The external carotid artery brings blood to structures outside the skull primarily the face and the internal carotid to structures inside the skull including the brain. Gross anatomy origin it arises most frequently between c3 and c5 vertebral level where the common carotid bifurcates to form the internal carotid and the ex.
External Carotid Artery Cardiovascular Anatomyzone
It contains specific sensory cells called baroreceptors.

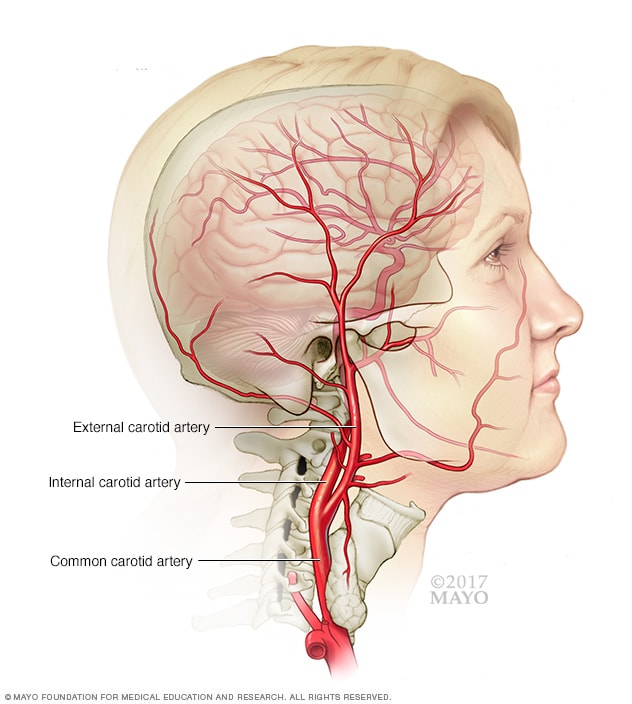
Carotid artery anatomy. The common carotid artery is a large elastic artery which provides the main blood supply to the head and neck region. Cervical segment or c1 identical to the commonly used cervical portion. The internal carotid arteries supply the brain with blood anatomy.
Each common carotid artery is divided into an external and internal carotid artery. The baroreceptors detect stretch as a measure of blood pressure. The segments of the internal carotid artery are as follows.
The right common carotid artery rcca originates in the neck from the brachiocephalic artery while the left common carotid artery lcca arises in the thorax from the arch of the aorta. The primary role of the internal carotid artery is to deliver blood to the forebrain. Adventitia the outer layer.
These arteries transfer blood to the structures inside and outside of the skull. Intima the smooth innermost layer. The left common carotid artery arises from the aortic arch within the superior mediastinum.
The internal carotid arteries together with the vertebral arteries which are the arteries of primary supply for the brain are distinguished by lying at some depth from the surface in their course to the organ by having curves or twists in their course and by having no larger collateral branches. Lacerum segment or c3. There is one common carotid artery on either side of the body and these arteries differ in their origin.
The internal carotid artery ica is a terminal branch of the common carotid artery. Like all arteries the carotid arteries are made of three layers of tissue. The carotid sinus is a dilated portion of the common carotid and internal carotid arteries.
Cavernous segment or c4 almost identical to the commonly used cavernous portion. The carotid arteries are the primary vessels supplying blood to the brain and face. Clinoid segment or c5.
Disorders or injury. Media the muscular middle layer. One of a pair found on each side of the neck the internal carotid artery branches off.
Petrous segment or c2.
 Carotid Stenosis Carotid Artery Disease Cincinnati Oh
Carotid Stenosis Carotid Artery Disease Cincinnati Oh
Blood Supply Of The Central Nervous System Gross Anatomy Of
 Carotid Artery Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock
Carotid Artery Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock
Common Carotid Artery Stepwards
 Carotid Artery Anatomy Chiropractic Neck Manipulation And
Carotid Artery Anatomy Chiropractic Neck Manipulation And
 Iliac Artery Anatomy Britannica
Iliac Artery Anatomy Britannica
 Common Carotid Artery An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Common Carotid Artery An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Topic 97 Internal Carotid Artery Anatomy 06 Studocu
Carotid Stenosis Carotid Artery Disease Cincinnati Oh
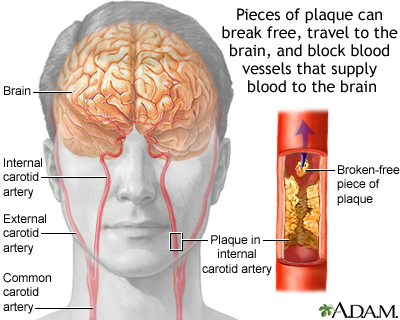 Atherosclerosis Of Internal Carotid Artery Medlineplus
Atherosclerosis Of Internal Carotid Artery Medlineplus
:watermark(/images/watermark_only.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/arteria-carotis-interna/mDfYCBz21jAKTY14gZHOVQ_Arteria_carotis_interna_01.png) Common Carotid Artery Anatomy Kenhub
Common Carotid Artery Anatomy Kenhub
 External Carotid Artery Anatomy Branches Study Com
External Carotid Artery Anatomy Branches Study Com
 The Internal Carotid Artery Human Anatomy
The Internal Carotid Artery Human Anatomy
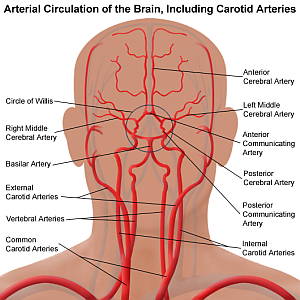 Vascular Anatomy Of The Neck Ent Clinic Sydney
Vascular Anatomy Of The Neck Ent Clinic Sydney
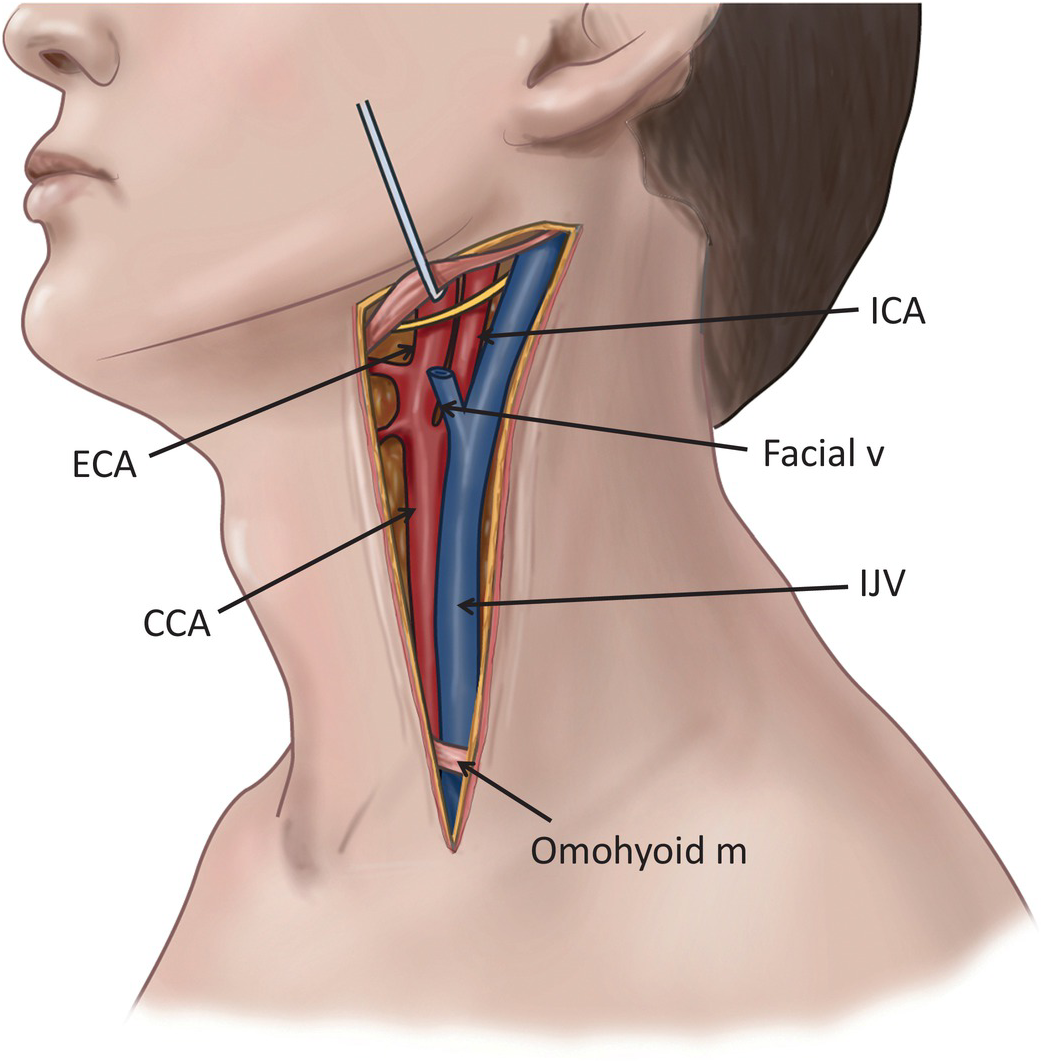 Carotid Artery And Internal Jugular Vein Injuries Chapter 8
Carotid Artery And Internal Jugular Vein Injuries Chapter 8
 Nerves Blood Vessels And Lymph Advanced Anatomy 2nd Ed
Nerves Blood Vessels And Lymph Advanced Anatomy 2nd Ed
 Anatomy Tutorial External Carotid Artery Branches
Anatomy Tutorial External Carotid Artery Branches
 Subclavian And Common Carotid Arteries Acland S Video
Subclavian And Common Carotid Arteries Acland S Video
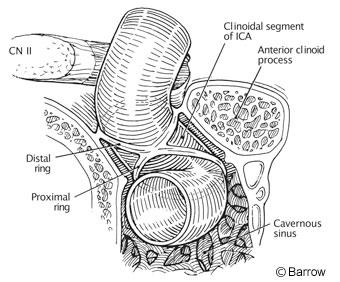 Microsurgical Anatomy Of The Clinoidal Segment Of The
Microsurgical Anatomy Of The Clinoidal Segment Of The
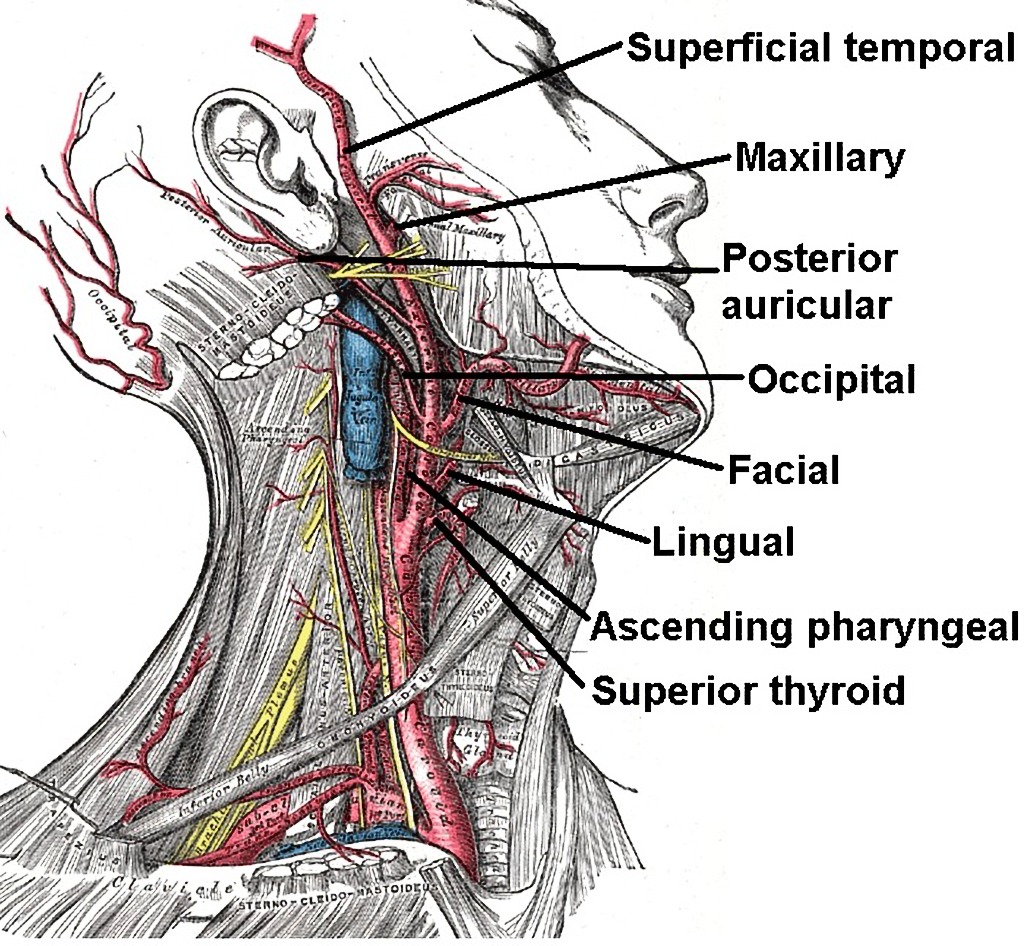 Branches Of The External Carotid Artery Gray S Anatomy
Branches Of The External Carotid Artery Gray S Anatomy
 File Gray S Anatomy With Markup Showing Carotid Artery
File Gray S Anatomy With Markup Showing Carotid Artery
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/11530/triangles-of-the-neck_english.jpg) Internal Carotid Artery Anatomy Segments And Branches Kenhub
Internal Carotid Artery Anatomy Segments And Branches Kenhub
 Carotid Artery Stenosis Wikipedia
Carotid Artery Stenosis Wikipedia

 Carotid Endarterectomy Background Indications
Carotid Endarterectomy Background Indications
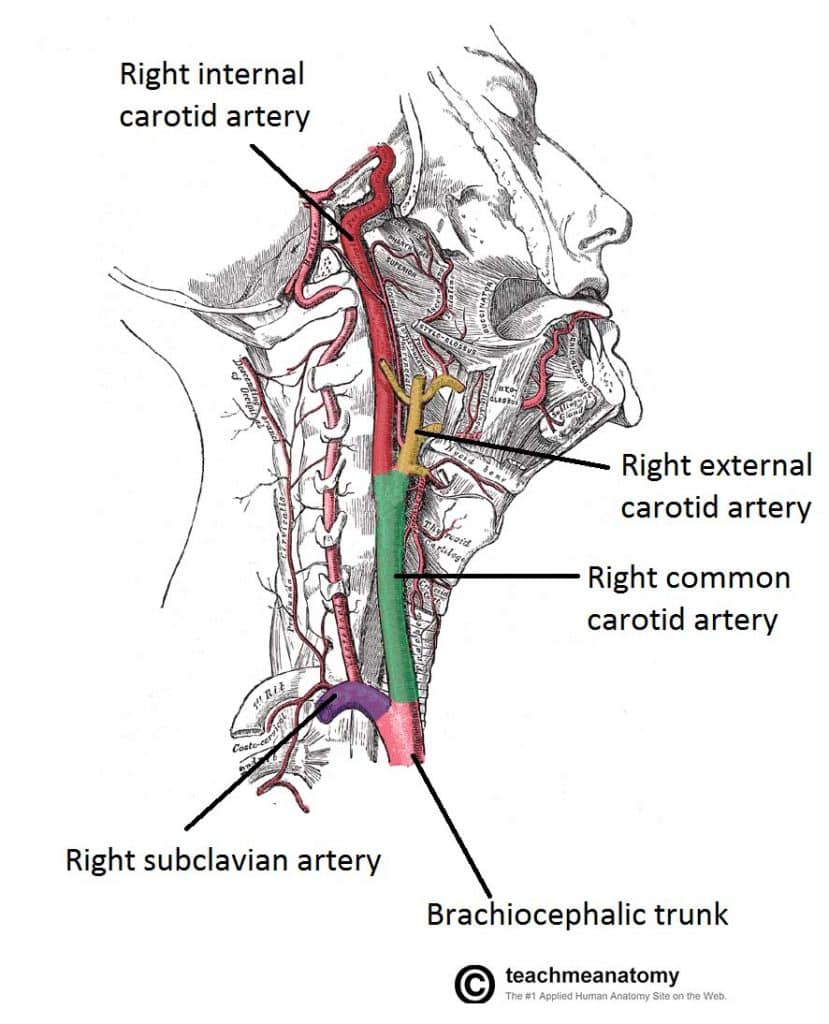 Major Arteries Of The Head And Neck Carotid Teachmeanatomy
Major Arteries Of The Head And Neck Carotid Teachmeanatomy
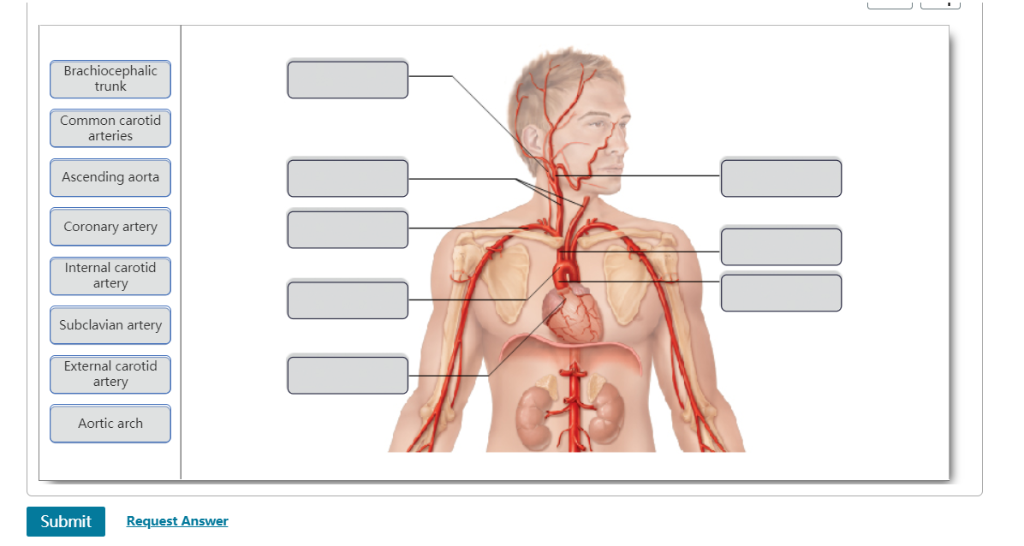 Solved Brachiocephalic Trunk Common Carotid Arteries Asce
Solved Brachiocephalic Trunk Common Carotid Arteries Asce
:watermark(/images/watermark_only.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/common-carotid-artery-3/HEiukC1QxeDTzCN2yghw_Common_Carotid_artery.png) Common Carotid Artery Anatomy Kenhub
Common Carotid Artery Anatomy Kenhub
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/carotid_artery-56a09aa13df78cafdaa329b0.jpg)
Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar