Emt Training Base
Airway Anatomy And Physiology Clinical Essentials
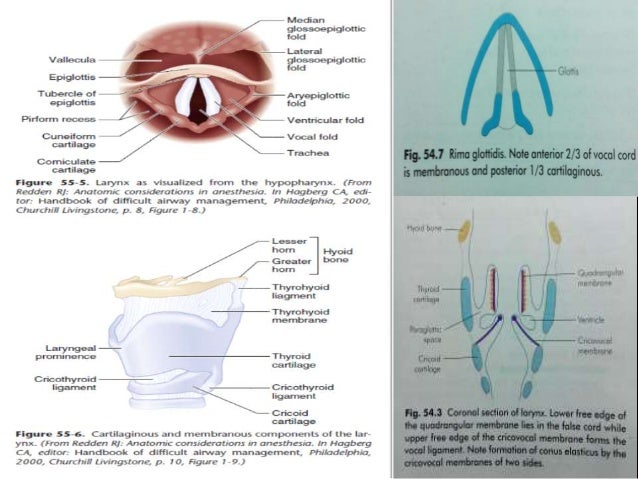
 The Mac Blade The Vallecula And The Hyoepiglottic Ligament
The Mac Blade The Vallecula And The Hyoepiglottic Ligament
 Airway And Respiratory Emergencies Anatomy Of The
Airway And Respiratory Emergencies Anatomy Of The
 Illustration Picture Of Anatomical Structures Airway
Illustration Picture Of Anatomical Structures Airway


Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar