Ventilation or breathing is the movement of air through the conducting passages between the atmosphere and the lungs. This is how fast you are breathing.
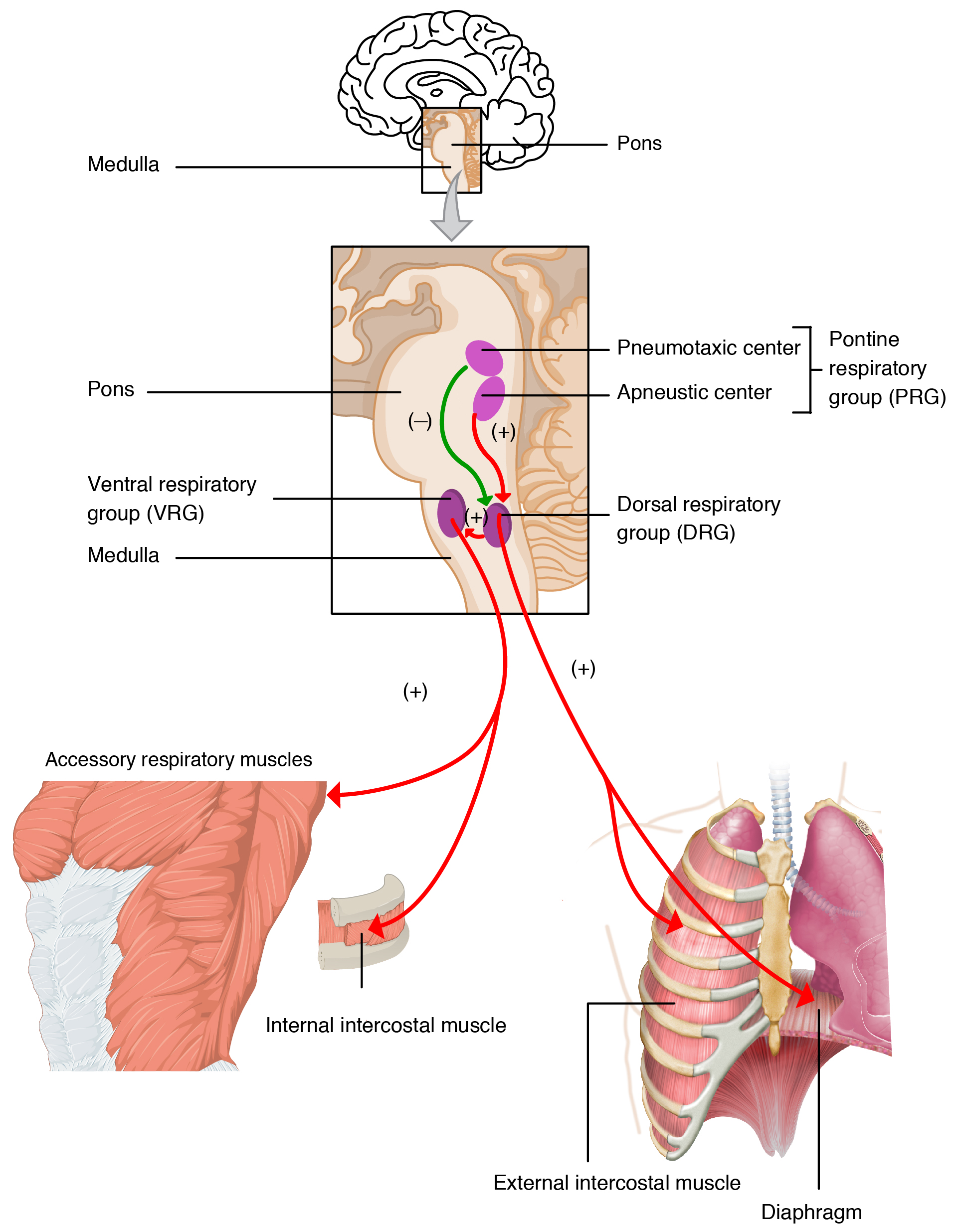 22 3 The Process Of Breathing Anatomy And Physiology
22 3 The Process Of Breathing Anatomy And Physiology
The exchange of air between the lungs and the atmosphere so that oxygen can be exchanged for carbon dioxide in the alveoli the tiny air sacs in the lungs.
Ventilation anatomy. Most anatomy labs deal with fluids resulting in a wet environment and creating a need for ground fault interrupted circuits gfci. Its determined by a patients minute ventilation page 68 2. Hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction an important safety mechanism is inhibited by majority of the anaesthetic drugs.
Anatomy lab planning guidelines. The result is typically a rhythmic consistent ventilation rate that provides the body with sufficient amounts of oxygen while adequately removing carbon dioxide. Mechanisms of pulmonary ventilation.
Ventilation anatomy physiology introduction. There are different ways of describing ventilation. Ventilation to perfusion ratio alters with anaesthesia body position and with one lung anaesthesia.
In respiratory physiology the process of exchange of air between the lungs and the ambient air. Ventilation describes the volume of air that flows into and out of the lungs per unit time. This is determined by the formula.
Understanding of ventilation perfusion and their relation with each other is important for understanding respiratory physiology. This is the process of moving air into and out of your lungs. For example the total volume of air that flows into and out of the lungs per minute is minute ventilation.
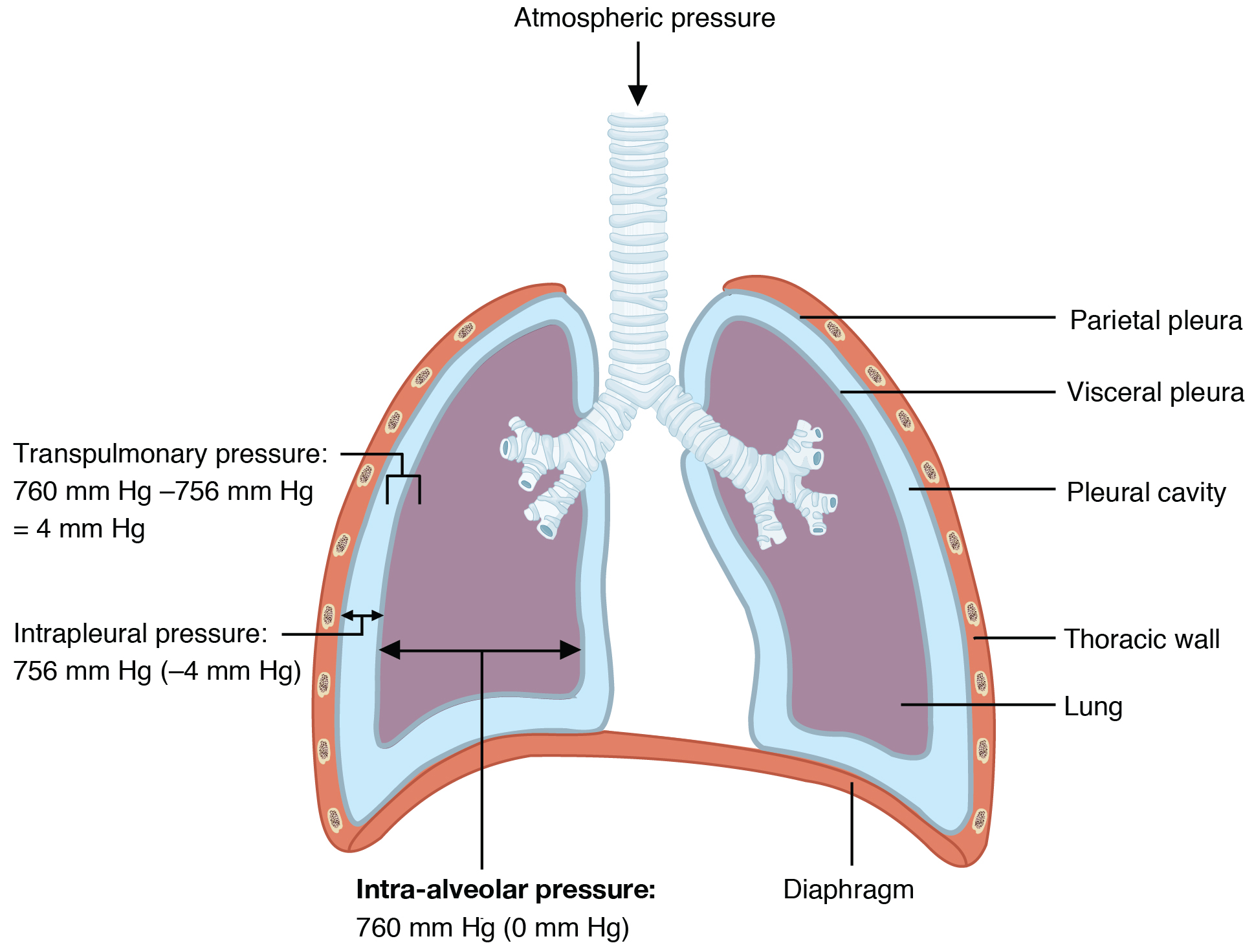
The air moves through the passages because of pressure gradients that are produced by contraction of the diaphragm and thoracic muscles. Tidal volume times rate. The control of ventilation is a complex interplay of multiple regions in the brain that signal the muscles used in pulmonary ventilation to contract.
Ventilation is the movement of air into and out of the lungs. See alveolar ventilation and pulmonary ventilation. The process or act of supplying a house or room continuously with fresh air.
During expiration the pressure within the pleural cavity increases to greater. In psychiatry verbalization of ones problems emotions or feelings. Its inhaling oxygen o2 into your lungs and exhaling carbon dioxide co2 out of your lungs.
During inspiration the pressure within the pleural cavity drops to less than. All products should have proper safety certification such as etl or ul. Anatomy physiology respiratory system.
 Week 13 Mechanics Of Ventilation Control Of Respiration
Week 13 Mechanics Of Ventilation Control Of Respiration
 How Ventilation Muscles Cause Inspiration And Expiration
How Ventilation Muscles Cause Inspiration And Expiration
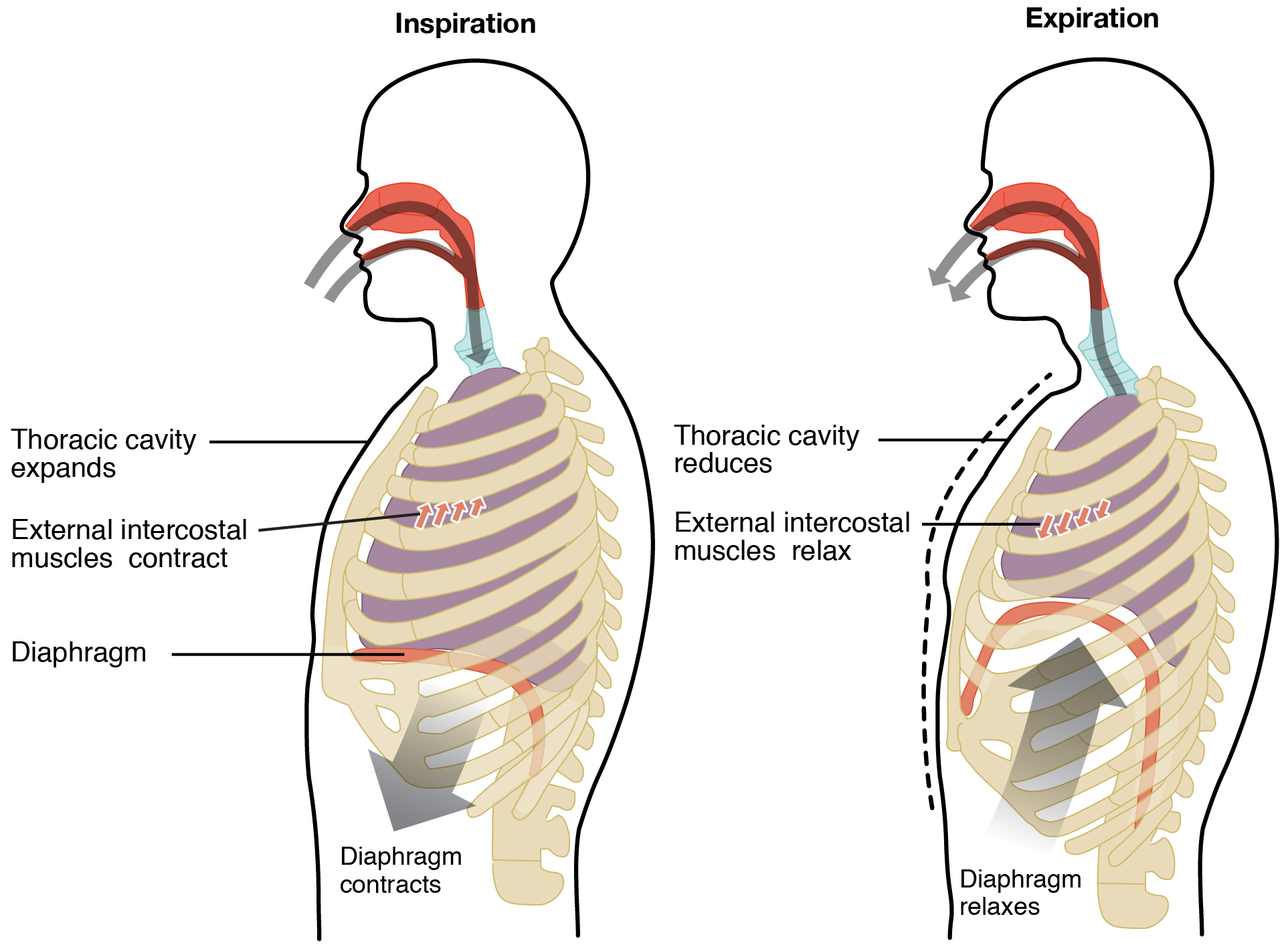 22 3 The Process Of Breathing Anatomy And Physiology
22 3 The Process Of Breathing Anatomy And Physiology
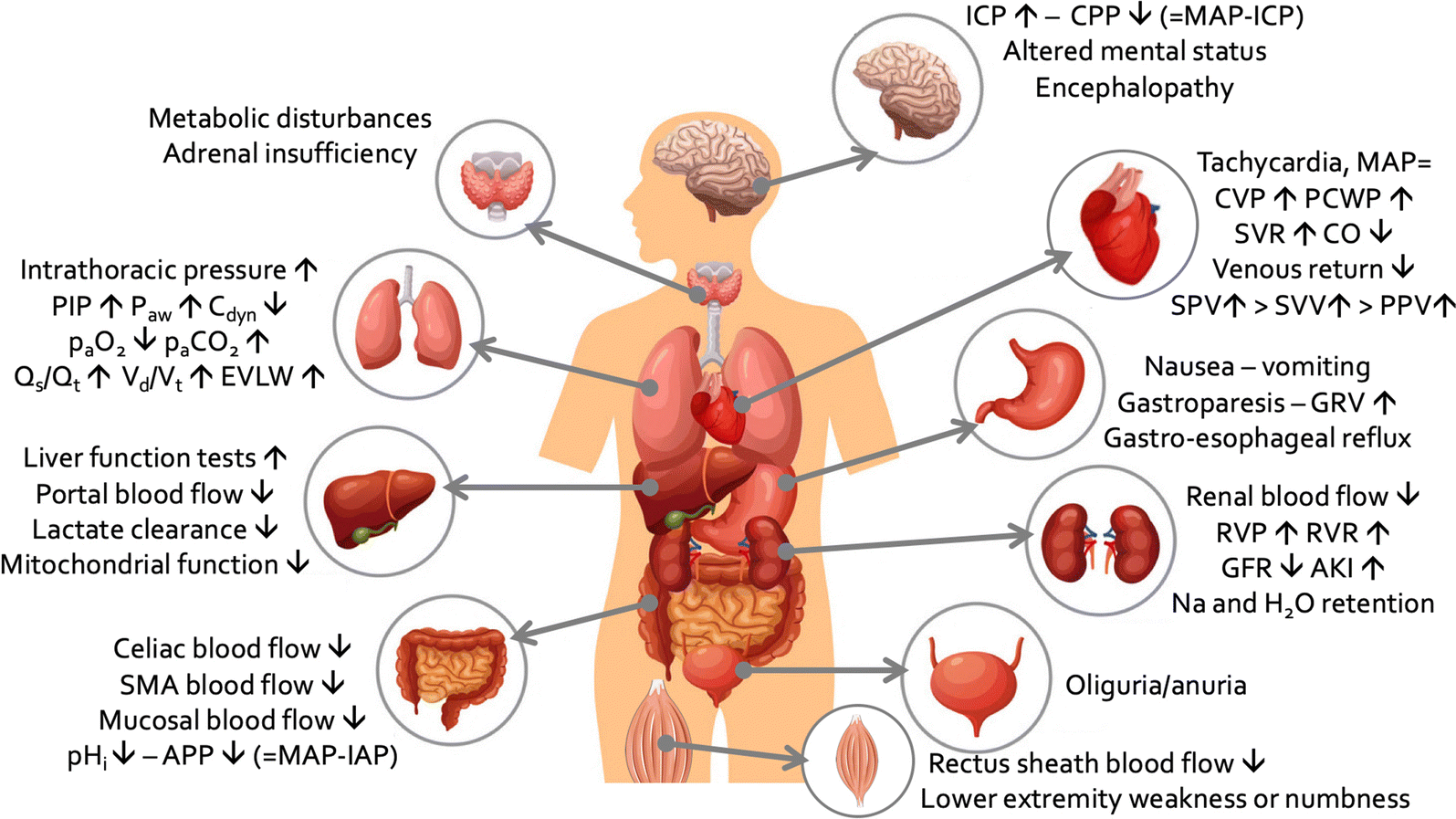 Ventilation In Patients With Intra Abdominal Hypertension
Ventilation In Patients With Intra Abdominal Hypertension
Control Of Ventilation Exercise Physiology
 Adult Invasive Mechanical Ventilation Orlando Health
Adult Invasive Mechanical Ventilation Orlando Health
 Pulmonary Ventilation Gas Exchange Stock Photo 212309875
Pulmonary Ventilation Gas Exchange Stock Photo 212309875
 Respiratory System Physiology Ventilation And Perfusion V Q Ratio Physiology
Respiratory System Physiology Ventilation And Perfusion V Q Ratio Physiology
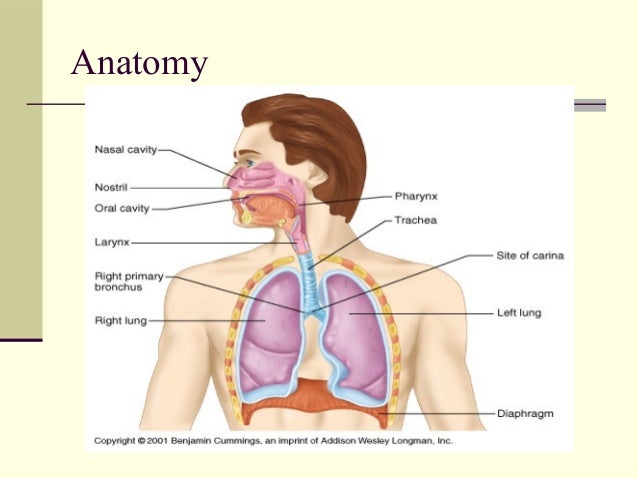 Basics Of Pediatric Ventilation
Basics Of Pediatric Ventilation

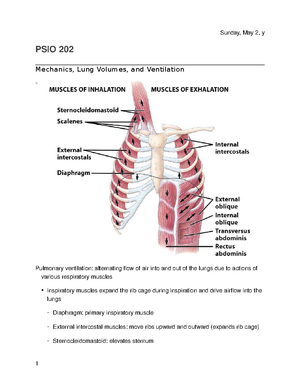 16 Mechanics Lung Volumes And Ventilation Psio 202
16 Mechanics Lung Volumes And Ventilation Psio 202
 Pulmonary Ventilation And Altitude Efficient Exercise
Pulmonary Ventilation And Altitude Efficient Exercise
 Ventilation Anatomy And Physiology
Ventilation Anatomy And Physiology
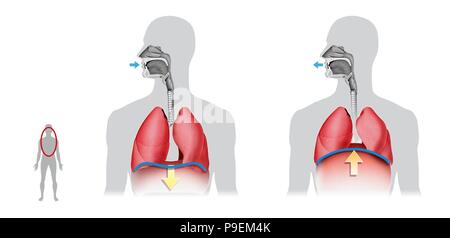 Pulmonary Ventilation Inspiration And Expiration Stock
Pulmonary Ventilation Inspiration And Expiration Stock
 Figure 3 From Oxygen Therapeutics And Mechanical Ventilation
Figure 3 From Oxygen Therapeutics And Mechanical Ventilation
 Lung Anatomy Lessons Tes Teach
Lung Anatomy Lessons Tes Teach
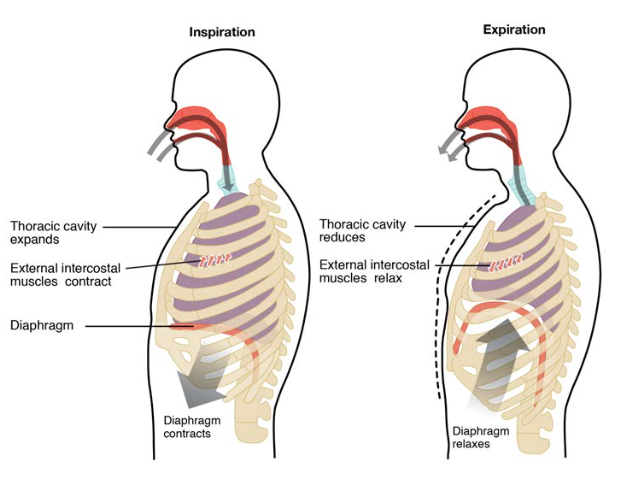 The Process Of Breathing Anatomy And Physiology Ii
The Process Of Breathing Anatomy And Physiology Ii
 Human Respiratory System The Mechanics Of Breathing
Human Respiratory System The Mechanics Of Breathing
 Chapter 3 Alveolar Ventilation Pulmonary Physiology 8e
Chapter 3 Alveolar Ventilation Pulmonary Physiology 8e
 Chapter 3 Alveolar Ventilation Pulmonary Physiology 8e
Chapter 3 Alveolar Ventilation Pulmonary Physiology 8e
Process Of Respiration Pulmonary Ventilation
Airway Anatomy And Physiology Clinical Essentials
 22 3 The Process Of Breathing Anatomy And Physiology
22 3 The Process Of Breathing Anatomy And Physiology

Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar