Once mastication is done the bolus is ready to be swallowed. Palate in vertebrate anatomy the roof of the mouth separating the oral and nasal cavities.
 S1b6 Anatomy Palate Lymph Nodes Of Head And Neck
S1b6 Anatomy Palate Lymph Nodes Of Head And Neck
The palate ˈpælɪt is the roof of the mouth in humans and other mammals.
:watermark(/images/watermark_only.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/hard-palate-2/8kcLkpxMABUuFTQaHKlZeA_Hard_palate.png)
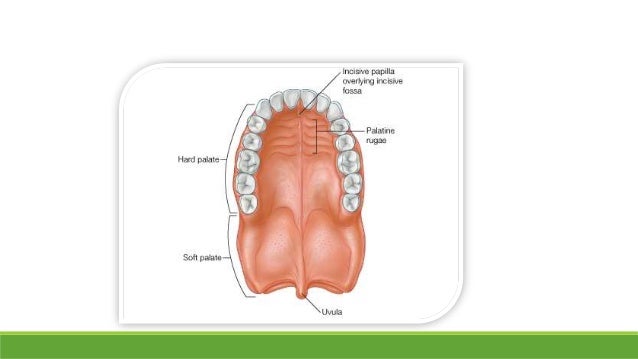
Anatomy of palate. When elevated for swallowing and sucking it completely blocks and separates the nasal cavity and nasal portion of the pharynx from the mouth and. The palate divides the nasal cavity and the oral cavity with the hard palate positioned anteriorly and the soft palate posteriorly. The palate is divided into two parts the anterior bony hard palate and the posterior fleshy soft palate.
A similar structure is found in crocodilians but in most other tetrapods the oral and nasal cavities are not truly separated. The anterior portion of the palate is bordered anteriorly and laterally by the maxillary teeth. The hard palate separates the oral and nasal cavities.
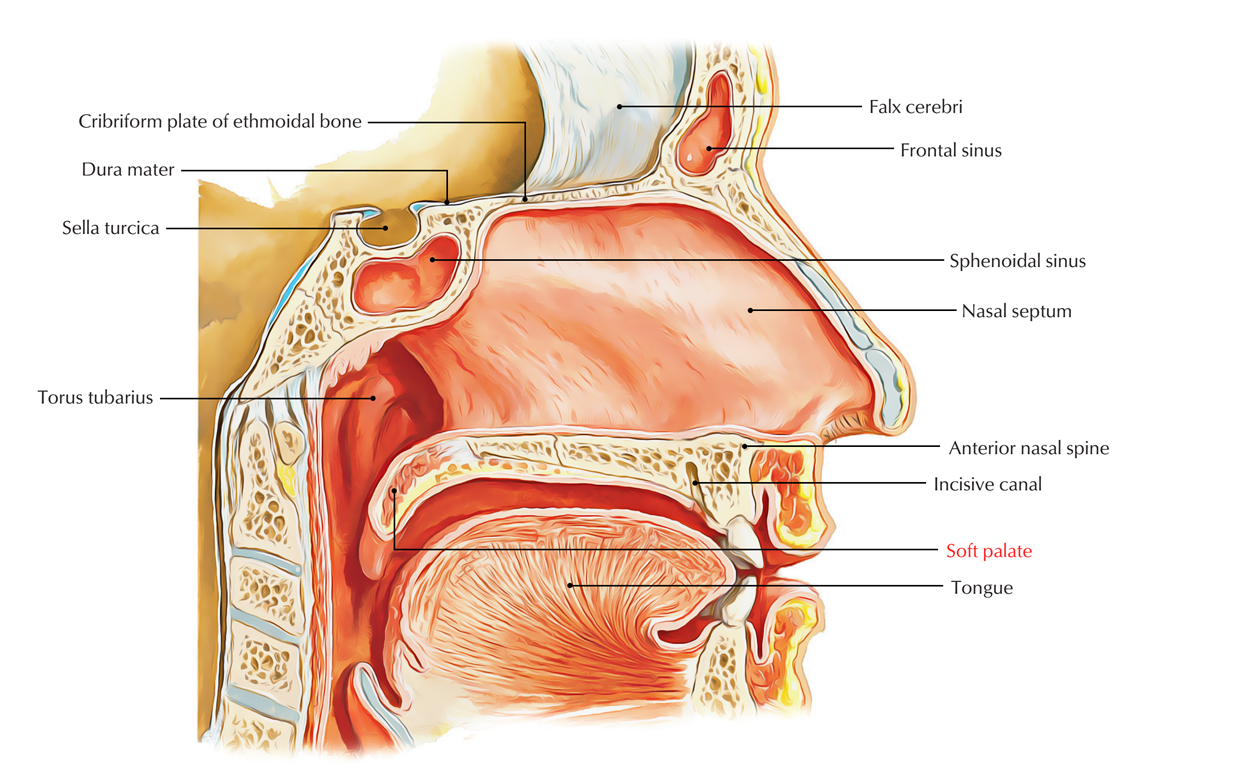
In palate the soft palate is composed of muscle and connective tissue which give it both mobility and support. The objective of the hard palate is both feeding and speech. Posteriorly it has no borders and hangs at an inferior angle towards the larynx.
The soft palate is bordered. The hard palate contains five foramina which include the incisive fossa a pair of greater palatine foramina and a pair of lesser palatine foramina. Anatomy and function of the hard palate.
It forms both the roof of the mouth and the floor of the nasal cavity. The incisive fossa contains the nasopalatine nerves and sits directly behind the central incisors. Posterolaterally however it forms part of the superior portion of the.
Inferiorly by the mucosa of the oral cavity. Soft palate anatomy muscles of the soft palate the tensor veli palatini figure 2 attaches to the scaphoid fossa and spine of the sphenoid and to the lateral surface of the cartilaginous portion of the auditory eustachian tube. This palate is very flexible.
Superiorly by the respiratory mucosa of the nasal cavity. It separates the oral cavity from the nasal cavity. Palatal mucosa the palate is covered by a thick stratified squamous epithelium ep supported by densely collagenous lamina propria l the mucosa of the hard palate is bound down to the underlying bone b by relatively dense submucosal tissue s containing a few accessory salivary glands.
Anatomy physiology of the oral nasal and laryngeal cavities. It consists of an anterior hard palate of bone and in mammals a posterior soft palate that has no skeletal support and terminates in a fleshy elongated projection called the uvula. The drawbridges come into play as the soft palate rises to close off the nasopharynx and the epiglottis drops down over the laryngeal opening due to the rising of the larynx.
Pathologic Anatomy Of The Soft Palate Part 2 The Soft
 Git Anatomy The Soft Palate And The Pharynx
Git Anatomy The Soft Palate And The Pharynx
 Hard Palate Anatomy Hard Palate Function Hard Palate
Hard Palate Anatomy Hard Palate Function Hard Palate
 Anatomy Of Oral Palatomaxillary Cancer
Anatomy Of Oral Palatomaxillary Cancer
Palate Useful Notes On The Palate Human Anatomy
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/448/palatum_molle_2_large_HifM8n5kVXZZmoKgYKovg.png) Soft Palate Anatomy Function And Muscles Kenhub
Soft Palate Anatomy Function And Muscles Kenhub
 Dr Nuas Hasab Jafar Morbid Anatomy And Pathophysiology In
Dr Nuas Hasab Jafar Morbid Anatomy And Pathophysiology In
Lips Cheeks And Palate Human Anatomy Organs
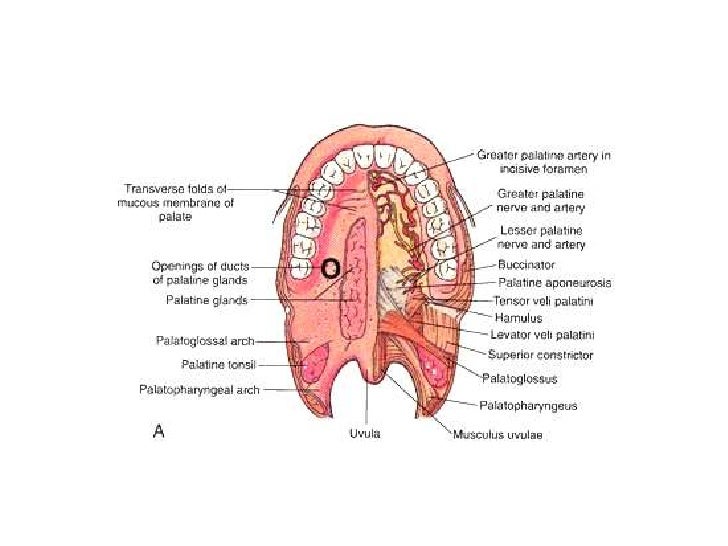 Anatomy And Histology Of Palate
Anatomy And Histology Of Palate
Pathologic Anatomy Of The Soft Palate Part 1 Embryology
 Hard Palate An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Hard Palate An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
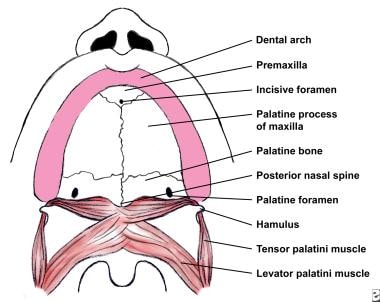 Cleft Lip And Palate And Mouth And Pharynx Deformities
Cleft Lip And Palate And Mouth And Pharynx Deformities
:watermark(/images/watermark_only.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/hard-palate-2/8kcLkpxMABUuFTQaHKlZeA_Hard_palate.png) Hard Palate Anatomy Function And Borders Kenhub
Hard Palate Anatomy Function And Borders Kenhub
Anatomy Physiology Dysphagia And Cleft Palate
 1000 Hard Palate Stock Images Photos Vectors Shutterstock
1000 Hard Palate Stock Images Photos Vectors Shutterstock
 Amazon Com Anatomy Soft Palate Suture Print Sra3 12x18
Amazon Com Anatomy Soft Palate Suture Print Sra3 12x18

 Mouth Anatomy Hard Palate And Teeth Art Print Medical Art Watercolor Maxilla Palatal Process Maxilla Dental Anatomy Art Speech Therapy Art
Mouth Anatomy Hard Palate And Teeth Art Print Medical Art Watercolor Maxilla Palatal Process Maxilla Dental Anatomy Art Speech Therapy Art
 Soft Palate Muscles Function Definition Human Anatomy Kenhub
Soft Palate Muscles Function Definition Human Anatomy Kenhub
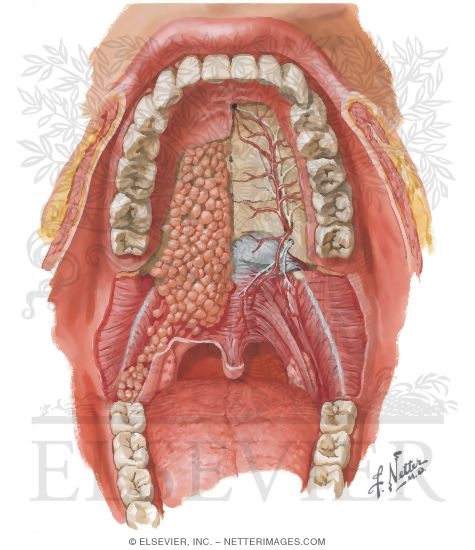

Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar