The roof is formed by fascia and the floor is formed by the splenius capitus levator scapulae and scalene muscles. The inferior belly crosses the posterior triangle travelling in an supero medial direction.
Triangles Of The Neck Posterior Daily Med Fact
The posterior triangle of the neck contains many muscles which make up the borders and the floor of the area.

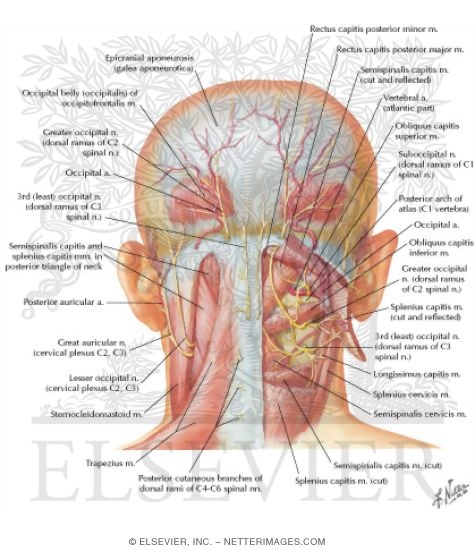
Anatomy of the posterior neck. The splenius capitis originates on the spinous processes of the vertebra the spinous processes of c7 to t4 and it inserts onto the back of the skull on the mastoid process and just below the superior nuchal line on the occipital bone. The clinical aspect of the anatomy contained in the posterior neck triangle is useful for a wide variety of medical specialties including anesthesiology otolaryngology physical medicine and rehabilitation and others. The nodes along the accessory are the first echelon for the nasopharynx and second echelon for the areas drained by the anterior.
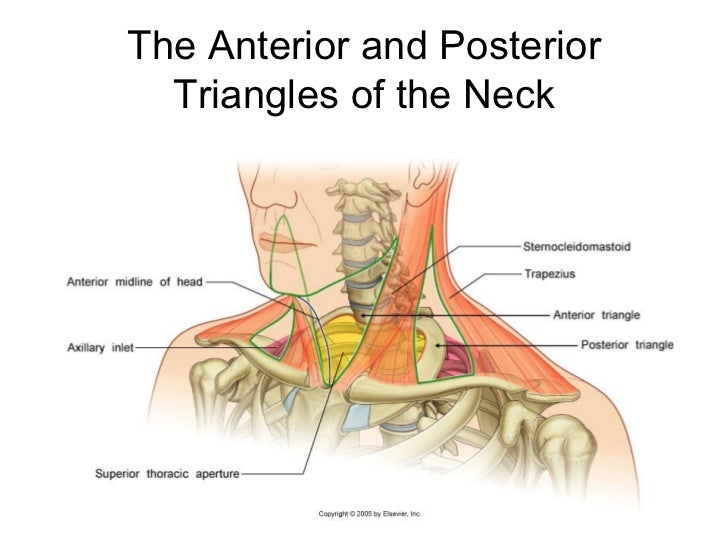
The base of the posterior triangle is formed by the middle third of the clavicle. The borders of the posterior triangle of the neck are formed by the trapezius muscle posteriorly the sternocleidomastoid muscle anteriorly and the omohyoid muscle inferiorly. Explore and learn about the muscles within the posterior triangle fo the neck with our 3d interactive anatomy atlas.
A significant muscle in the posterior triangle region is the omohyoid muscle. Those that are found along the accessory nerve and those related to the thyrocervical vessels. Muscles of the neck posterior triangle prevertebral and lateral muscles.
The posterior neck triangle is a clinically relevant anatomic region that contains many important vascular and neural structures. The posterior border of sternocleidomastoid and the anterior border of trapezius form the anterior and posterior borders of the posterior triangle of the neck respectively. Clinical anatomy for dummies.
The neck also contains the thyroid and parathyroid glands the esophagus larynx and trachea and also a number of lymph glands. It is split into two bellies by a tendon. Posterior nodes the posterior triangle contains lymph nodes that are arranged into two groups.
The posterior triangle or lateral cervical region is a region of the neck. Anatomy of the neck the neck contains a number of overlapping muscles blood vessels nerves and myriad structures all contained in a small space and liable to damage and distress.
64 Posterior Cervical Triangle Human Anatomy 2 Studocu
 Posterior Triangle Of Neck Anatomy Qa
Posterior Triangle Of Neck Anatomy Qa
:watermark(/images/watermark_5000_10percent.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/atlas_overview_image/1241/kvHhnCvRBbUcuMNwiE9Zbg_triangles-of-the-neck_english.jpg) Head And Neck Regions And Anatomy Kenhub
Head And Neck Regions And Anatomy Kenhub
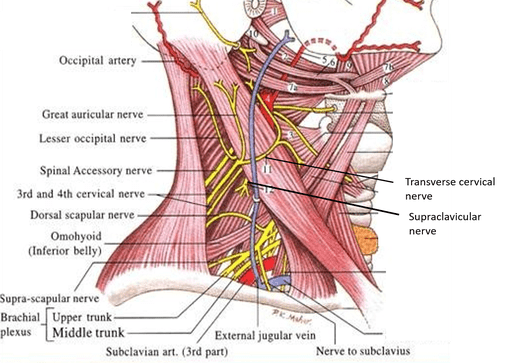 Posterior Triangle Of The Neck Anatomy Anatomyqa Com
Posterior Triangle Of The Neck Anatomy Anatomyqa Com
Medical Exhibits Demonstrative Aids Illustrations And Models
 Chapter 26 Triangles And Root Of The Neck The Big Picture
Chapter 26 Triangles And Root Of The Neck The Big Picture
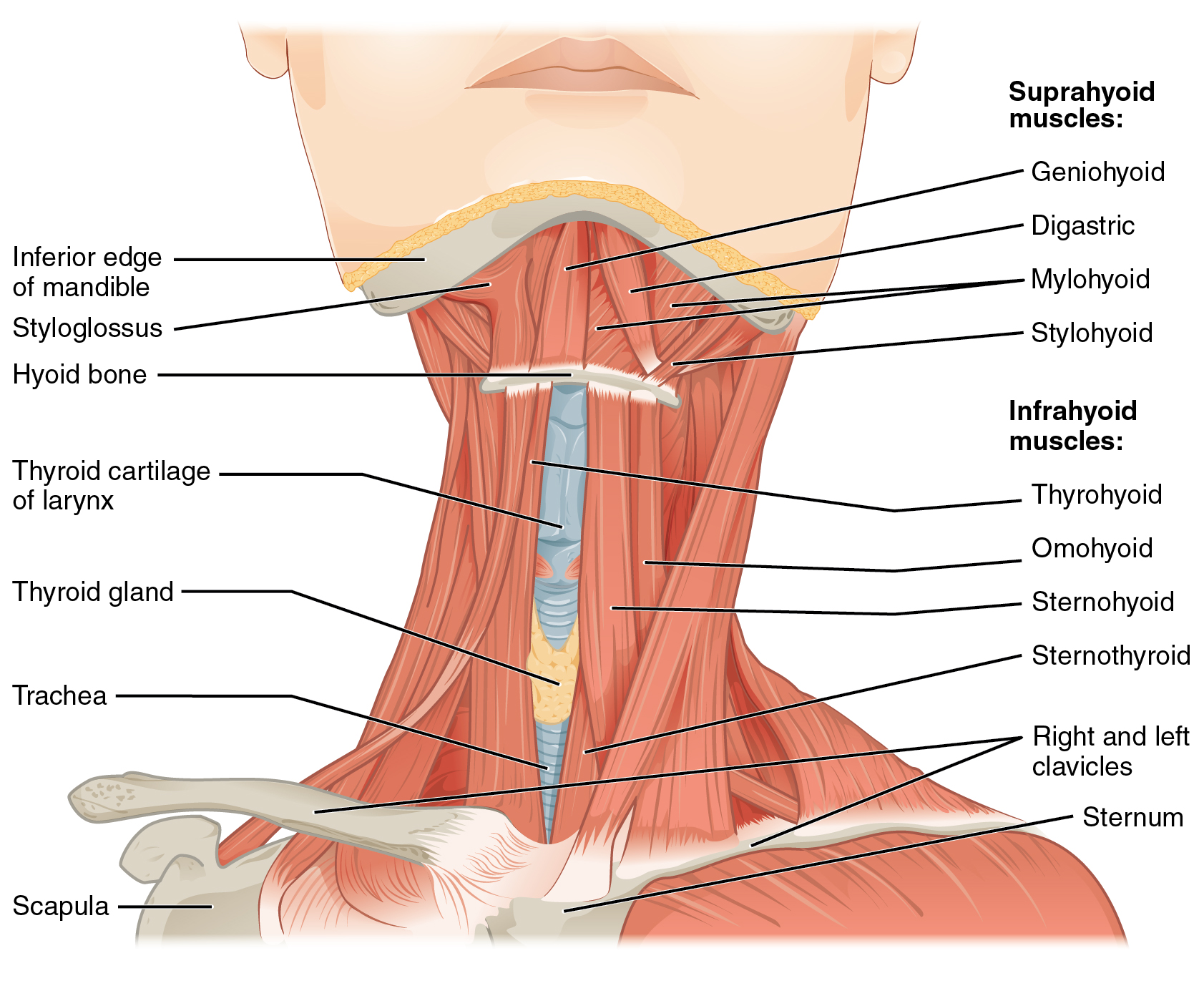 11 3 Axial Muscles Of The Head Neck And Back Anatomy And
11 3 Axial Muscles Of The Head Neck And Back Anatomy And
 Neck Muscles Anatomy Posterior Triangle Prevertebral And Lateral Muscles
Neck Muscles Anatomy Posterior Triangle Prevertebral And Lateral Muscles
Cervical Motor Control Part 1 Clinical Anatomy Of Cervical
 11138 15a Anatomy Of The Posterior Neck Anatomy Exhibits
11138 15a Anatomy Of The Posterior Neck Anatomy Exhibits
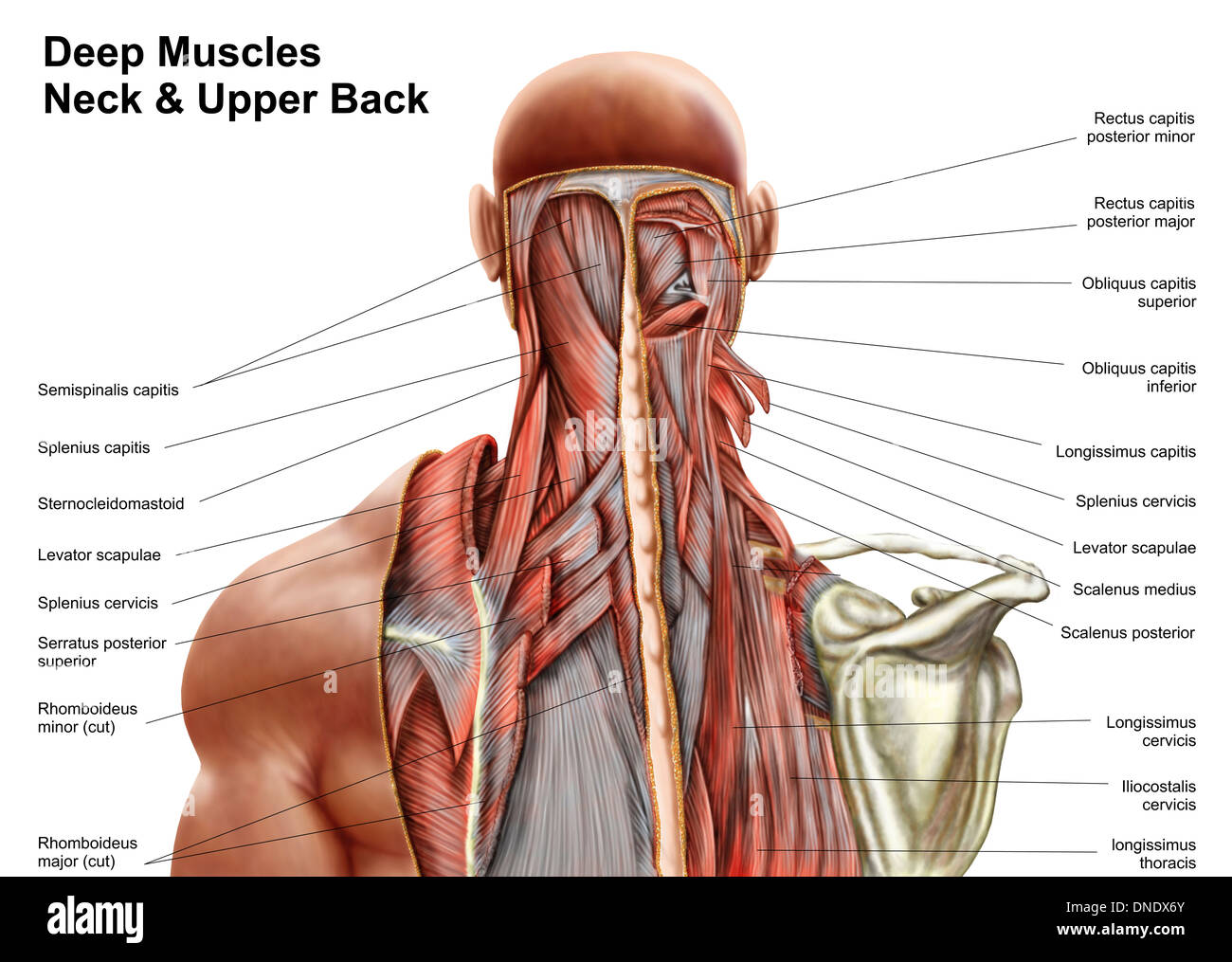 Human Anatomy Showing Deep Muscles In The Neck And Upper
Human Anatomy Showing Deep Muscles In The Neck And Upper
 Posterior Triangle Of The Neck
Posterior Triangle Of The Neck
 Anterior Triangle Of The Neck Head And Neck Anatomy
Anterior Triangle Of The Neck Head And Neck Anatomy
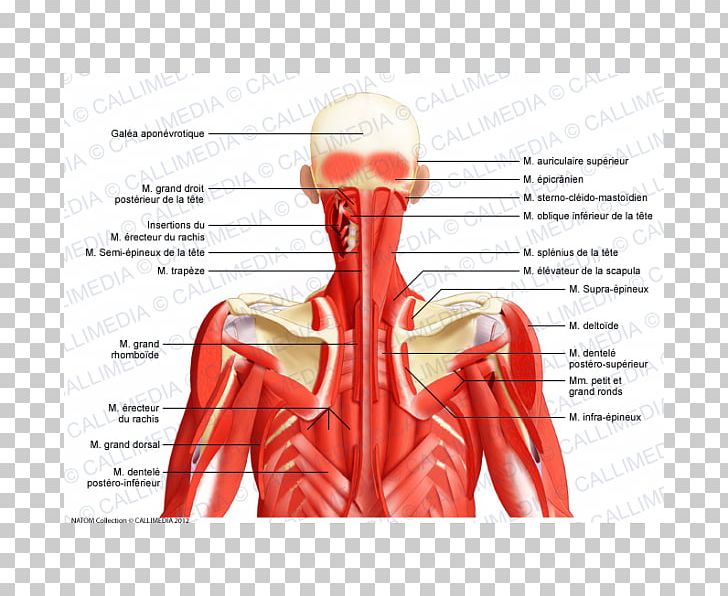 Posterior Triangle Of The Neck Head And Neck Anatomy Human
Posterior Triangle Of The Neck Head And Neck Anatomy Human
 Anatomic Relationships Lateral Neck Throat Anatomy Human
Anatomic Relationships Lateral Neck Throat Anatomy Human
 Anatomy Of The Head And Neck Medical Illustrations Showing
Anatomy Of The Head And Neck Medical Illustrations Showing
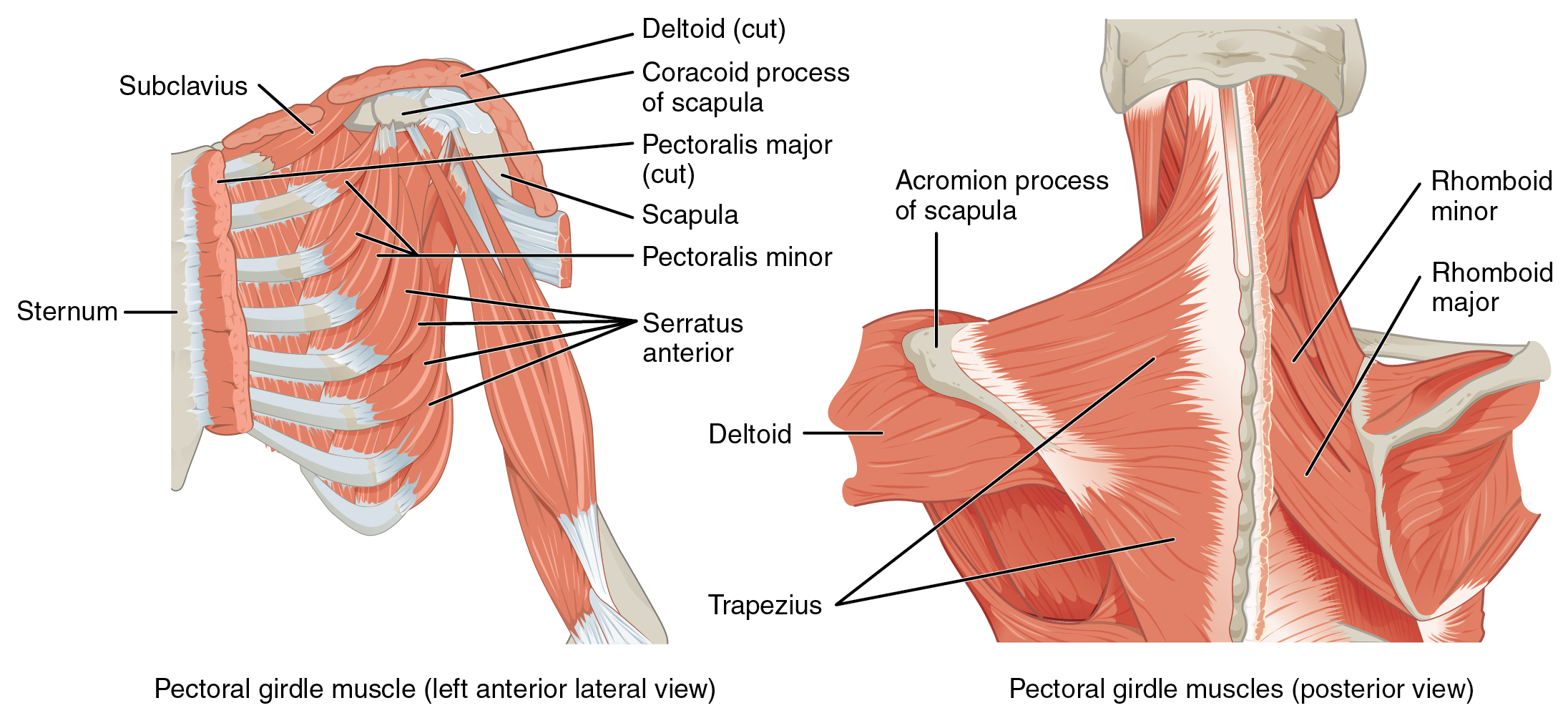 Extrinsic Back Muscles Anatomy Online Medical Library
Extrinsic Back Muscles Anatomy Online Medical Library
 Yoga Anatomy Yoga For Neck Pain And Neck Tension Yoga Journal
Yoga Anatomy Yoga For Neck Pain And Neck Tension Yoga Journal
Human Neck Useful Notes On The Posterior Triangle Of Human
 Posterior Triangle Of The Neck Muscle Head And Neck Anatomy
Posterior Triangle Of The Neck Muscle Head And Neck Anatomy
 Muscles Advanced Anatomy 2nd Ed
Muscles Advanced Anatomy 2nd Ed
Human Neck Useful Notes On The Posterior Triangle Of Human
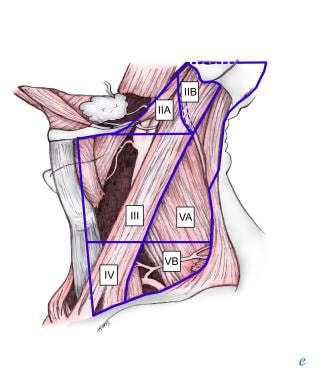 What Is The Anatomy Of The Level V Group Of Lymph Nodes In
What Is The Anatomy Of The Level V Group Of Lymph Nodes In
 Muscles Of Neck Lateral View Neck Muscle Anatomy
Muscles Of Neck Lateral View Neck Muscle Anatomy



Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar