Knowledge of the bony topography will result in a greater number of anatomic ligament reconstructions. A lack of familiarity leads to hesitancy when performing approaches in these areas of the knee.
The knee cap actually sits inside the patellar tendon.
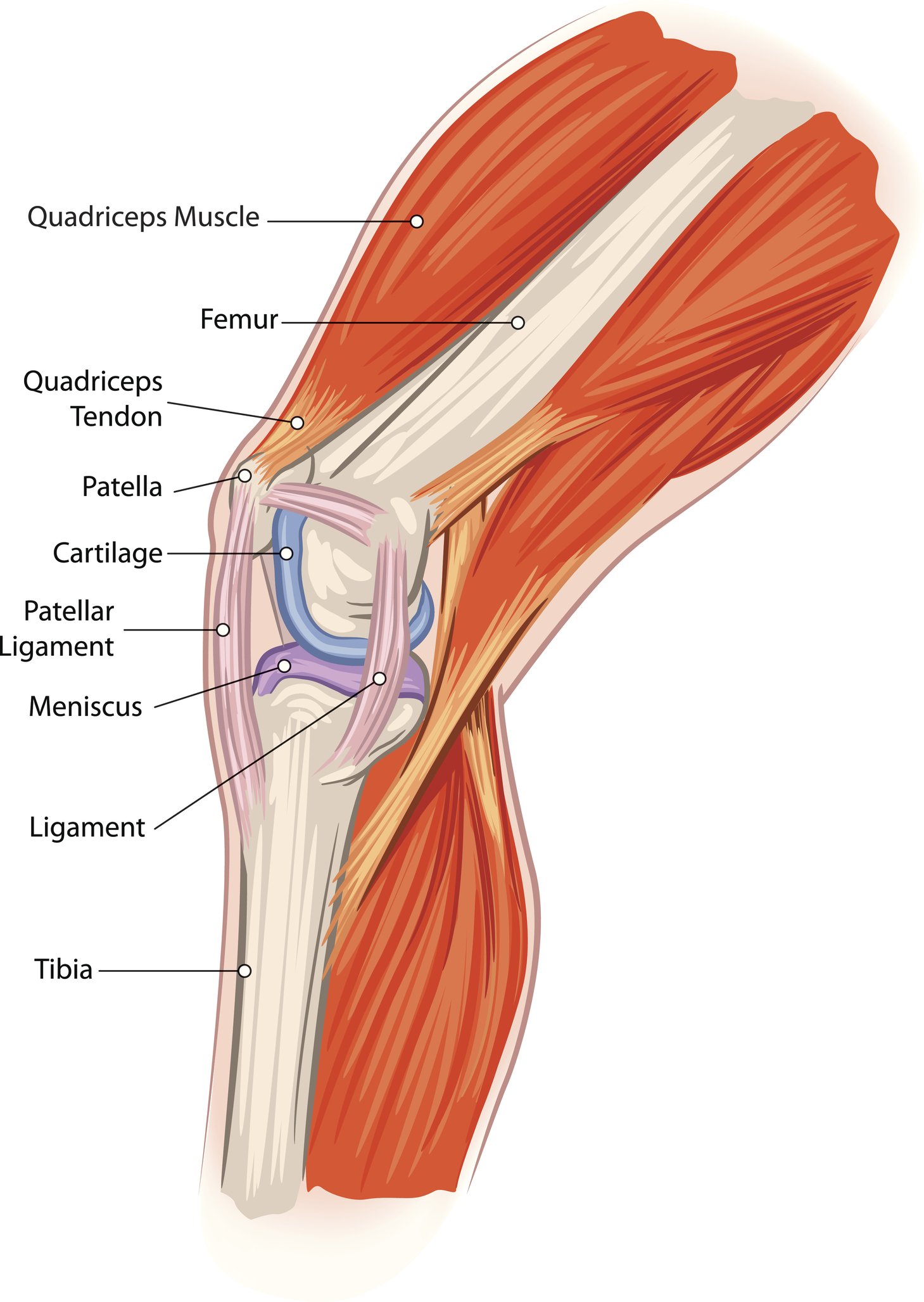
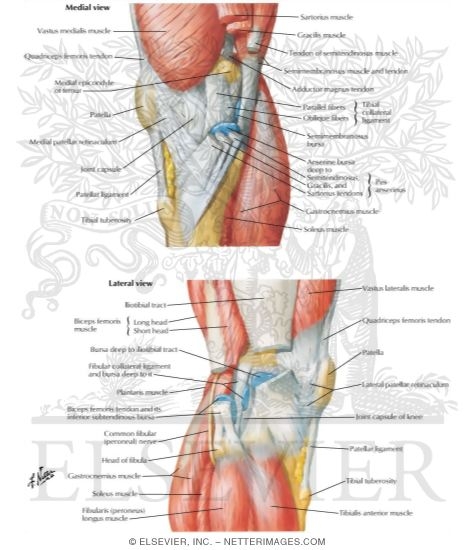
Knee anatomy lateral. Two c shaped pieces of cartilage called the medial and lateral menisci act as shock absorbers between the femur and tibia. The posterior and lateral anatomy of the knee joint presents a challenge to even the most experienced knee surgeon. Thus it has a much higher risk of not healing properly after injury than the medial aspect of the knee.
Lateral knee anatomy the lateral compartment of the knee contains several ligamentous and tendinous structures that are the first restraint against varus angulation and external internal rotation and anterior posterior translation of the leg bone. A lack of familiarity leads to hesitancy when performing approaches in these areas of the knee. The posterior and lateral anatomy of the knee joint presents a challenge to even the most experienced knee surgeon.
To act as shock absorbers by increasing surface area to further dissipate forces. Tendons are often overlooked as part of knee joint anatomy. The lateral meniscus sits on the lateral tibial plateau.
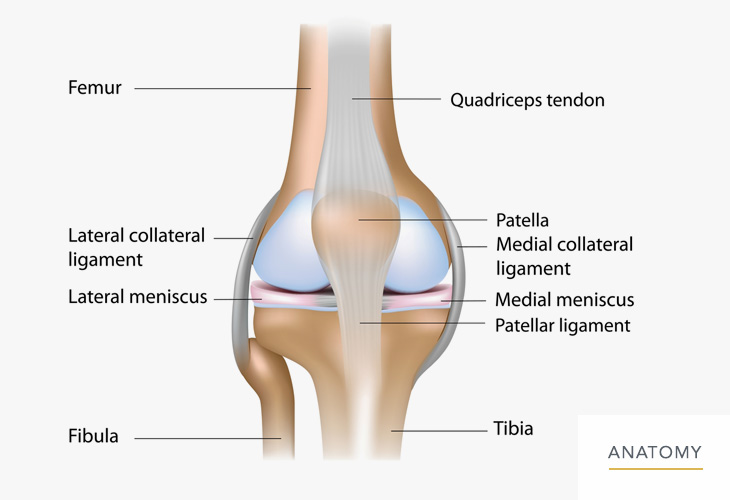
It is attached to the tibia as well as to the joint capsule of the knee. Tendons at the knee. The knee joint is a modified hinge joint between the femur tibia and patella.
It is the largest synovial joint in the body and allows flexion and extension of the leg as well as some rotation in the flexed position. The medial meniscus is a crescent shaped structure that exists on the inside of the knee. The main tendon found at the knee is the patellar tendon which links the quads muscles to the shin bone.
They are they soft tissues found at the end of muscles which link the muscle to bone. The bony shape of the posterolateral knee with the two convex opposing surfaces of the lateral femoral condyle and the lateral tibial plateau makes this portion of the knee inherently unstable compared to the medial aspect. To deepen the articular surface of the tibia thus increasing stability of the joint.
It acts as a shock absorber in the knee and adds stability to the knee joint. Knowledge of the bony topography will result in a greater number of anatomic ligament reconstructions. The medial and lateral menisci are fibrocartilage structures in the knee that serve two functions.
Numerous bursae or fluid filled sacs help the knee move smoothly. Soft tissue structures of the lateral knee attach to the distal femur. Lateral knee bony anatomy the bony anatomy of the lateral knee is essential for understanding not only key relationships of soft tissue structures but also functions as a key determinant of the inability of many lateral knee injuries to heal over time.
It is made of fibrocartilage.
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/11079/anatomy-knee-joint_english.jpg) Leg And Knee Anatomy Bones Muscles Soft Tissues Kenhub
Leg And Knee Anatomy Bones Muscles Soft Tissues Kenhub
 Knee Joint Picture Image On Medicinenet Com
Knee Joint Picture Image On Medicinenet Com
 The Knee Resource Posterolateral Corner Injury
The Knee Resource Posterolateral Corner Injury
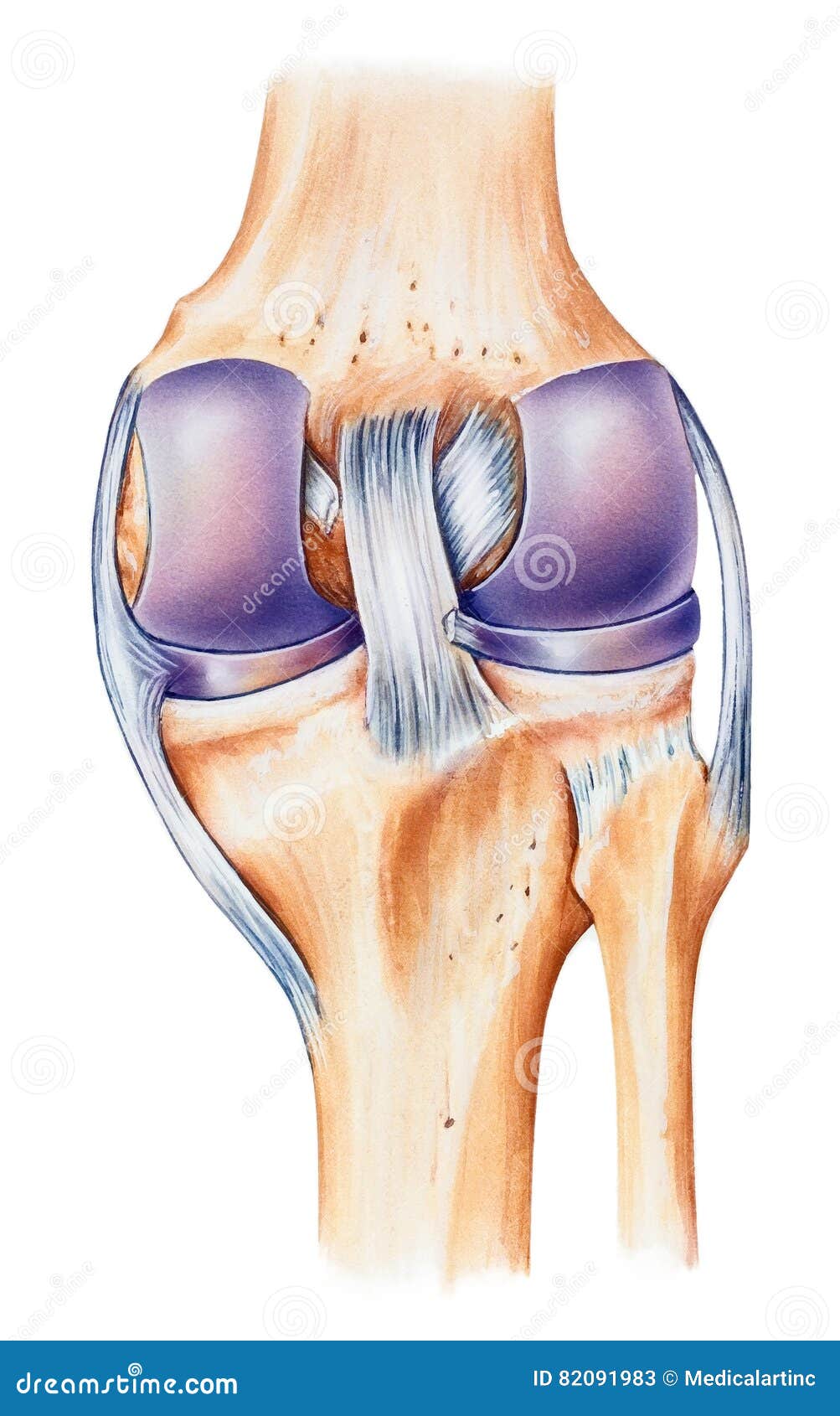 Knee Anatomy Dorsal View Stock Illustration
Knee Anatomy Dorsal View Stock Illustration
 Articular Capsule Of The Knee Joint Wikipedia
Articular Capsule Of The Knee Joint Wikipedia
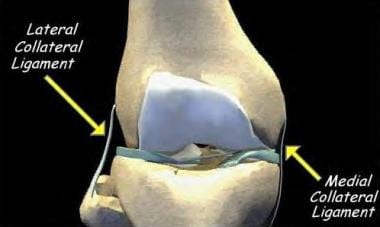 Lateral Collateral Knee Ligament Injury Background
Lateral Collateral Knee Ligament Injury Background
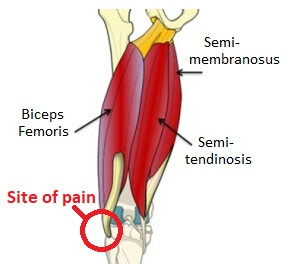 Lateral Knee Pain Pain On Outside Of Knee Knee Pain Explained
Lateral Knee Pain Pain On Outside Of Knee Knee Pain Explained
 Knee Human Anatomy Function Parts Conditions Treatments
Knee Human Anatomy Function Parts Conditions Treatments
Fractures Of The Proximal Tibia Shinbone Orthoinfo Aaos
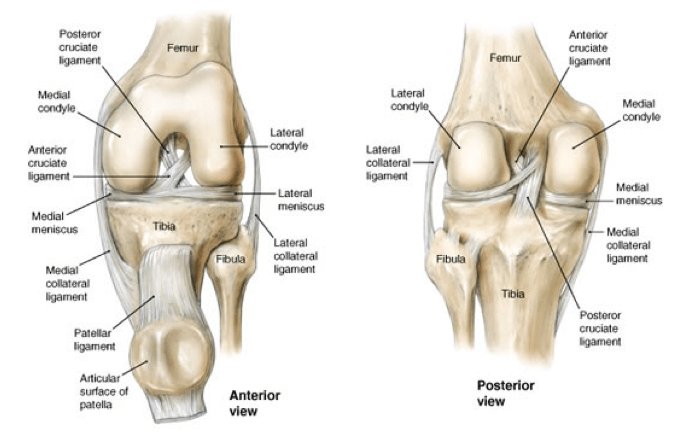 Knee Anatomy And Significance Bone And Spine
Knee Anatomy And Significance Bone And Spine
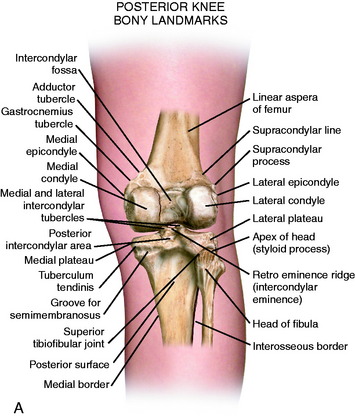 Lateral Posterior And Cruciate Knee Anatomy Clinical Gate
Lateral Posterior And Cruciate Knee Anatomy Clinical Gate
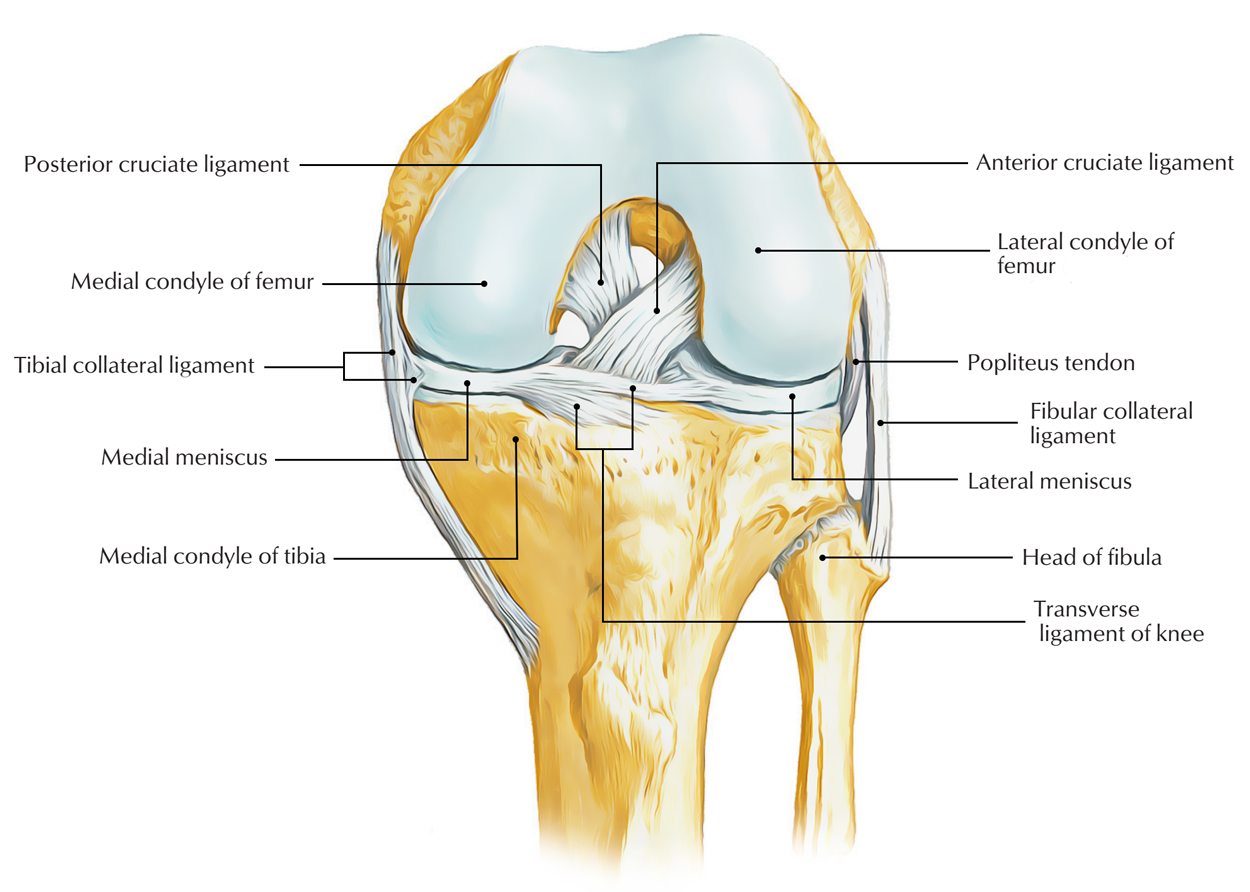 Easy Notes On Ligaments Of The Knee Joint Learn In Just 3
Easy Notes On Ligaments Of The Knee Joint Learn In Just 3
/188058334-crop-56aae7425f9b58b7d0091480.jpg) What Is Causing Your Knee Pain
What Is Causing Your Knee Pain
 Lateral Knee Injury Don T Get Sidelined By Iliotibial Band
Lateral Knee Injury Don T Get Sidelined By Iliotibial Band
 Human Anatomy For The Artist The Lateral Knee A Change Of
Human Anatomy For The Artist The Lateral Knee A Change Of
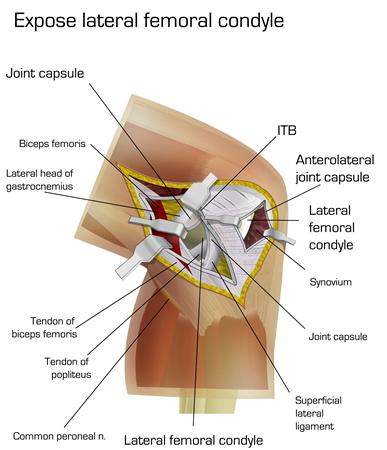 Lateral Approach To The Knee Approaches Orthobullets
Lateral Approach To The Knee Approaches Orthobullets
 Anatomy Of The Knee Central Coast Orthopedic Medical Group
Anatomy Of The Knee Central Coast Orthopedic Medical Group
Anatomy Knee Restoration Center Of Indiana
 A Guide To Your Knees Well Guides The New York Times
A Guide To Your Knees Well Guides The New York Times
 Knee Calf Orthopedic Specialist Of Northern California
Knee Calf Orthopedic Specialist Of Northern California
 Derived Copy Of Anatomy Of Selected Synovial Joints
Derived Copy Of Anatomy Of Selected Synovial Joints


Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar