A macula contains numerous receptor cells called hair cells from which numerous stereocilia long microvilli and a single kinocilium a true cilium extend into a glycoprotein gel the otolithic membrane. In general equilibrium pertains to the condition of achieving balanced thereby resulting in a stable system.
 The Inner Ear Sense Of Balance And Hearing
The Inner Ear Sense Of Balance And Hearing
The maculea play an.

Equilibrium definition anatomy. Static and dynamic equilibrium. The state to which a system evolveseg sustained periodic oscillations. Equilibrium a state of constancy in a system.
Equilibrium receptors in the inner ear are called the what. There are four excitable tissues in our body and all of them have different em values. 2 functions of the vestibular apparatus.
Medical definition of equilibrium 1. The rates of the forward and reverse reactions are equal and the concentrations of the reactants and products remain constant. Anatomy anatomy and physiology.
In biology the term equilibrium may pertain to varying concepts. A population might be in static equilibriumno pasa nadaie no births or deaths or in dynamic equilibriumie same numbers of births and deaths. Equilibrioception genetic equilibrium homeostatic equilibrium nutritive equilibrium punctuated equilibrium and equilibrium theory.
Some of them are as follows. A sensory receptor called a macula is located in the walls of the saccule and utricle the two bulblike sacs of the vestibule. Cards return to set details.
Static equilibrium when a system reaches a point of stability in which no parts are still moving. Cardiac muscle cell 80mv. 42 anatomy of the ear and physiology of hearing and equilibrium.
Free energy the energy in a system capable of causing a reaction. Skeletal muscle cell 90 millivolts mv smooth muscle cell 55mv. Equilibrium a point in a reaction in which the lowest free energy exists on both sides of a chemical equation.
Along with hearing the inner ear is responsible for encoding information about equilibrium the sense of balance which it does in the vestibule and semicircular canals structures that are sometimes collectively referred to as the vestibular apparatus fig. Resting membrane potential em originates from the different concentrations of ions expressed in mmoll at the inner and outer surface of the cell membrane. Several types of sensory receptors provide information to the brain for the maintenance of equilibrium.
A state of balance between opposing forces or actions that is either static as in a body acted on by forces whose resultant is zero or dynamic as in a reversible chemical reaction when the velocities in both directions are equal.
 Ch 15 Inner Ear Static Dynamic Equilibrium
Ch 15 Inner Ear Static Dynamic Equilibrium
 The Vestibular System Definition Anatomy Function
The Vestibular System Definition Anatomy Function
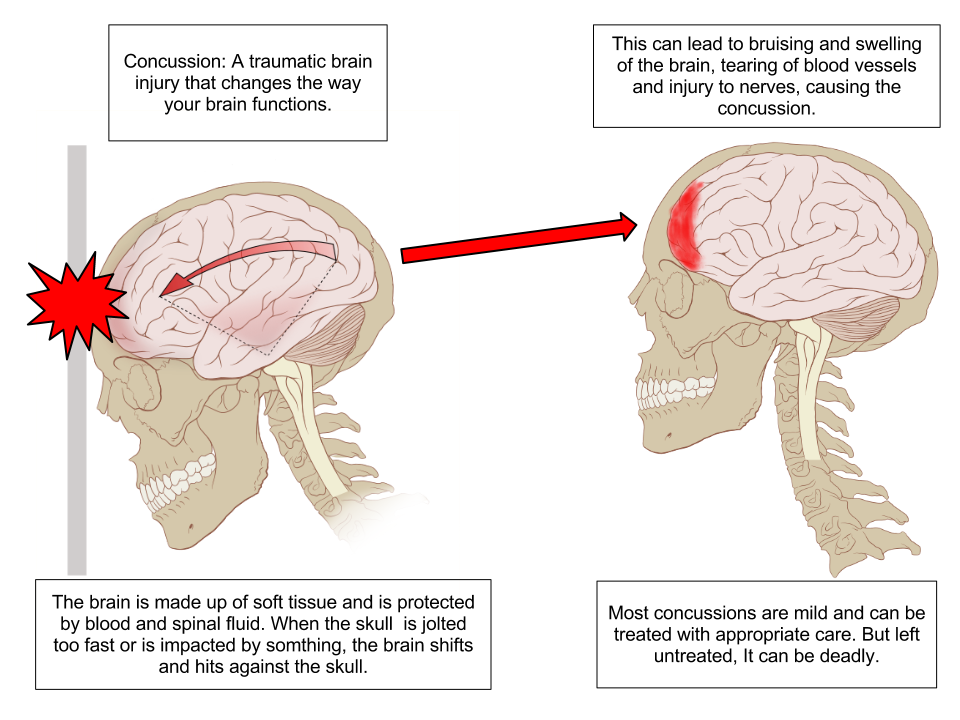 Physical Model For Terminal Velocity Body Physics Motion
Physical Model For Terminal Velocity Body Physics Motion
Vestibular And Balance Disorders Explained Causes And Effects
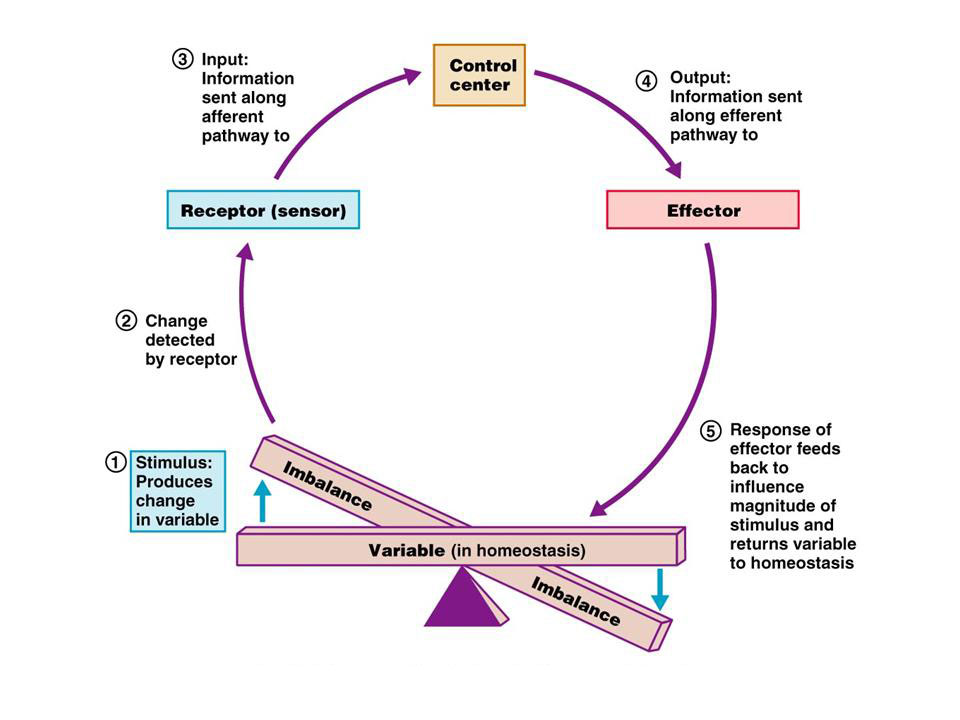 Homeostasis Positive Negative Feedback Mechanisms
Homeostasis Positive Negative Feedback Mechanisms
Special Senses Anatomy Physiology
 Hearing And Equilibrium Boundless Anatomy And Physiology
Hearing And Equilibrium Boundless Anatomy And Physiology
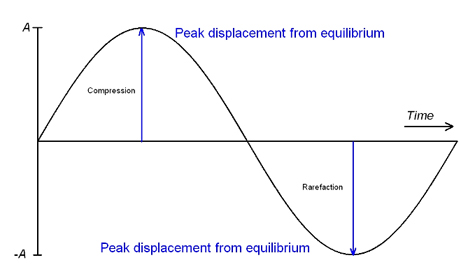 Understanding Sound What Is Sound Pro Audio Files
Understanding Sound What Is Sound Pro Audio Files
Ch 15 Inner Ear Static Dynamic Equilibrium
 Equilibrium And Human Movement Basic Biomechanics 7e
Equilibrium And Human Movement Basic Biomechanics 7e
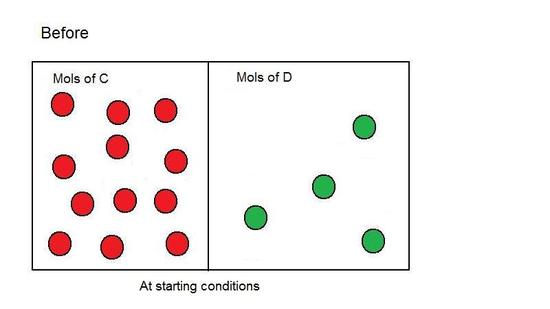 Dynamic Equilibrium Chemistry Libretexts
Dynamic Equilibrium Chemistry Libretexts
/anatomy-of-the-brain-cerebellum-373216_final-87543856311e4c0380bd1fa616c84f41.png) Anatomy Of The Cerebellum And Its Function
Anatomy Of The Cerebellum And Its Function
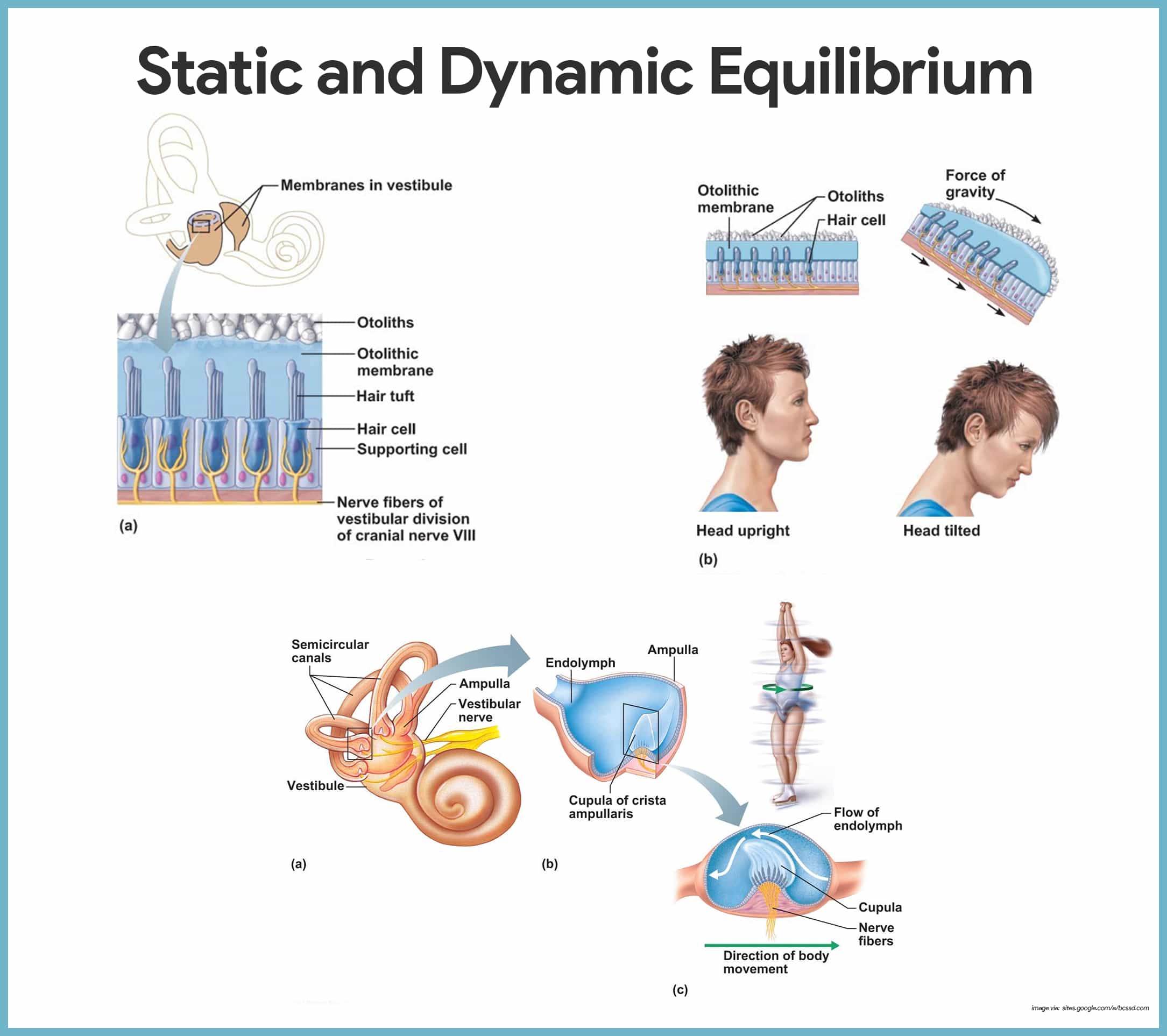 Special Senses Anatomy And Physiology Nurseslabs
Special Senses Anatomy And Physiology Nurseslabs
 Ears And Hearing Anatomy Pictures And Information
Ears And Hearing Anatomy Pictures And Information
 Human Ear Structure Function Parts Britannica
Human Ear Structure Function Parts Britannica
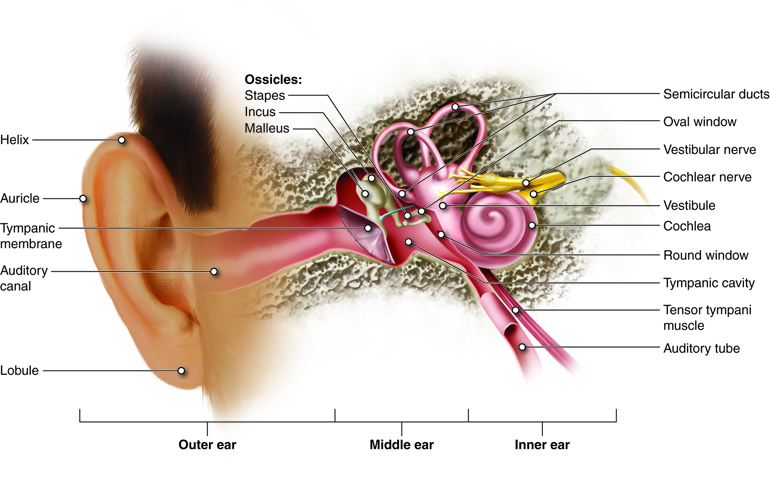 Hearing And Equilibrium Anatomy And Physiology
Hearing And Equilibrium Anatomy And Physiology
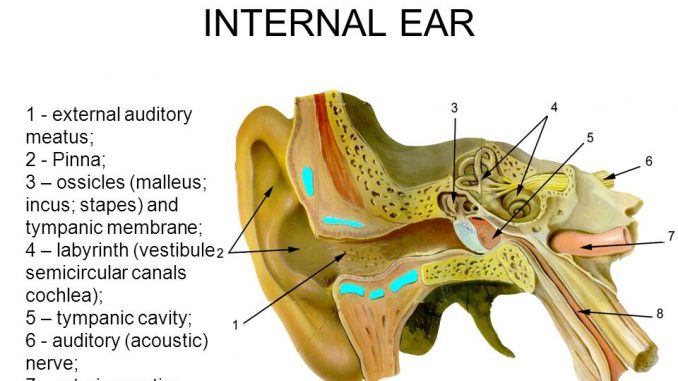 Human Ear Structure And Anatomy Online Biology Notes
Human Ear Structure And Anatomy Online Biology Notes
 Genetic Equilibrium Definition And Examples Biology
Genetic Equilibrium Definition And Examples Biology
 Difference Between Static And Dynamic Equilibrium Biology
Difference Between Static And Dynamic Equilibrium Biology
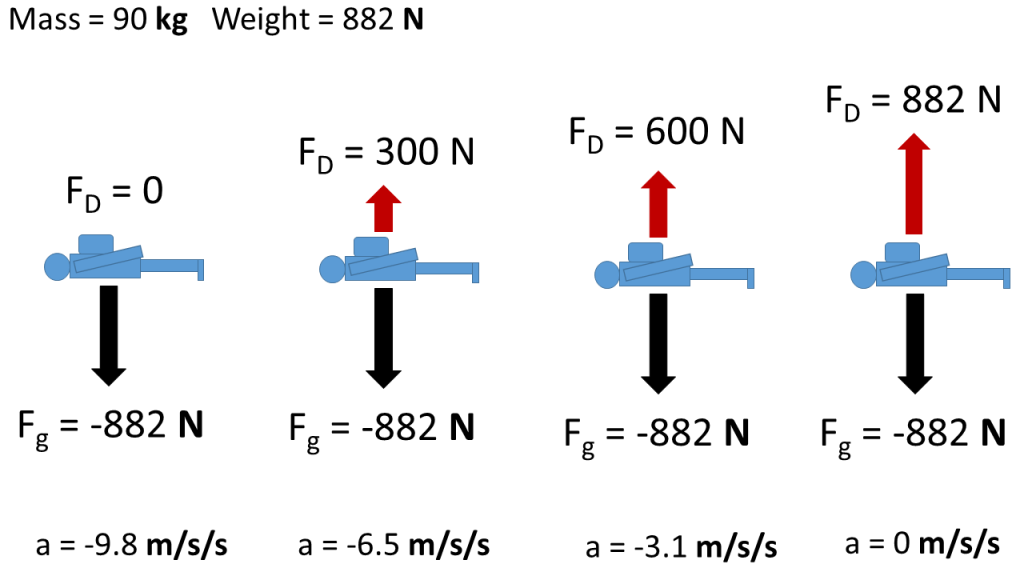 Physical Model For Terminal Velocity Body Physics Motion
Physical Model For Terminal Velocity Body Physics Motion
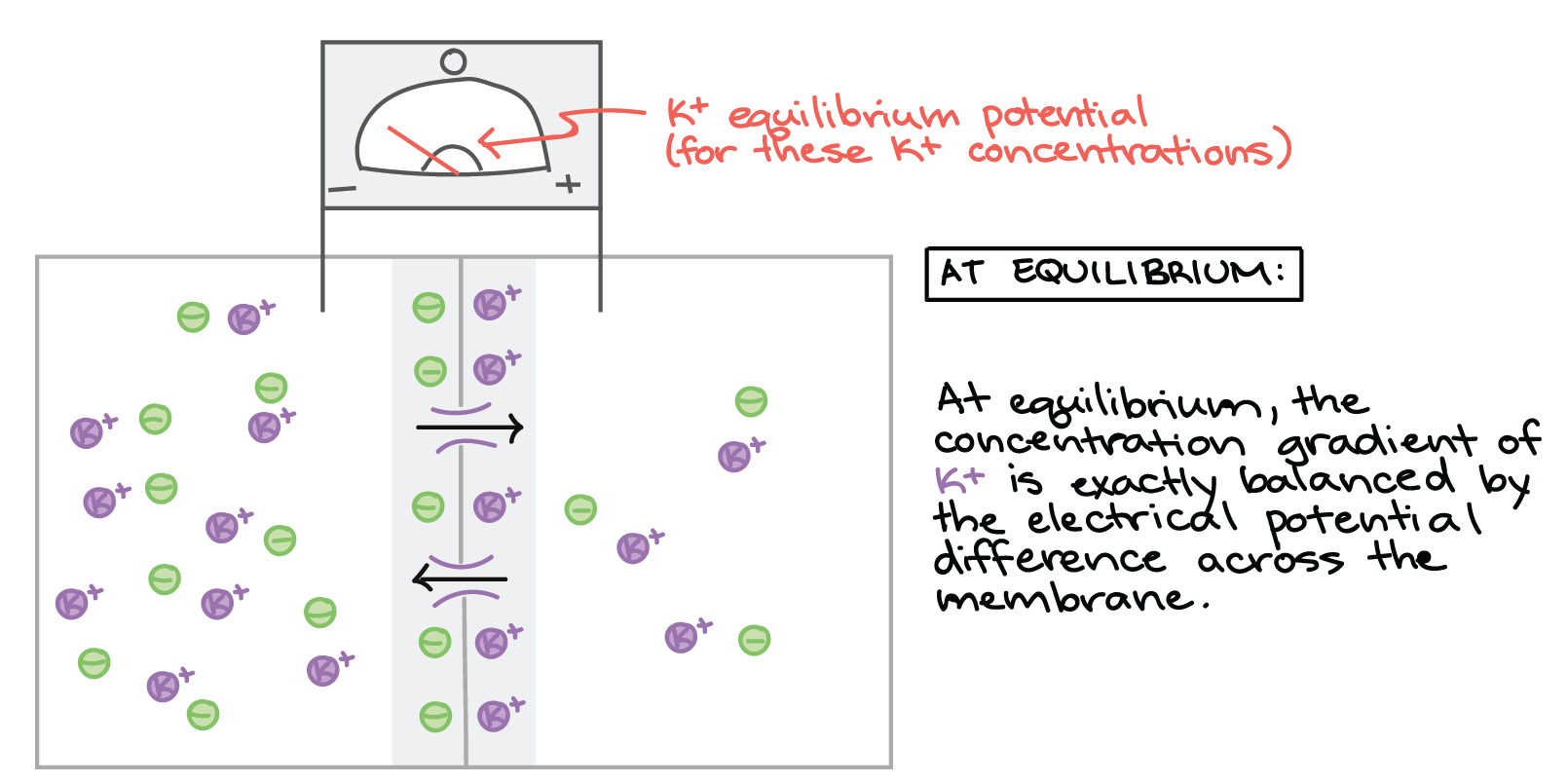 Membrane Potential Resting Membrane Potential Article
Membrane Potential Resting Membrane Potential Article
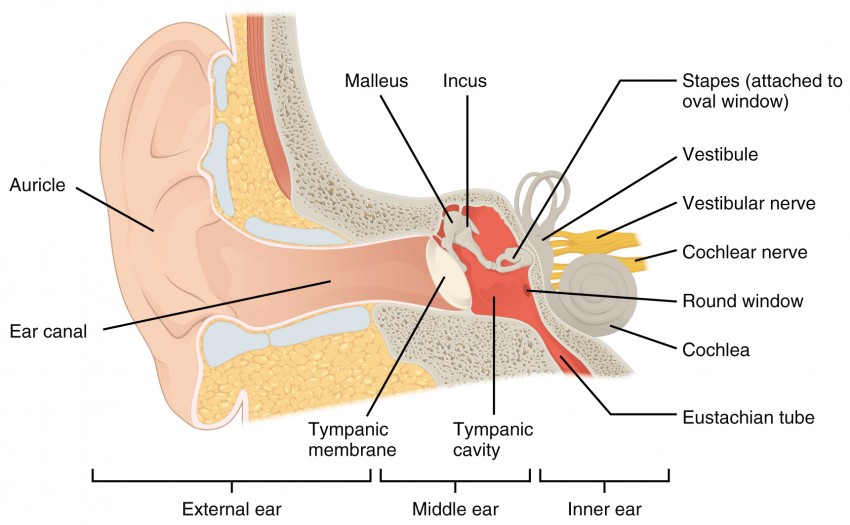 Audition And Somatosensation Anatomy And Physiology I
Audition And Somatosensation Anatomy And Physiology I
What Is Necessary For A Chemical Reaction To Reach Dynamic
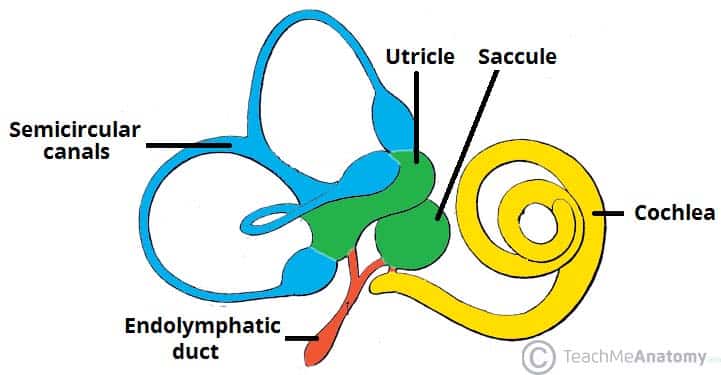 The Inner Ear Bony Labyrinth Membranous Labryinth
The Inner Ear Bony Labyrinth Membranous Labryinth
 Equilibrium Constant Definition And Expression Biology
Equilibrium Constant Definition And Expression Biology
 Lab 2 Hearing And Equilibrium Anatomy Physiology 111
Lab 2 Hearing And Equilibrium Anatomy Physiology 111



Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar