Anatomy of the floor of the mouth the floor of the mouth is a horizontally aligned u shaped space situated in the part of the oral cavity that lies beneath the tongue. The floor of mouth is an oral cavity subsite and is a common location of oral cavity squamous cell carcinoma.
Mouth Useful Notes On Mouth Human Anatomy
Floor of the mouth lined with smooth thin mucous membrane stratified squamous epithelium boundaries.

Floor of the mouth anatomy. The mouth consists of 2 regions the vestibule and the oral cavity proper. Pillar inferior mylohyoid muscle superior mucous membrane lining wwwindiandentalacademyco m 3. It provides structural support to the floor of the mouth and pulls the larynx forward during swallowing.
Anatomy of a mouth. The vestibule is the area between the teeth lips and cheeks. It is formed predominately by mylohyoid a muscle that inserts into both sides of the mandible and attaches the anterior part of the body of the hyoid.
Part of the mandible either sides body of mandible posterior base of the ant. The teeth are held within the jaw bones and serve several important functions beyond allowing you to chew. Its boundaries are defined by the lips cheeks hard and soft palates and glottis.
The floor the floor of the oral cavity consists of several structures. Centrally the geniohyoid overlies the mylohyoid. Mouth in human anatomy orifice through which food and air enter the body.
The floor of the mouth is a muscular layer that lies below the tongue and extends between the body of the mandible. Gross anatomy the floor of mouth is a u shaped space which extends and includes from the oral cavity mucosa superiorly and the mylohyoid muscle sling 23. The mouth opens to the outside at the lips and empties into the throat at the rear.
The floor of the mouth is a small horseshoe shaped region situated beneath the movable part of the tongue and above the muscular diaphragm formed by the mylohyoid muscles and above this diaphragm is the genohyoid muscle. Muscular diaphragm comprised of the bilateral mylohyoid muscles. Anatomy of floor mouth pdf floor of the mouth source.
Anatomy of the mouth. For purposes of surgical planning the floor of the mouth is defined as the space between the mucosal surface and the mylohyoid muscle sling and comprising both structures 1. The oral cavity is bounded at the sides and in front by the alveolar process containing the teeth and at the back by the isthmus of the fauces.
Geniohyoid muscles pull the larynx forward during swallowing. It is divided into two sections. The mouth oral cavity consists of several components including the teeth gingiva gums tongue palate cheeks lips and floor of the mouth.
With the exception of the teeth the mouth is lined by mucous membranes.
 Ranula Plunging Cyst And Surgery
Ranula Plunging Cyst And Surgery
 The Anatomy Of The Oral Cavity The Sublingual And Buccal
The Anatomy Of The Oral Cavity The Sublingual And Buccal
 Science Source Tongue And Oral Floor Artwork
Science Source Tongue And Oral Floor Artwork
 Oral Cavity Definition Anatomy Functions Diagram
Oral Cavity Definition Anatomy Functions Diagram
Biomolecules And Biomarkers In Oral Cavity Bioassays And
 Oral Cavity An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Oral Cavity An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
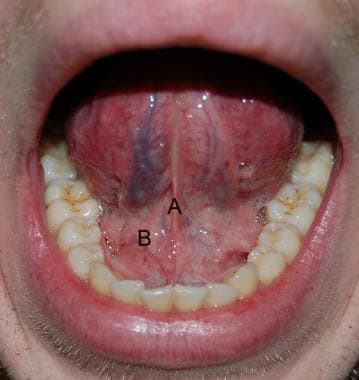 Mouth Anatomy Overview Gross Anatomy Oral Vestibule
Mouth Anatomy Overview Gross Anatomy Oral Vestibule
Why Does The Bottom Of Your Mouth Feel Hard When You Press
 Oral Cavity Pharynx Radio Anatomy
Oral Cavity Pharynx Radio Anatomy
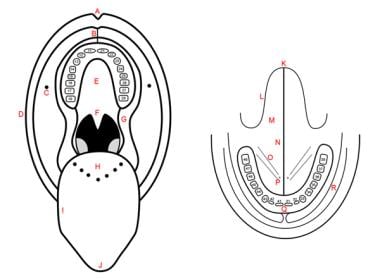 Mouth Anatomy Overview Gross Anatomy Oral Vestibule
Mouth Anatomy Overview Gross Anatomy Oral Vestibule
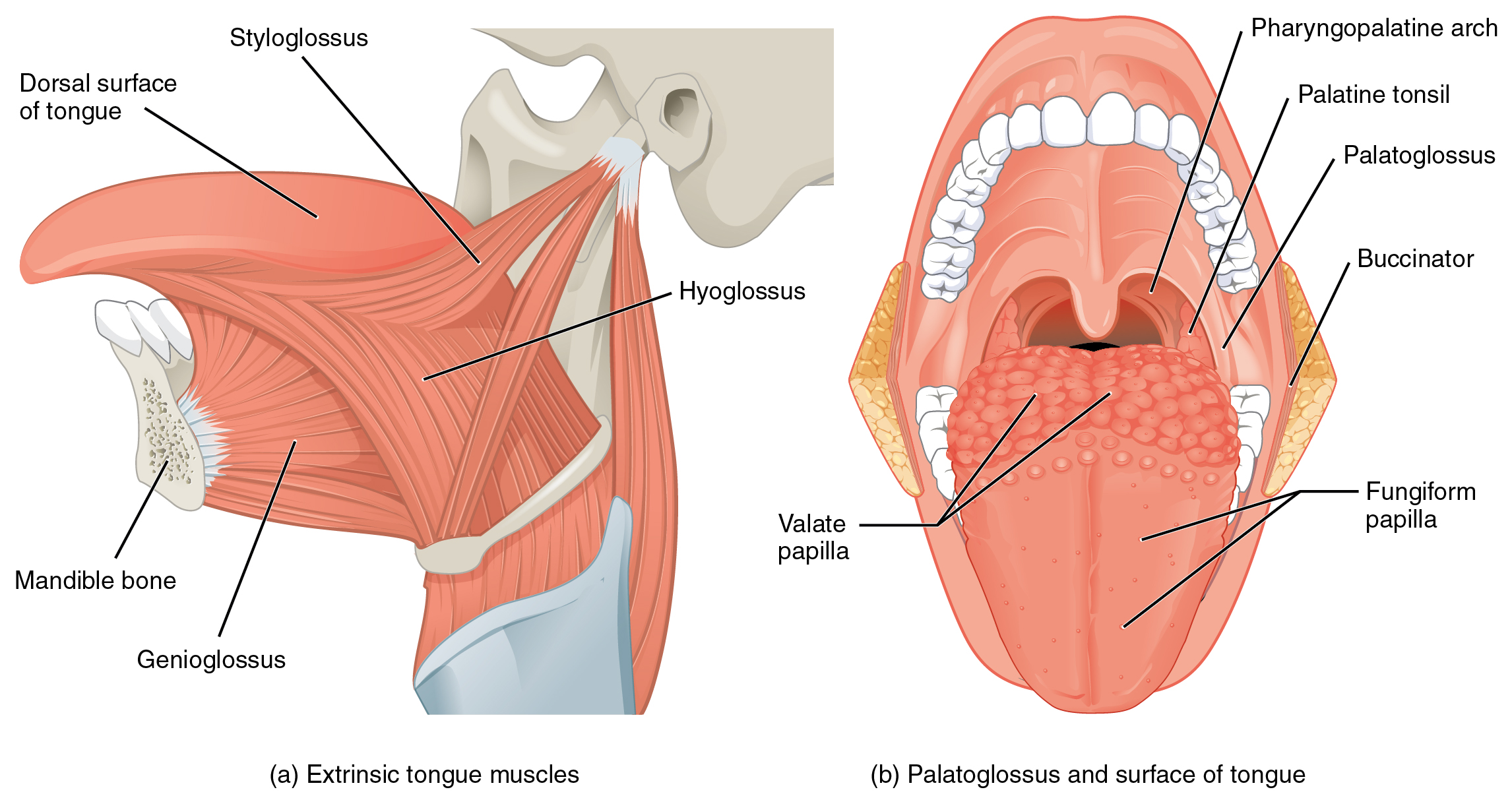 11 3 Axial Muscles Of The Head Neck And Back Anatomy And
11 3 Axial Muscles Of The Head Neck And Back Anatomy And
 Oral Cavity Pharynx Atlas Of Anatomy
Oral Cavity Pharynx Atlas Of Anatomy
 Review Of The Arterial Vascular Anatomy For Implant
Review Of The Arterial Vascular Anatomy For Implant
 Patient Resource Publishing Head And Neck Oral
Patient Resource Publishing Head And Neck Oral
 Boundaries Of The Oral Cavity Inferior Border Floor Of
Boundaries Of The Oral Cavity Inferior Border Floor Of
 Lingual Nerve Gross Anatomy Anatomy Head And Neck Medical Animations
Lingual Nerve Gross Anatomy Anatomy Head And Neck Medical Animations
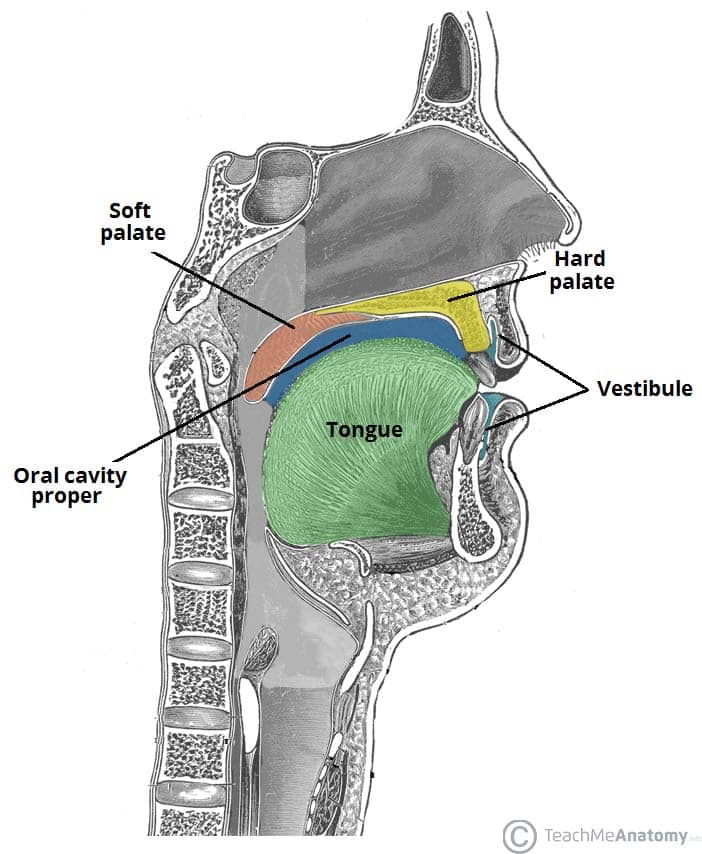 The Oral Cavity Divisions Innervation Teachmeanatomy
The Oral Cavity Divisions Innervation Teachmeanatomy
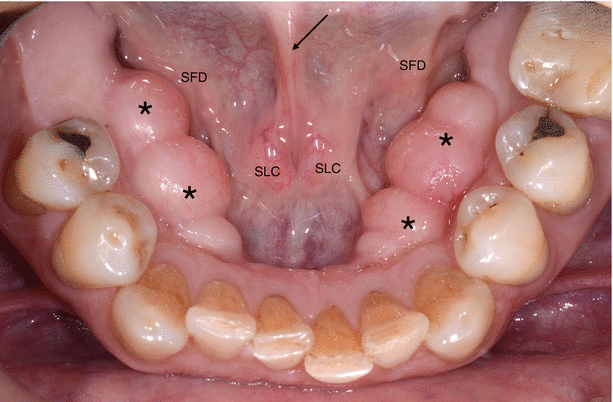
 Clinical Aspects Of The Sublingual Mass Note That The
Clinical Aspects Of The Sublingual Mass Note That The
 Human Anatomy The Definitive Visual Guide By Stasha C Issuu
Human Anatomy The Definitive Visual Guide By Stasha C Issuu
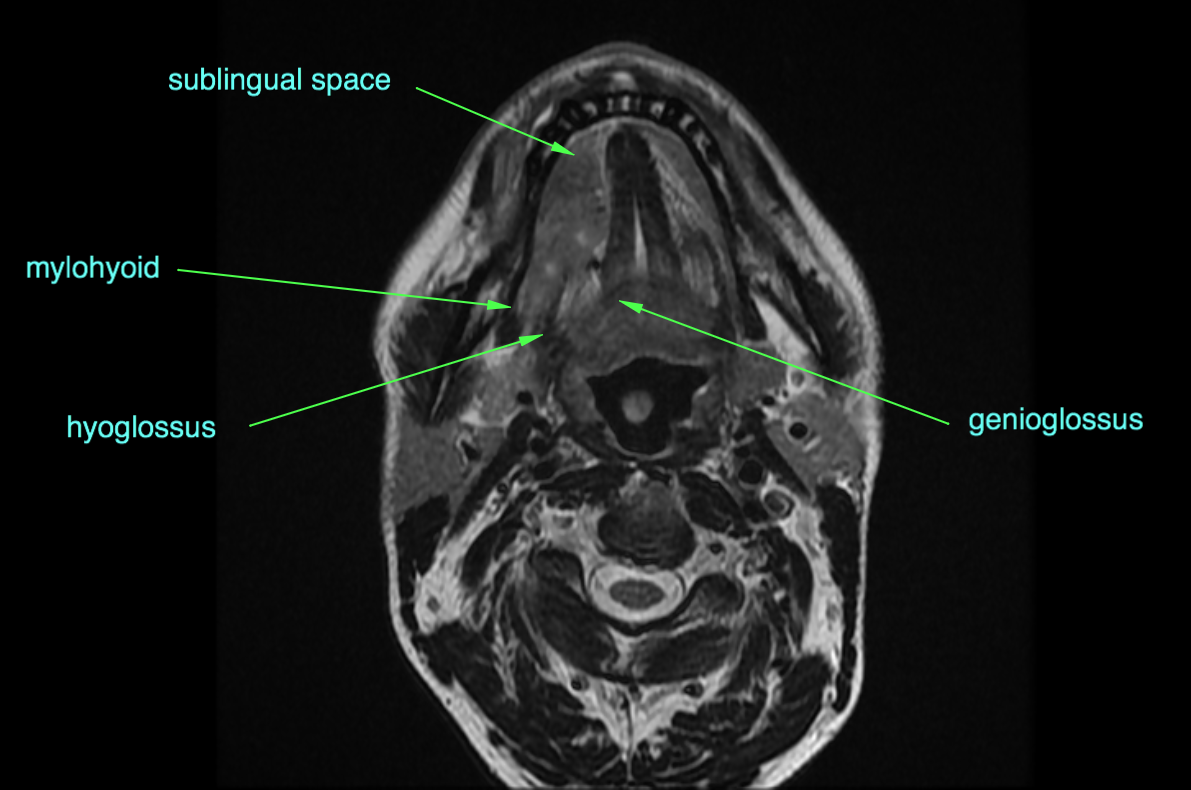 Tongue And Floor Of Mouth Neoplasm Image Radiopaedia Org
Tongue And Floor Of Mouth Neoplasm Image Radiopaedia Org
Lingual Nerve Block Selective Anesthesia For Tongue And
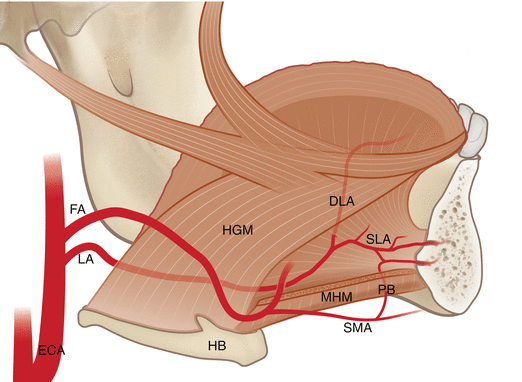

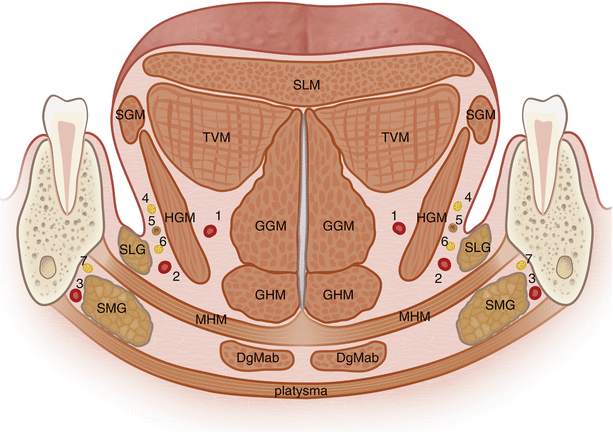


Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar