The body is flat and they feature a tail that is long and thin. What makes rays unusual is that their wing like fins stretch out flat from their bodies making them look like a disc with a tail.
Rays Enchanted Learning Software
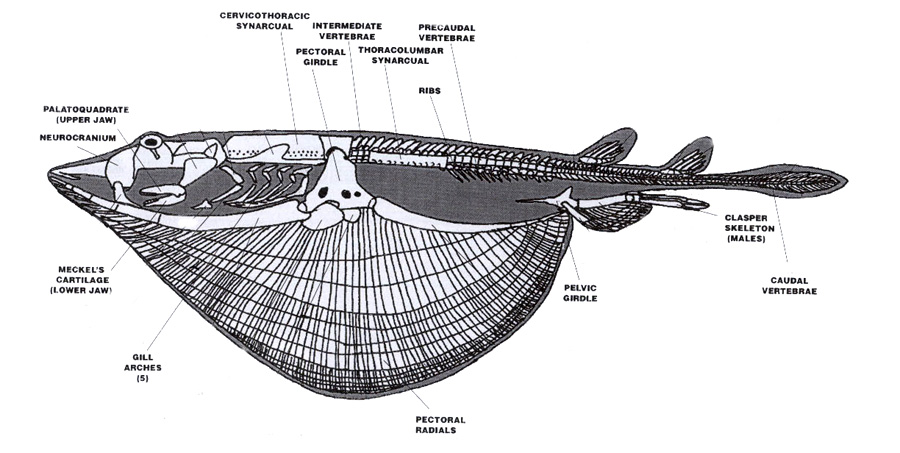
Sharks and rays have skeletons made of flexible cartilage instead of bone.
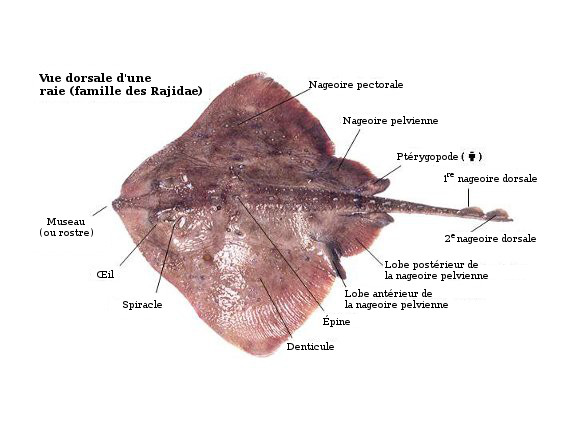
Stingray anatomy. Stingray any of a number of flat bodied rays noted for the long sharp spines on their tails. They inhabit warm temperate and tropical waters sometimes in great abundance. Their pectoral fins can grow up to a total width of 79 inches which they use to stir up the sandy ocean floor to either reveal crustaceans and small fish or bury themselves to hide from predators or prey.
They accomplish this by maintaining concentrations of organic solutes namely urea and an enzyme called trimethylamine oxide or tmao within their bodies. The tail is where the stingers are located. The stingray has a very interesting shape to it.
Females typically reach 28 inches 71 cm in width and weigh 36 pounds 16 kg. They normally live in coastal tropical and subtropical marine waters making it possible for them to come in contact with humans. Although urea is toxic to fish the tmao counteracts the protein de stablizing effects of urea.
Posterior anatomy of a stingray. Stingrays are a flat bodied cartilaginous fish with one or more barbed stingers located midway on the tail. Stingrays are disk shaped and have flexible tapering tails armed in most species with one or more saw edged venomous spines.
The cownose ray is classified as a stingray due to the very close relation to both sharks and skates. These diamond shaped rays are olive brown to green grey on top and creamy white underneath. Cownose rays grow rapidly and male rays often reach about 35 inches 89 cm in width and weigh 26 pounds 12 kg.
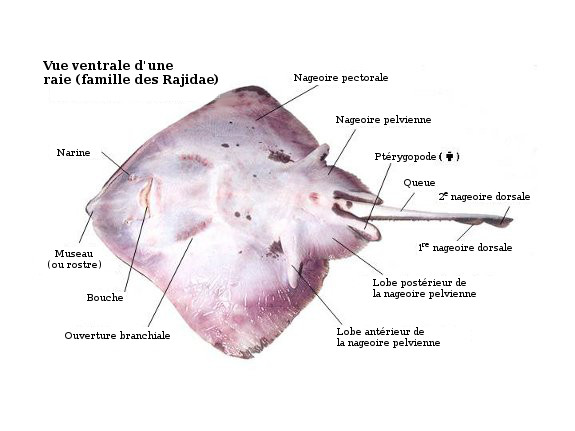
The venom is very strong in the stingers and it could result in a person becoming very ill or even dying. A stingrays eyes are on the dorsal side of the body topupper side. Stingrays have an anatomy composed of a flattened body and on their body consists of pectoral fins joined to their head and trunk with their tail behind.
1 pelvic fins 2 caudal tubercles 3 stinger 4 dorsal fin 5 claspers 6 tail the venom of the stingray has been relatively unstudied due to the mixture of venomous tissue secretions cells and mucous membrane cell products that occurs upon secretion from the spinal blade. On the underside of the stingray lies the mouth nostrils and gill slits. Freshwater stingray morphology physiology.
They spend the majority of their time inactive partially buried in sand often moving only with the sway of the tide. Stingrays are commonly found in the shallow coastal waters of temperate seas. Stingrays are members of the group of fish that also includes sharks and skates.
 Archive Image From Page 290 Of The Cyclopaedia Of Anatomy And
Archive Image From Page 290 Of The Cyclopaedia Of Anatomy And
 David Our Captain Giving Us A Anatomy Lesson On The Stingray
David Our Captain Giving Us A Anatomy Lesson On The Stingray
This Is What Baby Stingrays Look Like Pics
 M Chaise Gilbert On Twitter Anyone Want An Update On The
M Chaise Gilbert On Twitter Anyone Want An Update On The

 Dasyatis Sabina Discover Fishes
Dasyatis Sabina Discover Fishes
 Stingray Anatomy And Ultrasound Mafiadoc Com
Stingray Anatomy And Ultrasound Mafiadoc Com
 Manta Ray Anatomy Manta Ray Facts And Information
Manta Ray Anatomy Manta Ray Facts And Information
Freshwater Stingrays Of The Amazon
 Anatomy Stingray Drawing Mva05012 Fotosearch
Anatomy Stingray Drawing Mva05012 Fotosearch
 Stingray Anatomy Sharks Ocean Sea Animal Science
Stingray Anatomy Sharks Ocean Sea Animal Science
 Medical Management Of Rays Veterian Key
Medical Management Of Rays Veterian Key
 Ray Anatomy Photo Ray Anatomy Photos Phillip Colla Natural
Ray Anatomy Photo Ray Anatomy Photos Phillip Colla Natural
 Anatomy Of The Manta Ray Squidtoons
Anatomy Of The Manta Ray Squidtoons
Search Page 319 Morton Publishing
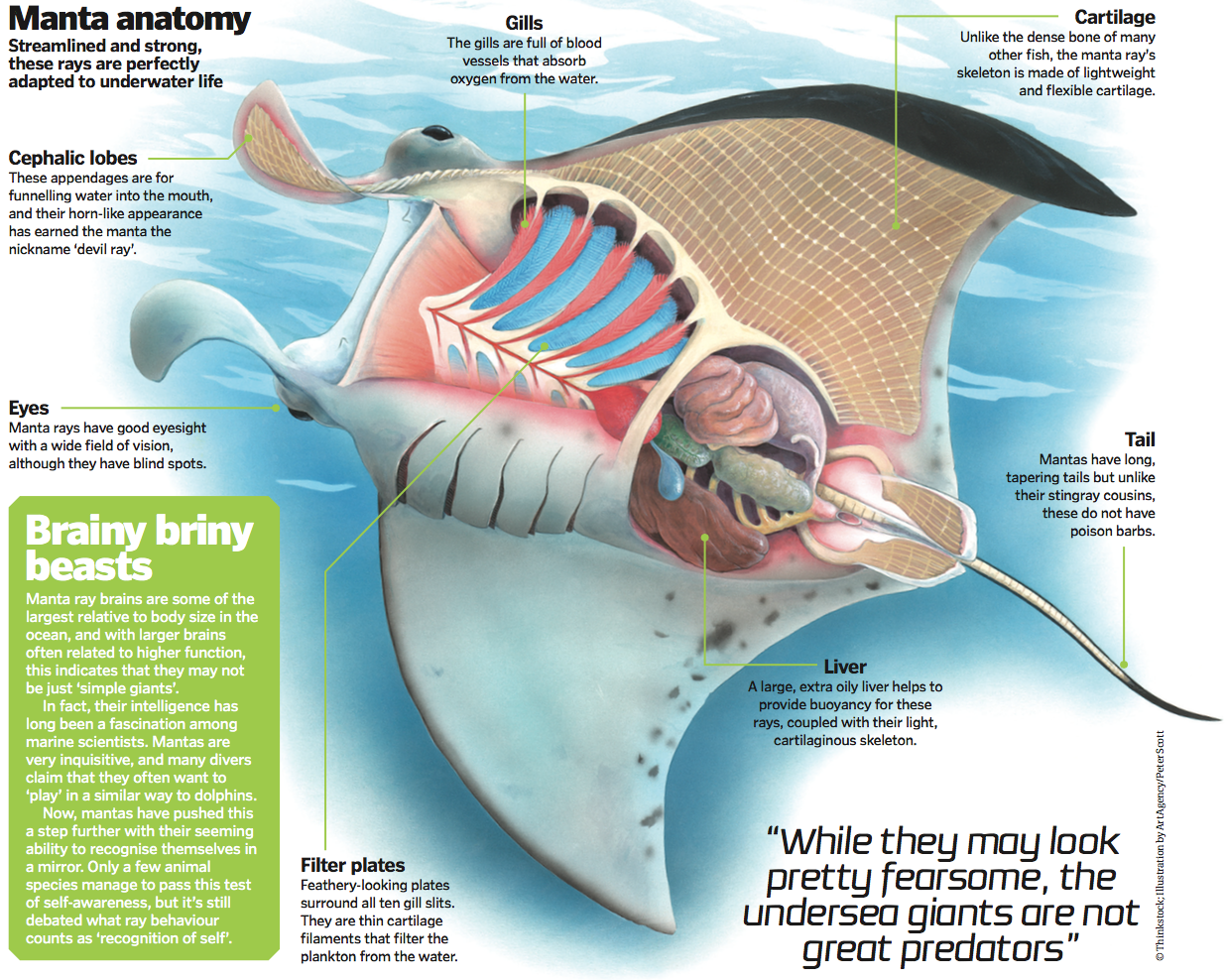 Meet The Manta Ray Large Enough To Cover Your Car They Re
Meet The Manta Ray Large Enough To Cover Your Car They Re
 Flippers And Fins Stingrays Have Six Senses Zero Bones
Flippers And Fins Stingrays Have Six Senses Zero Bones
 Carolina Formalin Stingray Teaching Supplies Biology Classroom
Carolina Formalin Stingray Teaching Supplies Biology Classroom
 Stingray Teeth Manta Ray Manta Birostris Faq Manta
Stingray Teeth Manta Ray Manta Birostris Faq Manta
 Stingray Anatomy By Russockshitha On Deviantart
Stingray Anatomy By Russockshitha On Deviantart
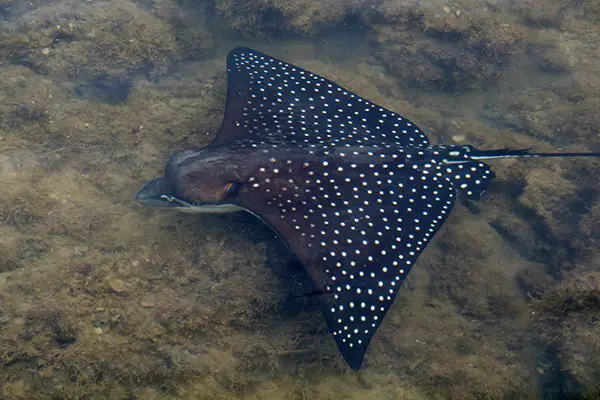 Spotted Eagle Ray Facts Anatomy Diet Habitat Behavior
Spotted Eagle Ray Facts Anatomy Diet Habitat Behavior
 Stingray Anatomy T Shirt Sharks Rays Oceanography Sea Life White Shirt Tee Shirts From Liguo0039 11 87 Dhgate Com
Stingray Anatomy T Shirt Sharks Rays Oceanography Sea Life White Shirt Tee Shirts From Liguo0039 11 87 Dhgate Com
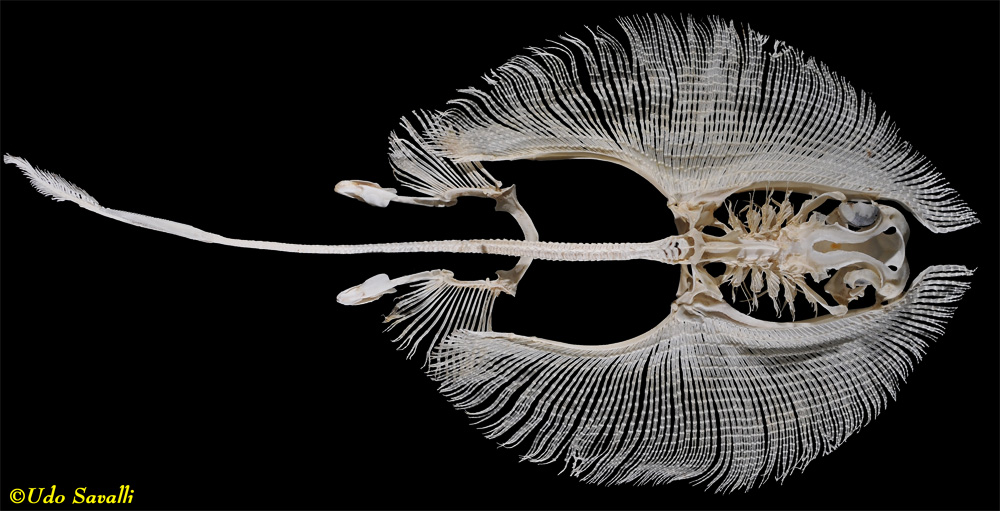



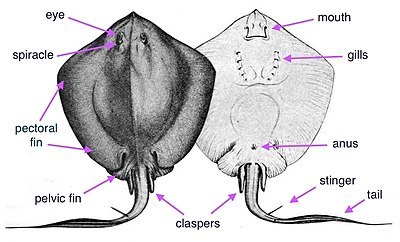

Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar