It transports the blood from the surface skin and subcutaneous tissues where it collects in the deep veins. The anatomy and physiology of venous return are described with an emphasis on the differences between standing and walking and the interplay between the venous systems of both the foot and the calf.

The left common iliac vein runs deep to the right common iliac artery to drain into the vena cava which lies to the right of the aorta.

Venous system anatomy. The deep venous system includes the iliac femoral popliteal and deep femoral veins. The superficial venous system includes the reticular veins as well as the great greater and small lesser saphenous veins and their tributaries. Choose from 500 different sets of venous system anatomy flashcards on quizlet.
The reticular veins a network of veins parallel to the skin surface and lying between the saphenous fascia and dermis drain the lower extremity skin and subcutaneous tissue. The circulatory system works thanks to constant pressure from the heart and valves throughout the body. The superficial subcutaneous venous system in the legs includes the long saphenous vein and the short saphenous vein.
Learn venous system anatomy with free interactive flashcards. Most carry deoxygenated blood from the tissues back to the heart but the pulmonary and umbilical veins both carry oxygenated blood to the heart. Anatomy of the venous system.
The cortical veins lie superficially unlike cortical arteries and are adherent to the deep surface of the arachnoid mater so that they keep the sulci open 2. The cerebral venous system somewhat unlike the majority of the rest of the body does not even remotely follow the cerebral arterial system. Grossly the venous system is composed of venules and small and great veins which serve to return blood from tissues to the heart see the image below.
Vein structure the walls of your veins are made up of three different layers. A short wide vein that carries blood to the liver from the organs of the digestive system. Veins are blood vessels that carry blood towards the heart.
This pressure ensures that veins carry blood to the heart and arteries transport it away. The venous system refers to the network of veins that work to deliver deoxygenated blood back to your heart. The systemic venous system brings deoxygenated blood from tissues and organs back to the right atrium of the heart whereas the pulmonary venous system brings oxygenated blood from the pulmonary circulation back to the left atrium of the heart.
The external iliac vein runs deep and is joined by the internal iliac vein which drains blood from the pelvis forming the common iliac vein.
 Vascular System 3 Diseases Affecting The Venous System
Vascular System 3 Diseases Affecting The Venous System
 Spinal Veins An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Spinal Veins An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Blood Supply And Venous Drainage Enlarged Thyroid
 Venous Drainage Of The Lower Extremity Anatomy
Venous Drainage Of The Lower Extremity Anatomy
 Internal External Vertebral Venous Plexuses Median Stock
Internal External Vertebral Venous Plexuses Median Stock
Exercise For Lower Body Parts Bsn Creatine Review The
 Venous System Circulatory System Medical Coding Anatomy
Venous System Circulatory System Medical Coding Anatomy
 Blood Supply And Venous Drainage Of The Kidney Harold E
Blood Supply And Venous Drainage Of The Kidney Harold E
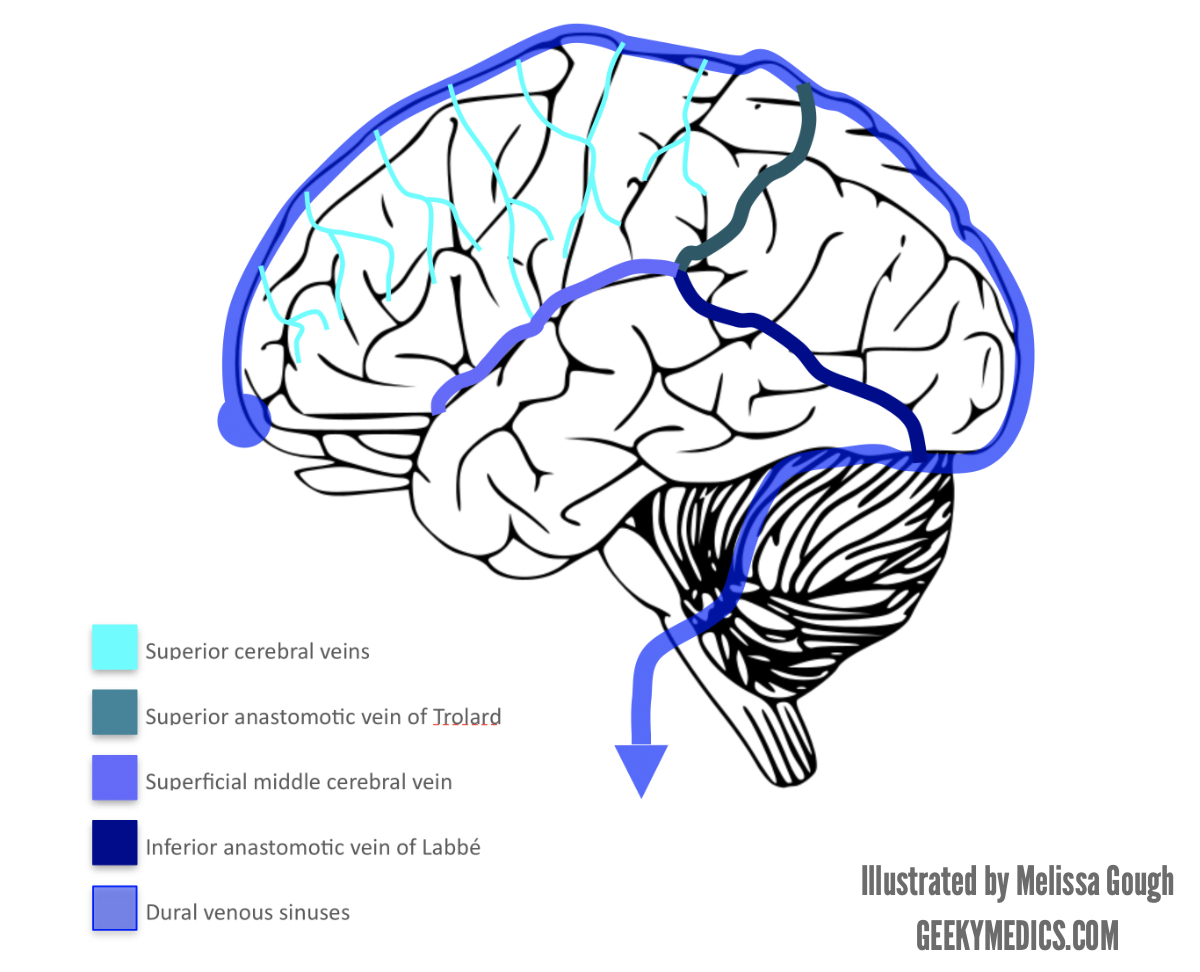 Venous Drainage Of The Brain Anatomy Geeky Medics
Venous Drainage Of The Brain Anatomy Geeky Medics

 Illustration Human Figure With Venous System Heart Vein
Illustration Human Figure With Venous System Heart Vein
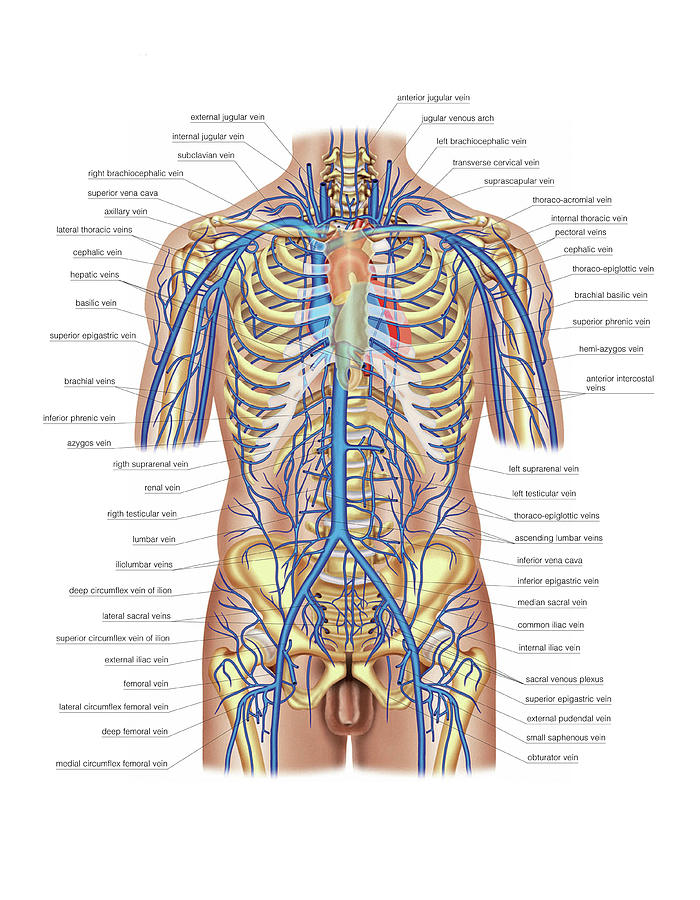
 Venous System Of The Upper Body
Venous System Of The Upper Body
 Science Source Venous System Of The Esophagus Artwork
Science Source Venous System Of The Esophagus Artwork
 The Venous System Of The Male Human Body 1543 At Science
The Venous System Of The Male Human Body 1543 At Science
 Veins Types Venous System Clinical Significance How To
Veins Types Venous System Clinical Significance How To
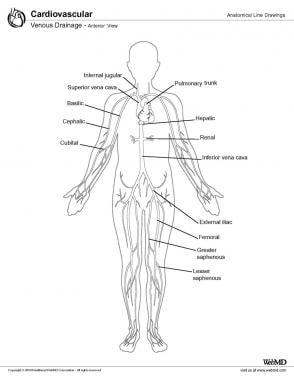 Venous Drainage Anatomy Overview Microscopic Anatomy
Venous Drainage Anatomy Overview Microscopic Anatomy
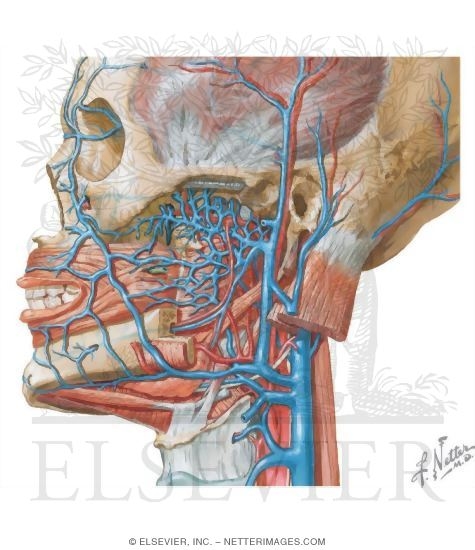 Vascular Supply Of The Face Venous Drainage
Vascular Supply Of The Face Venous Drainage
Chapter 126 Development Of The Venous System The Inferior


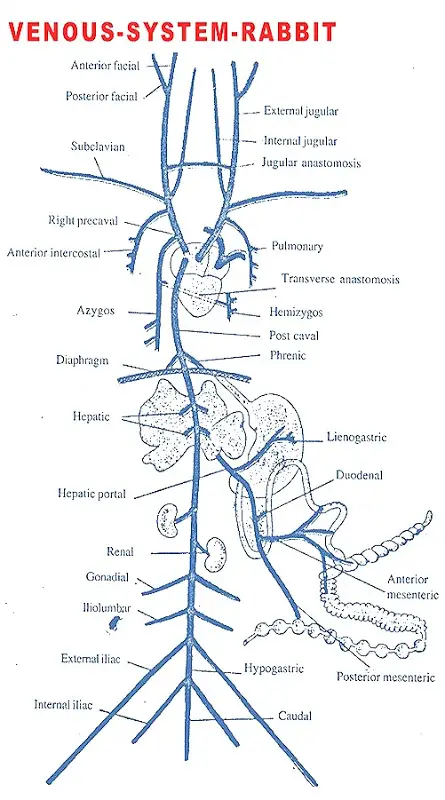

Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar