There are numerous structures that contribute stability to the hip. Radiographs are often necessary to rule out injuries in collision athletes after a direct blow to the bone leading to a subperiosteal hematoma and often.
Muscles Of Hip And Thigh Lateral View Spontaneous Muscle
The hip joint is a ball and socket synovial joint formed by an articulation between the pelvic acetabulum and the head of the femur.
Lateral hip anatomy. Lateral rotation of hip assists abduction of hip when hip is flexed internal surface of obturator membrane posterior bony margins of obturator foramen medial surface of greater trochanter of femur nerve to the obturator internus and superior gemellus. The movements of the hip joint is thus performed by a series of muscles which are here presented in order of importance with the range of motion from the neutral zero degree position indicated. Traditionally lateral hip pain was thought to be primarily due to inflammation of the trochanteric bursa which is a sac of fluid that is found between the tendons that attach the gluteal muscles onto the greater trochanter.
Hip horizontal beam lateral view although technically demanding it is the most versatile hip radiograph utilised in trauma bays and general radiography rooms. Lets quickly go over the anatomy of your lateral hip to help you better understand how this injury occurs. This term has also been used to describe avulsions or fractures about the lateral hip.
Iliofemoral ligament pubofemoral ligament. The capsule and its associated ligaments. The term hip pointer refers to a contusion of the iliac crest figure 1.
It forms a connection from the lower limb to the pelvic girdle and thus is designed for stability and weight bearing rather than a large range of movement. Your glute medius is a large fan shaped muscle that runs from the lateral part of your pelvis iliac crest and connects with a single tendon to your femur. The ball and socket bony structure.
L5s1 branch of the sacral plexus internal pudendal artery. Standard anatomical terms of location deal unambiguously with the anatomy of animals including humans. It requires minimal patient movement on the affected side while providing high quality diagnostic images that can be replicated both intraoperatively and postoperatively 13 4.
The surrounding muscles including the abductors gluteus medius and minimus and external. Lateral or external rotation 30 with the hip extended 50 with the hip flexed. All vertebrates including humans have the same basic body plan they are strictly bilaterally symmetrical in early embryonic stages and largely bilaterally symmetrical in adulthood.
11 the glute minimus is a smaller muscle that fits right behind the glute medius attaching also to the femur bone. That is they have mirror image left and right halves if divided down the middle.
 Laminated Anatomy And Injuries Of The Hip Poster Hip Joint Anatomical Chart 18 X 27
Laminated Anatomy And Injuries Of The Hip Poster Hip Joint Anatomical Chart 18 X 27
 Deep Six Lateral Rotators Attachments And Actions
Deep Six Lateral Rotators Attachments And Actions
Lateral Hip Pain With Golf Dynamic Physio Therapy Naples
![]() Issues Around The Hip From Tendonitis To Bursitis Beacon
Issues Around The Hip From Tendonitis To Bursitis Beacon
 Deep Six Lateral Rotators Attachments And Actions
Deep Six Lateral Rotators Attachments And Actions
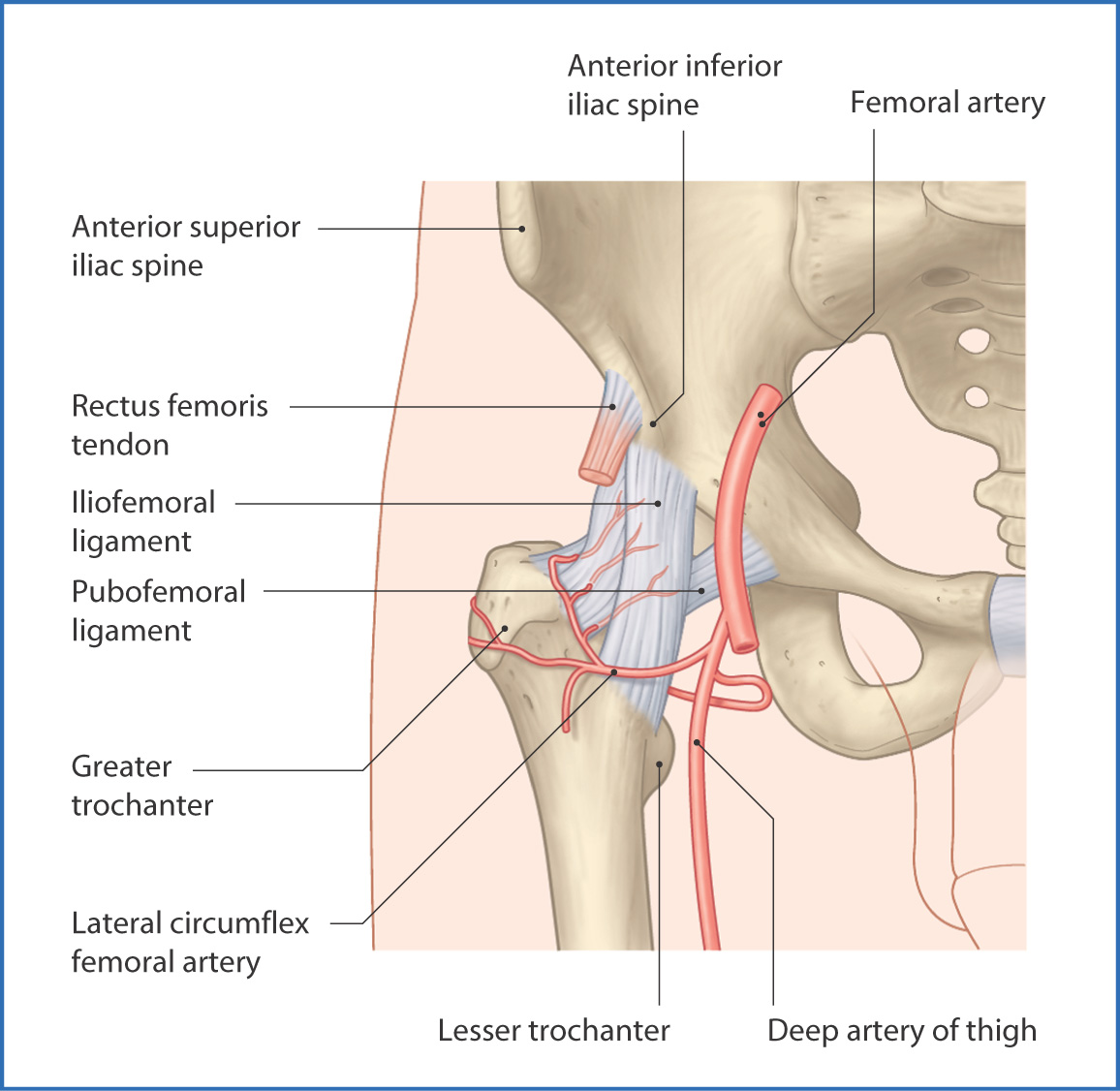 Hip Anatomy Recon Orthobullets
Hip Anatomy Recon Orthobullets
![]() Issues Around The Hip From Tendonitis To Bursitis Beacon
Issues Around The Hip From Tendonitis To Bursitis Beacon
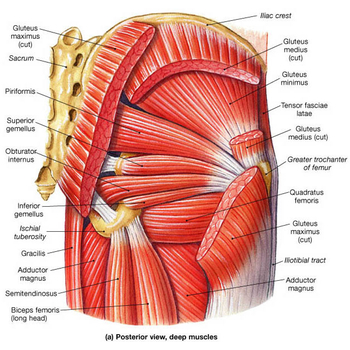 Hip Osteoarthritis Physiopedia
Hip Osteoarthritis Physiopedia
Hip Radiographic Anatomy Wikiradiography
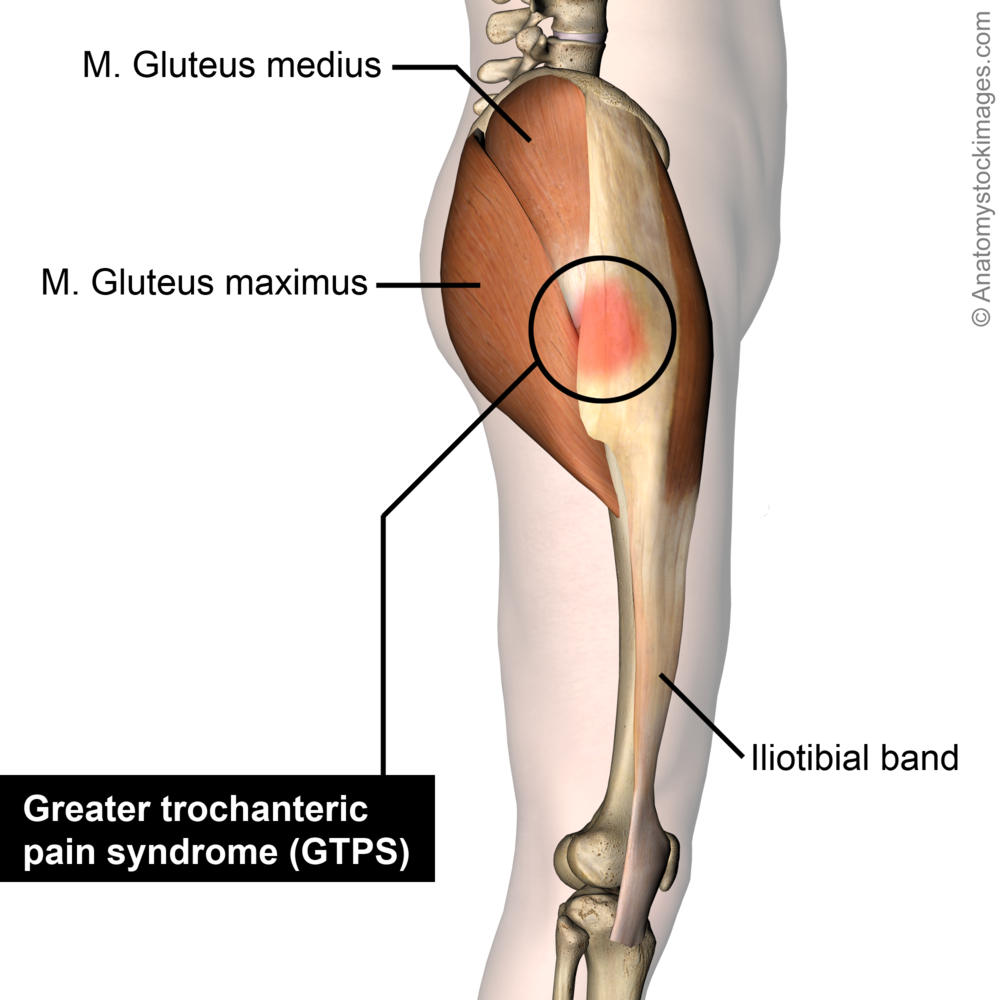 Why Does The Outside Of My Hip Hurt What To Do About It
Why Does The Outside Of My Hip Hurt What To Do About It
 Hip And Knee Chart 20x26 Clinicalposters
Hip And Knee Chart 20x26 Clinicalposters
 Muscles Of The Hips And Thighs Human Anatomy And
Muscles Of The Hips And Thighs Human Anatomy And
 Muscles Of Hip Thigh Anatomy 3300 With Turner At The Ohio
Muscles Of Hip Thigh Anatomy 3300 With Turner At The Ohio
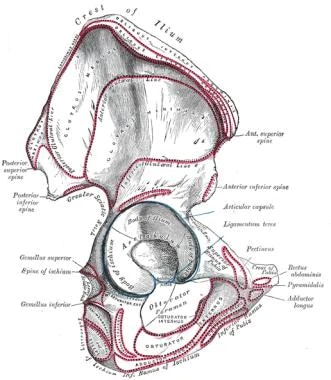 Hip Joint Anatomy Overview Gross Anatomy
Hip Joint Anatomy Overview Gross Anatomy
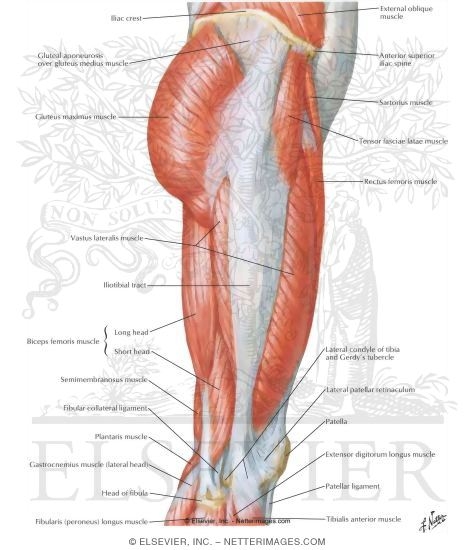 Muscles Of Hip And Thigh Lateral View
Muscles Of Hip And Thigh Lateral View
 Illitibial Band Syndrome Symptoms Treatment Exercises
Illitibial Band Syndrome Symptoms Treatment Exercises
 Muscles Of The Hips And Thighs Human Anatomy And
Muscles Of The Hips And Thighs Human Anatomy And
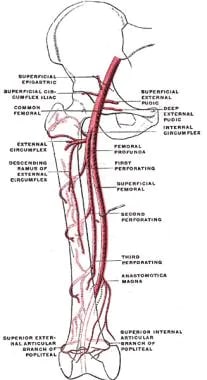 Hip Joint Anatomy Overview Gross Anatomy
Hip Joint Anatomy Overview Gross Anatomy
 Management Of Acute Hip Fracture Nejm
Management Of Acute Hip Fracture Nejm
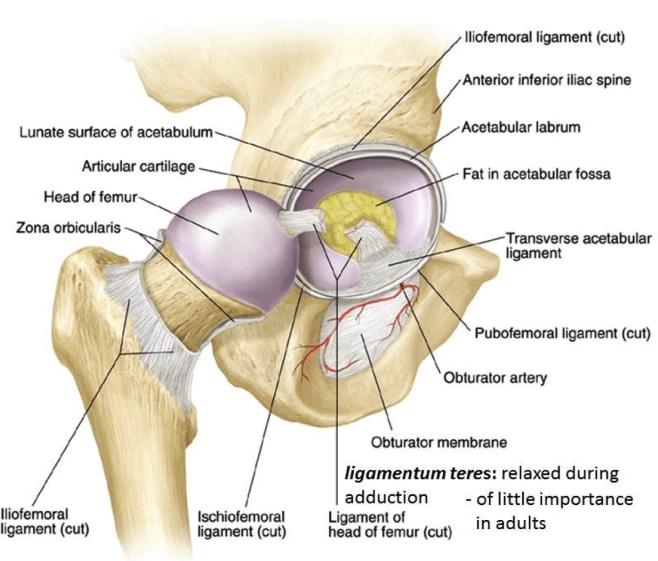 Hip Anatomy Recon Orthobullets
Hip Anatomy Recon Orthobullets
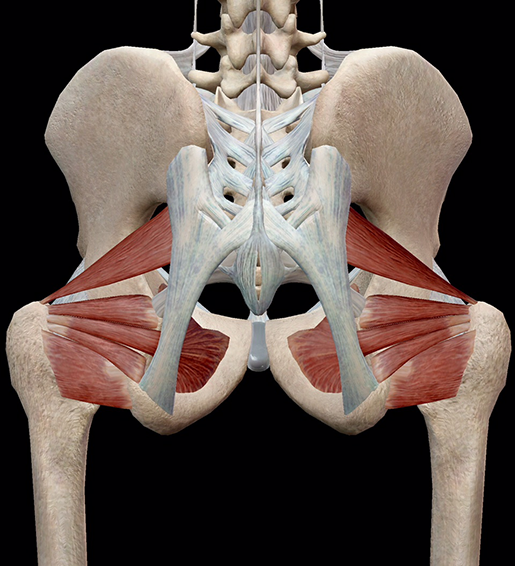 Learn Muscle Anatomy Lateral Rotators
Learn Muscle Anatomy Lateral Rotators
 Hip Anatomy Pictures Function Problems Treatment
Hip Anatomy Pictures Function Problems Treatment
 Hip Flexors An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Hip Flexors An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar