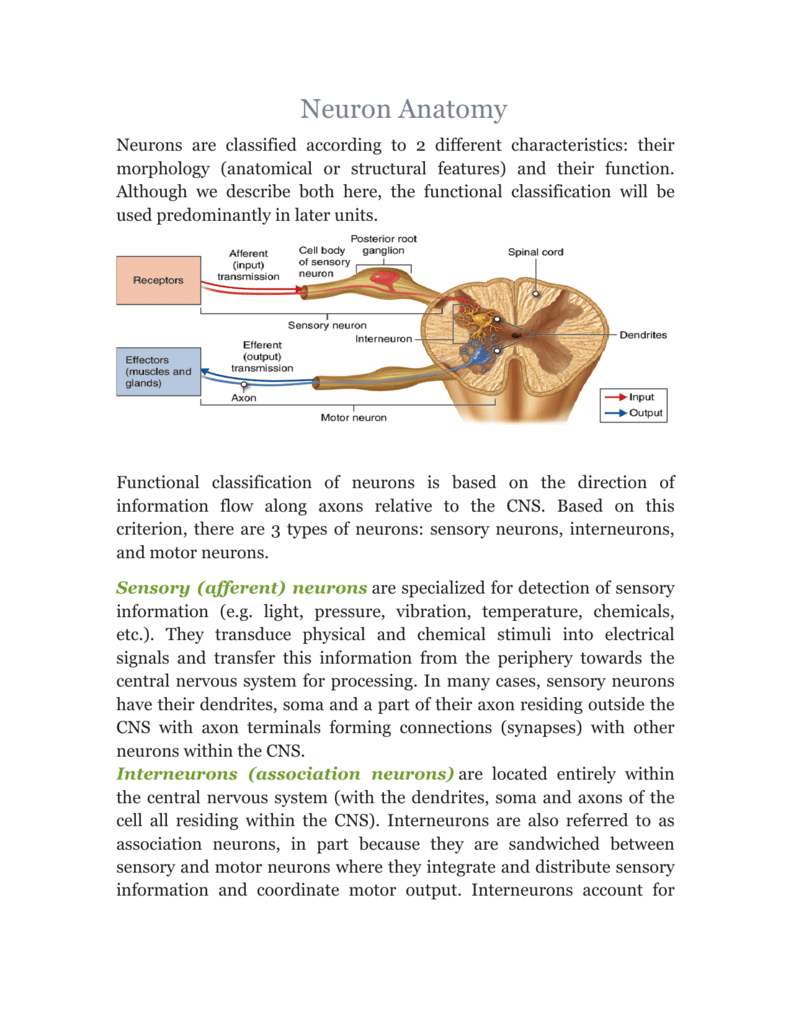
One example is the kidney which retains water if blood pressure is too low. Receptors detect changes in stimuli and message the brain about these changes while effectors take care of the changes by turning the stimuli back to its normal range.
 Autonomic Nervous System Human Anatomy And Physiology
Autonomic Nervous System Human Anatomy And Physiology
Biology any small molecule that effects the function of an enzyme by binding to an allosteric site.
Effectors anatomy. Function in reflexive muscle movement. In this manner effector molecules act as ligands that can increase or decrease enzyme activity gene expression or cell signaling. Reflex senses the stimulus and the affector the nerve cell that directly activates the muscle.
In the field of anatomy and physiology effectors refer to organs andor cells that respond to a stimulus. The sensors integrating center and effectors are the basic components of every homeostatic response. The brain will send.
Asked in human anatomy and. Effector effectors plural effecter effecters plural biology any muscle organ etc. These are a theoretical minimum rather than an observed functional arrangement of cells in the body of an animal see instinct.
A muscle gland or organ capable of responding to a stimulus especially a nerve impulse. Varieties of instinctive behaviour. Biochemistry a small molecule or protein that alters biochemical processes in a cell.
For example skeletal muscles can be classified as effectors. That can respond to a stimulus from a nerve. Biology the part of a nerve that carries a stimulus to a muscle etc.
An effector is any organ or tissue that receives information from the integrating center and acts to bring about the changes needed to maintain homeostasis. In biochemistry an effector molecule is usually a small molecule that selectively binds to a protein and regulates its biological activity. A nerve ending that carries impulses to a muscle gland or organ and activates muscle.
 There Are Multiple Classifications Of Nerve Fibers Including
There Are Multiple Classifications Of Nerve Fibers Including
 Anatomy And Physiology Autonomic Nervous System Ppt Video
Anatomy And Physiology Autonomic Nervous System Ppt Video
Bio 222 Human Anatomy Physiology The Autonomic Nervous
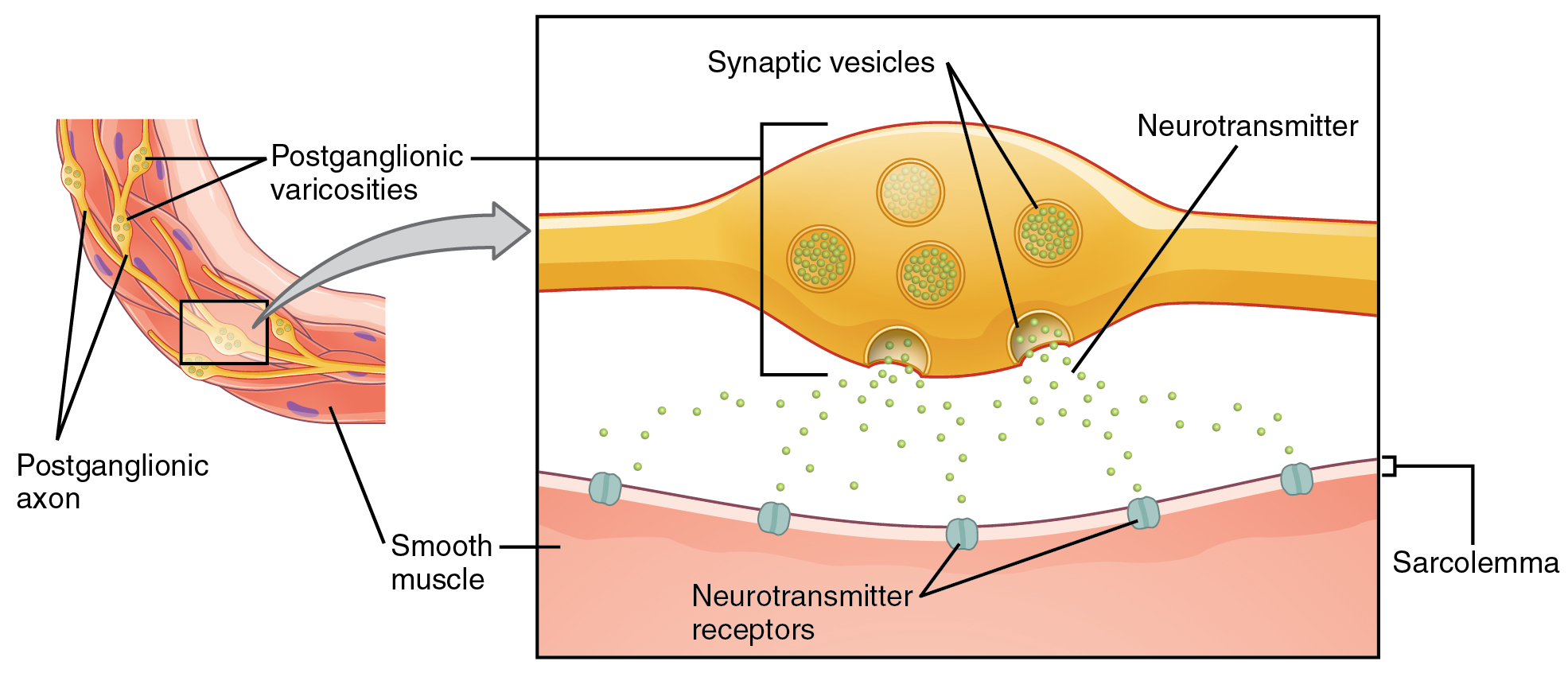 15 1 Divisions Of The Autonomic Nervous System Anatomy And
15 1 Divisions Of The Autonomic Nervous System Anatomy And
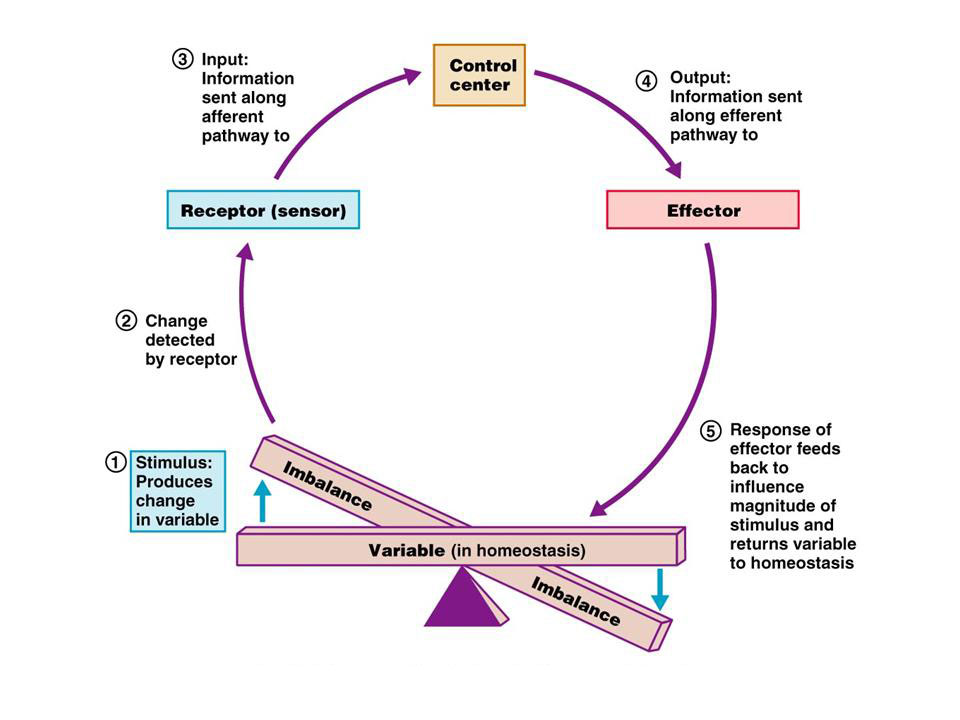 Homeostasis Positive Negative Feedback Mechanisms
Homeostasis Positive Negative Feedback Mechanisms
 Anatomy And Physiology Semester 1 Final Project Group 1
Anatomy And Physiology Semester 1 Final Project Group 1
 Human Anatomy And Physiology For Lifelong Learning
Human Anatomy And Physiology For Lifelong Learning
 Hlsc 1200u Lecture 1 Anatomy And Physiology Chapter 1
Hlsc 1200u Lecture 1 Anatomy And Physiology Chapter 1
 Hole S Anatomy Physiology Textbook Used Kolbe Academy
Hole S Anatomy Physiology Textbook Used Kolbe Academy
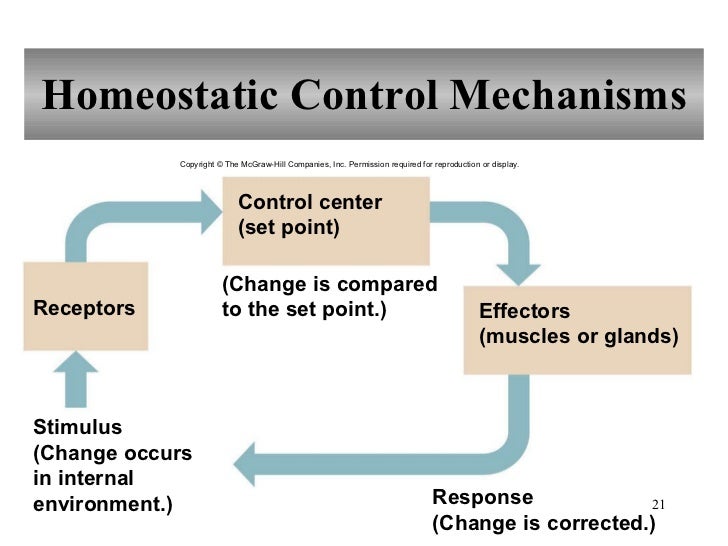 Chapter 1 Introduction To Human Anatomy And Physiology
Chapter 1 Introduction To Human Anatomy And Physiology
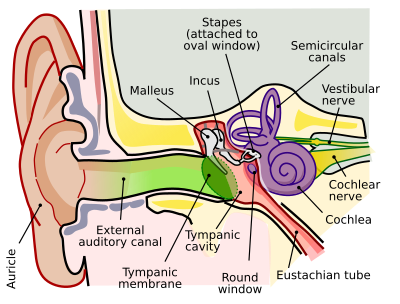 Sensory Systems Auditory Anatomy Wikibooks Open Books For
Sensory Systems Auditory Anatomy Wikibooks Open Books For
Ch 13 Basic Reflex Terminology
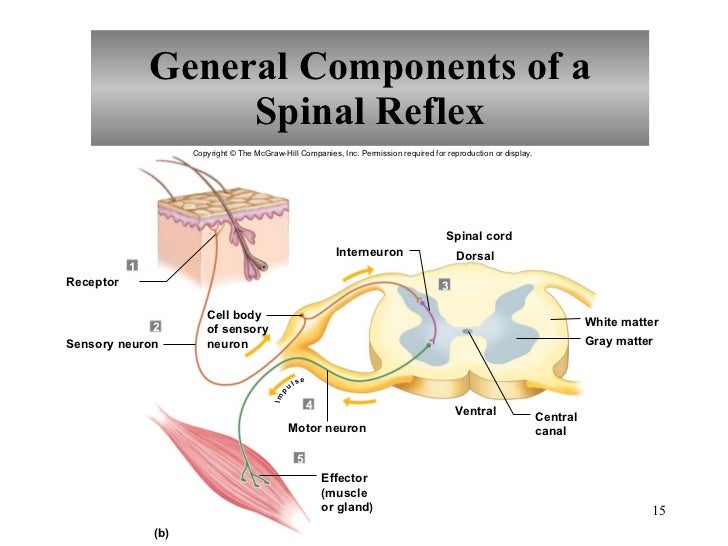 Chapter 11 Nervous System Ii Divisions Of The Nervous System
Chapter 11 Nervous System Ii Divisions Of The Nervous System
Cbio 2200 Exam 5 Notes Cbio 2200 Anatomy And Physiology I
 Feedback Loops Anatomy And Physiology I
Feedback Loops Anatomy And Physiology I
Nervous Tissue Study Guide Biol 114 Studocu
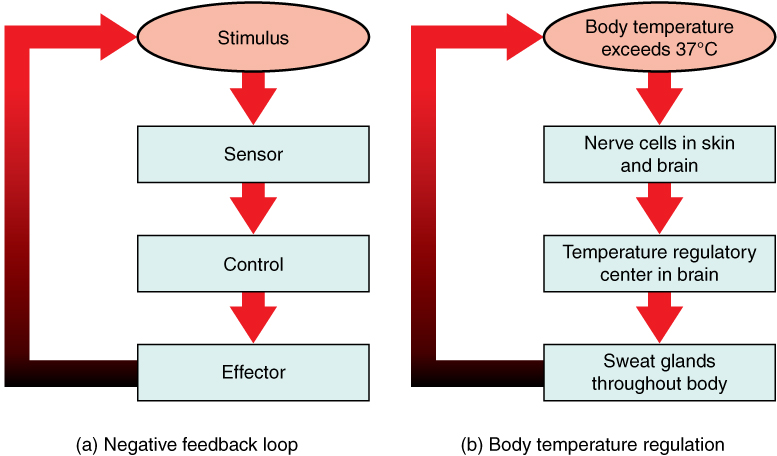 1 5 Homeostasis Anatomy And Physiology
1 5 Homeostasis Anatomy And Physiology
 Homeostasis Nature S Balance Malouff S Anatomy
Homeostasis Nature S Balance Malouff S Anatomy
 Autonomic Reflexes And Homeostasis Anatomy And Physiology I
Autonomic Reflexes And Homeostasis Anatomy And Physiology I
 Exam1 141 Studyguide F17 Bio 141 Nova Studocu
Exam1 141 Studyguide F17 Bio 141 Nova Studocu
 Introductory Anatomy And Physiology Text Lab Manual Top Hat
Introductory Anatomy And Physiology Text Lab Manual Top Hat
 Hole S Anatomy Physiology Textbook Used Kolbe Academy
Hole S Anatomy Physiology Textbook Used Kolbe Academy
 Are Muscles And Glands Part Of The Central Nervous System
Are Muscles And Glands Part Of The Central Nervous System
 Nervous System Explore The Nerves With Interactive Anatomy
Nervous System Explore The Nerves With Interactive Anatomy
 Msap Week 2 Autonomics Of Peripheral Nervous System Anatomy
Msap Week 2 Autonomics Of Peripheral Nervous System Anatomy
 Effectors Of Innate Immune Responses To Infection Medical
Effectors Of Innate Immune Responses To Infection Medical


Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar