The rib cage is collectively made up of long curved individual. Contributing to their role in protecting the internal thoracic organs.
There are two classifications of ribs atypical and typical.
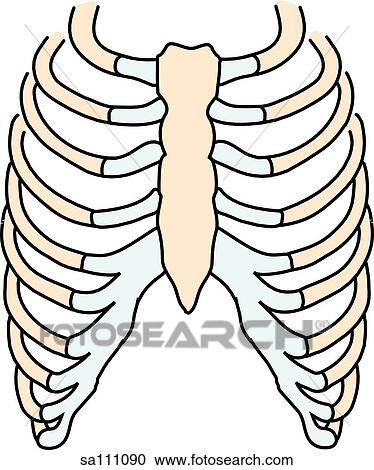
Anatomy of ribs. The typical rib consists of a head neck and body. In vertebrate anatomy ribs are the long curved bones which form the rib cage part of the axial skeleton. The ribs partially enclose and protect the chest cavity where many vital organs including the heart and the lungs are located.
The ribs the twelve pairs of ribs which are embedded within the walls of the muscular structures attach in the posterior to a thoracic vertebra. The typical ribs have a generalised structure while the atypical ribs have variations on this structure. The ribs are elastic arches of bone which form a large part of the thoracic skeleton.
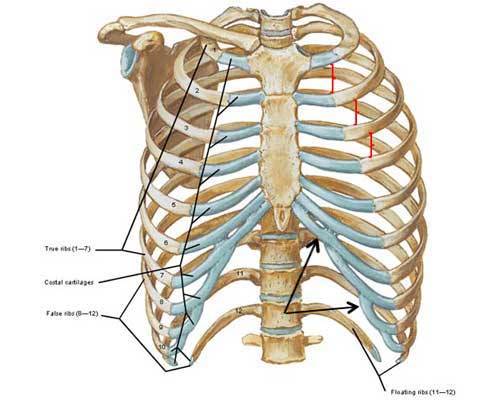
The true ribs ribs 1 7 attach to the sternum by costal cartilages. They are extremely light but highly resilient. Ribs 8 through 12 are deemed false ribs.
The last two pairs of false ribs are also known as floating ribs 1112. The first 7 pairs use the sternum as their anchor via the ribs individual costal cartilage as an attachment vessel. One facet articulates with the numerically corresponding vertebrae and the other articulates with the vertebrae above.
The ribs are curved flat bones which form the majority of the thoracic cage. The head is wedge shaped and has two articular facets separated by a wedge of bone. They serve to protect the lungs heart and other internal organs of the thorax.
In some animals especially snakes ribs may provide support and protection for the entire body. The first 7 pairs are also called true ribs. A typical human rib cage consists of 24 ribs in 12 pairs the sternum and xiphoid process the costal cartilages and the 12 thoracic vertebrae.
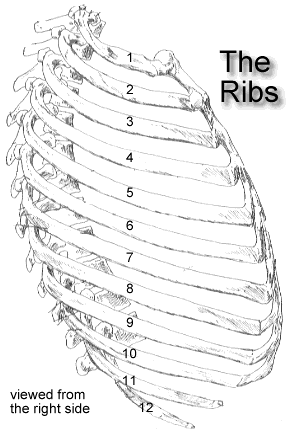
They are twelve in number on either side. There are twelve pairs of ribs all of which articulate with the vertebral column. Lateral view of a pair of ribs articulating with the thoracic vertebrae.
There are twelve 12 pairs of ribs and all articulate posteriorly with the thoracic vertebrae. In humans the rib cage also known as the thoracic cage is a bony and cartilaginous structure which surrounds the thoracic cavity and supports the shoulder girdle to form the core part of the human skeleton. The ribs are anchored posteriorly to the 12 thoracic vertebrae.
In most tetrapods ribs surround the chest enabling the lungs to expand and thus facilitate breathing by expanding the chest cavity. The sternum consists of the manubrium body and xiphoid process. The ribs are classified as true ribs 17 and false ribs 812.
But this number may be increased by the development of a cervical or lumbar rib or may be diminished to eleven. The flexible hyaline cartilage makes the breathing process easier.
 Bucket Handle Movement Of Ribs Anatomy Behind It Physiosunit
Bucket Handle Movement Of Ribs Anatomy Behind It Physiosunit
 Thoracic Cage Anatomy Body Human
Thoracic Cage Anatomy Body Human
 Ribs With Scapula Anatomy Art Print Poster
Ribs With Scapula Anatomy Art Print Poster
 Anterior View Of The Skeletal Anatomy Of The Body Ribs
Anterior View Of The Skeletal Anatomy Of The Body Ribs
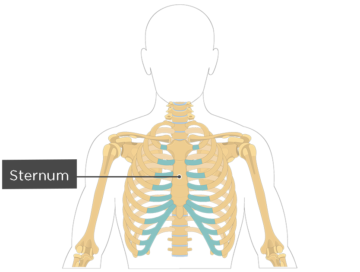 Ribs And Sternum Rib Cage Anatomy And Function
Ribs And Sternum Rib Cage Anatomy And Function
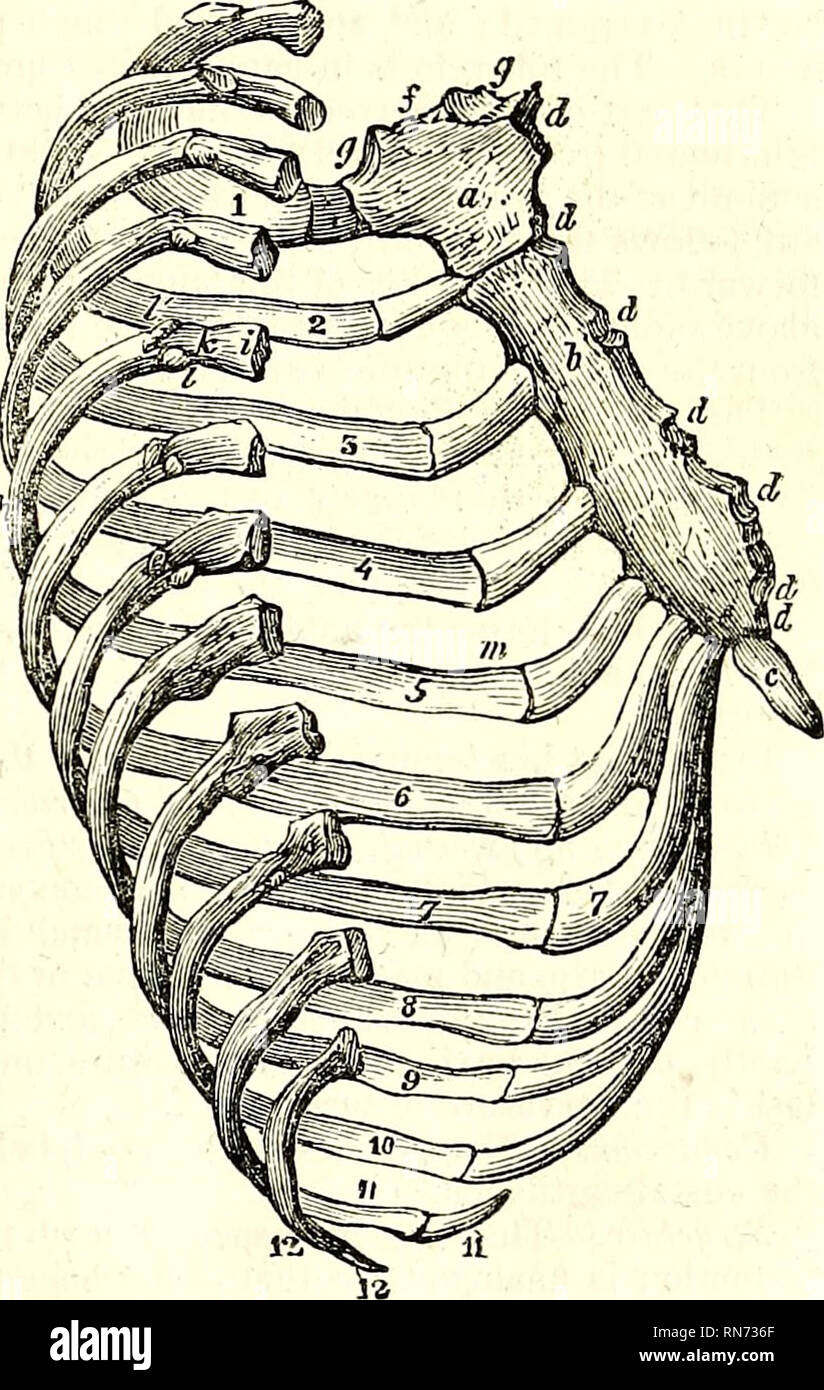 The Anatomy Of The Human Body Human Anatomy Anatomy The
The Anatomy Of The Human Body Human Anatomy Anatomy The
 9 Interesting Facts About The Ribs Mental Floss
9 Interesting Facts About The Ribs Mental Floss
How Many Ribs Are There In The Body Quora
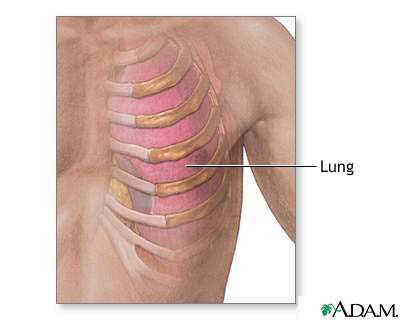 Ribs And Lung Anatomy Medlineplus Medical Encyclopedia Image
Ribs And Lung Anatomy Medlineplus Medical Encyclopedia Image
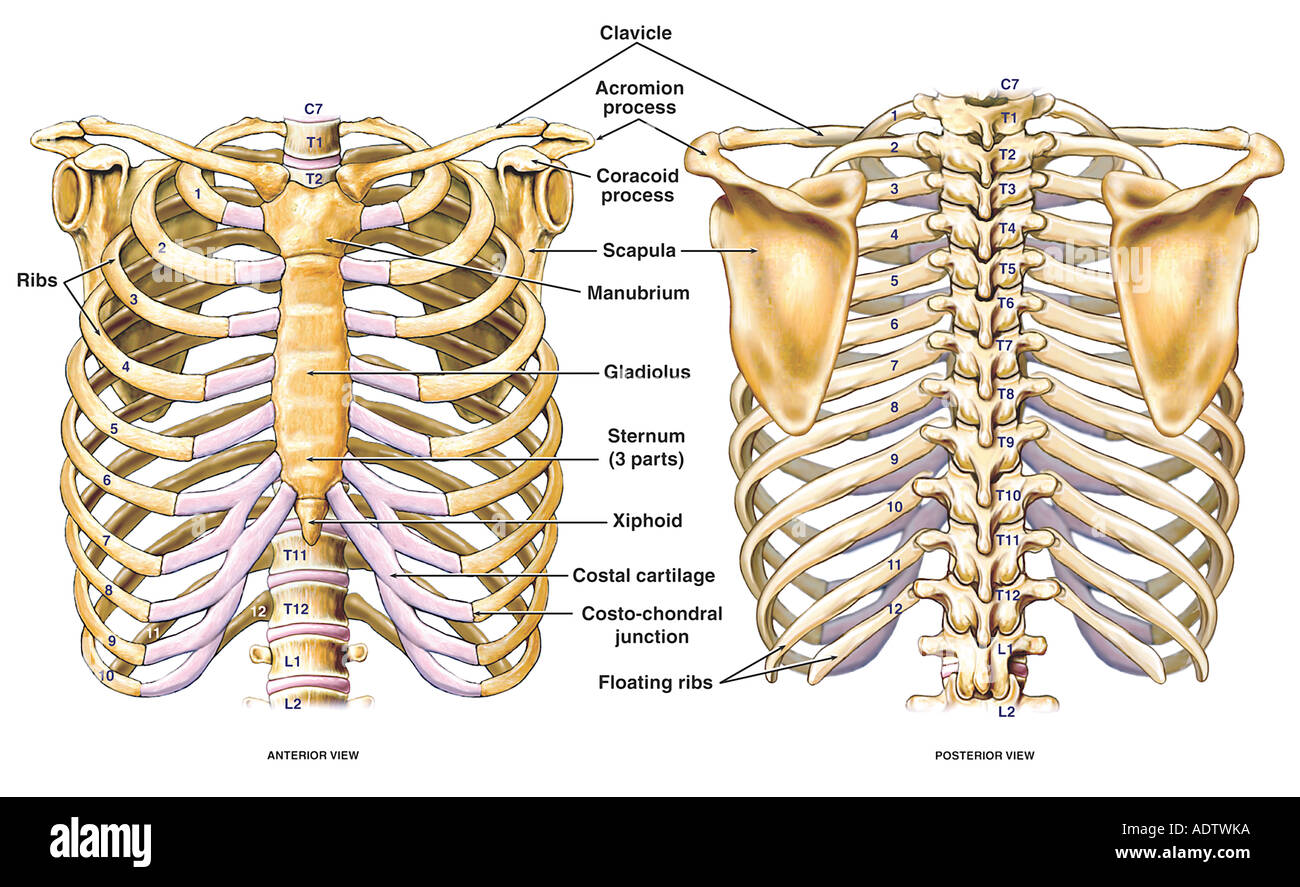 Thoracic Chest And Back Skeletal Skeleton Anatomy Featuring
Thoracic Chest And Back Skeletal Skeleton Anatomy Featuring
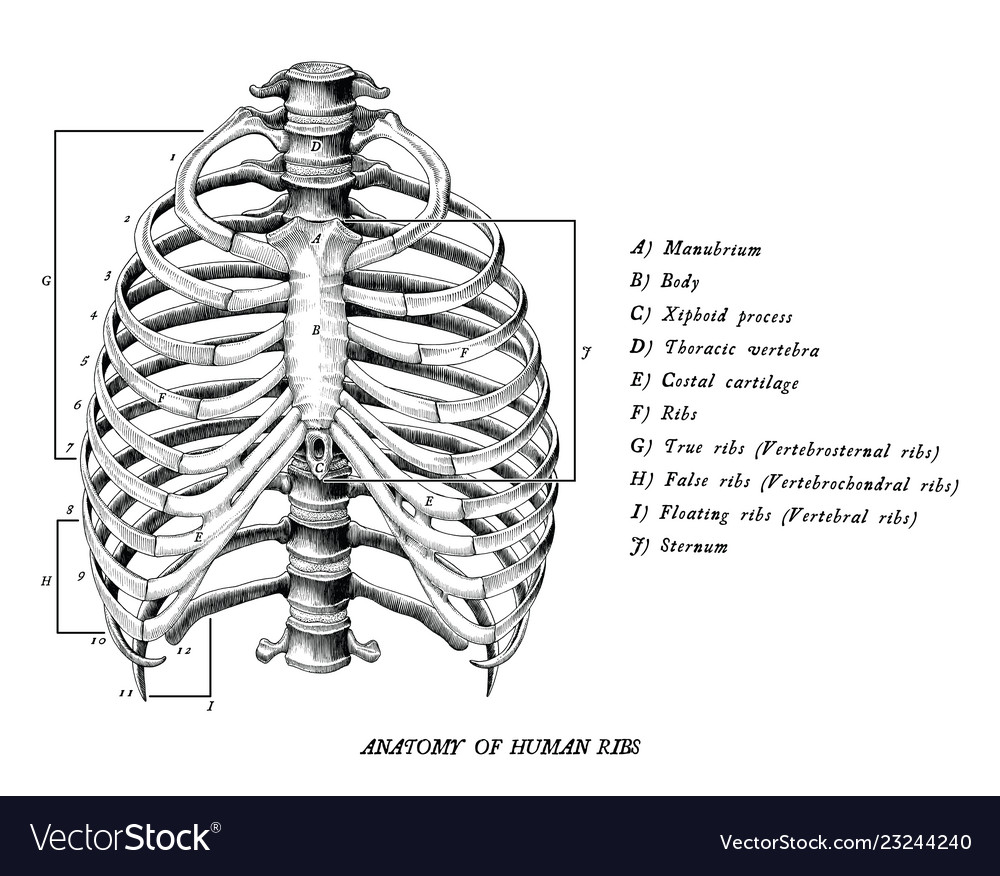 Anatomy Of Human Ribs Hand Draw Vintage Clip Art
Anatomy Of Human Ribs Hand Draw Vintage Clip Art
 Horse Anatomy How Many Ribs Does A Horse Have Best Horse
Horse Anatomy How Many Ribs Does A Horse Have Best Horse
 Anatomy Human Rib Cage 3d Model
Anatomy Human Rib Cage 3d Model
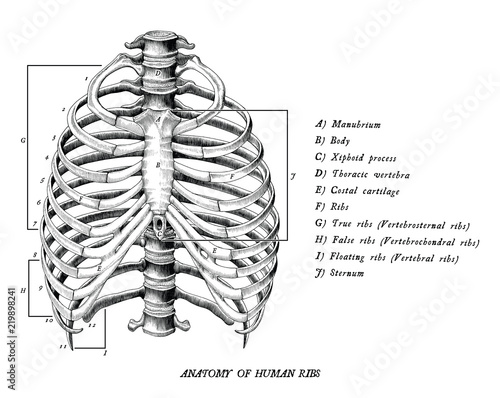 Anatomy Of Human Ribs Hand Draw Vintage Clip Art Isolated On
Anatomy Of Human Ribs Hand Draw Vintage Clip Art Isolated On
 Rib Cage Anatomy Bones Of The Thoracic Wall Costae
Rib Cage Anatomy Bones Of The Thoracic Wall Costae
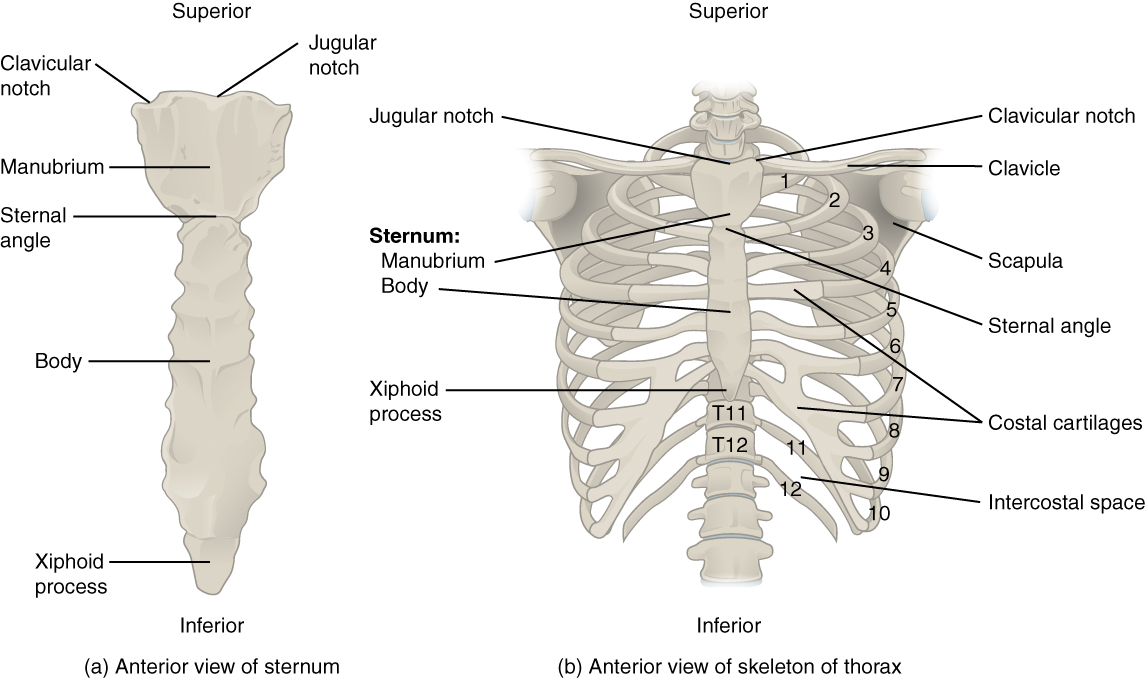 7 4 The Thoracic Cage Anatomy And Physiology
7 4 The Thoracic Cage Anatomy And Physiology
 The Anatomy Of The Ribs And The Sternum And Their
The Anatomy Of The Ribs And The Sternum And Their
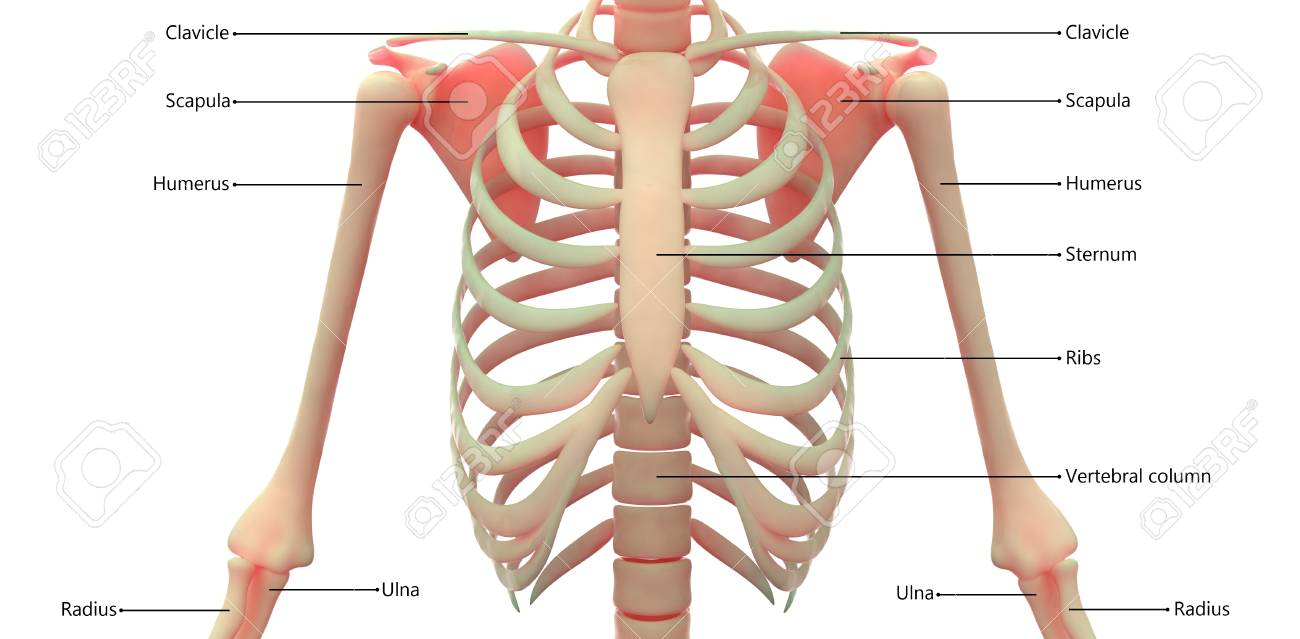 Human Body Bone Joint Pains Anatomy Ribs
Human Body Bone Joint Pains Anatomy Ribs
 3d Illustration Of Skeleton Ribs Anatomy Stock Illustration
3d Illustration Of Skeleton Ribs Anatomy Stock Illustration
 Ribs Anatomy Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock
Ribs Anatomy Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock
 Rib Cage Lesson For Kids Anatomy Facts Study Com
Rib Cage Lesson For Kids Anatomy Facts Study Com
 The Ribs And Some Sutherland Biomechanics Cranial
The Ribs And Some Sutherland Biomechanics Cranial




Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar