There are three types of muscles. Describe the differences between single unit smooth muscle and multiunit smooth muscle.
 Three Types Of Muscle Video Khan Academy
Three Types Of Muscle Video Khan Academy
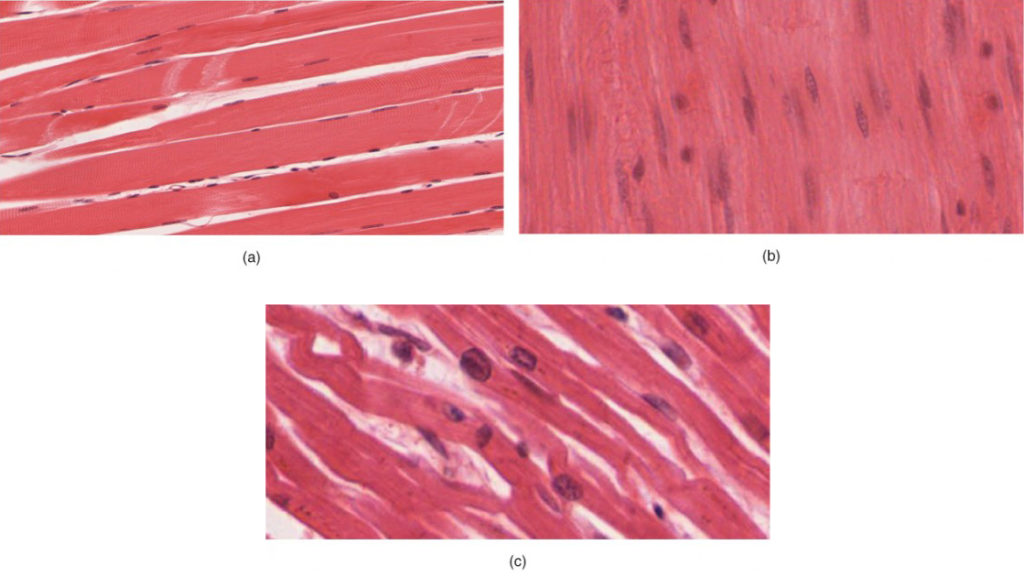
It consists of narrow spindle shaped cells with a single centrally located nucleus.

Smooth muscle definition anatomy. Skeletal muscles smooth muscles and the cardiac muscles. Smooth muscle definition smooth muscle is a type of muscle tissue which is used by various systems to apply pressure to vessels and organs. Smooth muscles can contract over a wider range of resting lengths because the actin and myosin filaments in smooth muscle are not as rigidly organized as those in skeletal and cardiac muscle.
Smooth muscle also called involuntary muscle muscle that shows no cross stripes under microscopic magnification. In contrast the smooth muscle lacks striations. Muscle tissue that contracts without voluntary control having fine myofibrils but lacking transverse striations and found in the walls of internal organs blood vessels and hair follicles.
Smooth muscle is composed of sheets or strands of smooth muscle cells. Muscle tissue that contracts without conscious control having the form of thin layers or sheets made up of spindle shaped unstriated cells with single nuclei and found in the walls of the internal organs such as the stomach intestine bladder and blood vessels excluding the heart. Smooth muscle generally forms the supporting tissue of blood vessels and hollow internal organs such as the stomach intestine and bladder.
Smooth muscle is a type of tissue found in the walls of hollow organs such as the intestines uterus and stomachyou can also find smooth muscle in the walls of passageways including arteries and veins of de cardiovascular systemthis type of involuntary non striated muscle is also found in the tracts of the urinary respiratory and reproductive systems. Both the skeletal muscles and the cardiac muscles have striations when viewed under the microscope. Muscle tissue that contracts without conscious control having the form of thin layers or sheets made up of spindle shaped unstriated cells with single nuclei and found in the walls of the internal organs such as the stomach intestine bladder and blood vessels excluding the heart.
It is considered smooth because it does not have the microscopic lines the striations seen in the other two types of muscle. Smooth muscle so named because the cells do not have striations is present in the walls of hollow organs like the urinary bladder uterus stomach intestines and in the walls of passageways such as the arteries and veins of the circulatory system and the tracts of the respiratory urinary and reproductive systems figure 1ab. The muscular system encompasses all the muscles of the animal body.
Smooth muscle tissue unlike striated muscle contracts slowly and automatically. Medical definition of smooth muscle.
 Muscular System Muscles Of The Human Body
Muscular System Muscles Of The Human Body
 Sarcolemma Definition And Function Biology Dictionary
Sarcolemma Definition And Function Biology Dictionary
 What Is The Strongest Muscle In The Human Body Library Of
What Is The Strongest Muscle In The Human Body Library Of
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/3241/EBqW2Iaai2iY2SRzmvz6g_Smooth_muscle_fibers.png) Smooth Muscle Histology Kenhub
Smooth Muscle Histology Kenhub
 Muscular System Biology 1600 With Paulette Butt At College
Muscular System Biology 1600 With Paulette Butt At College
 Your Muscles For Kids Nemours Kidshealth
Your Muscles For Kids Nemours Kidshealth
 Dictionary Normal Smooth Muscle The Human Protein Atlas
Dictionary Normal Smooth Muscle The Human Protein Atlas
 What Is Smooth Muscle What Does Smooth Muscle Mean Smooth Muscle Meaning Explanation
What Is Smooth Muscle What Does Smooth Muscle Mean Smooth Muscle Meaning Explanation
 Muscle Tissue And Motion Anatomy And Physiology I
Muscle Tissue And Motion Anatomy And Physiology I

 Contractile Mechanism Of Smooth Muscle
Contractile Mechanism Of Smooth Muscle
 Muscle Spasms Causes Treatment Medications Symptoms
Muscle Spasms Causes Treatment Medications Symptoms

 11 Functions Of The Muscular System Diagrams Facts And
11 Functions Of The Muscular System Diagrams Facts And
 Bisci 107 L 30 33 Muscle Biological Sciences 107 With
Bisci 107 L 30 33 Muscle Biological Sciences 107 With
 Muscle Tissue And Motion Anatomy And Physiology I
Muscle Tissue And Motion Anatomy And Physiology I
 Latch Mechanism Smooth Muscle Simplified View
Latch Mechanism Smooth Muscle Simplified View
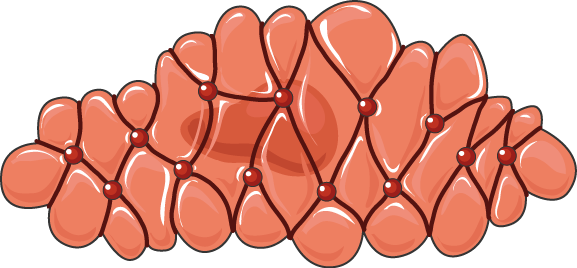 Smooth Muscle Contracted Servier Medical Art
Smooth Muscle Contracted Servier Medical Art
 Ivyrose Holistic Muscle Components Associated Structures
Ivyrose Holistic Muscle Components Associated Structures
 11 Functions Of The Muscular System Diagrams Facts And
11 Functions Of The Muscular System Diagrams Facts And
 Human Muscle Cell Types Interactive Anatomy Guide
Human Muscle Cell Types Interactive Anatomy Guide
:watermark(/images/watermark_only.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/smooth-muscle-bundle/MNblRhrjntdMdmcBKVe1UA_Smooth_muscle_bundle.png) Smooth Muscle Structure Function Location Kenhub
Smooth Muscle Structure Function Location Kenhub
Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar