Half of the membraneous labyrinth the cochlea is dedicated to converting sound waves into neural signals while the other half the vestibular system is dedicated to deriving your sense of balance. Most people dont find it difficult to walk across a gravel driveway transition from walking on a sidewalk to grass or get out of bed in the middle of the night without stumbling.
Activation of distal muscles is primarily the responsibility of the somatosensory system.

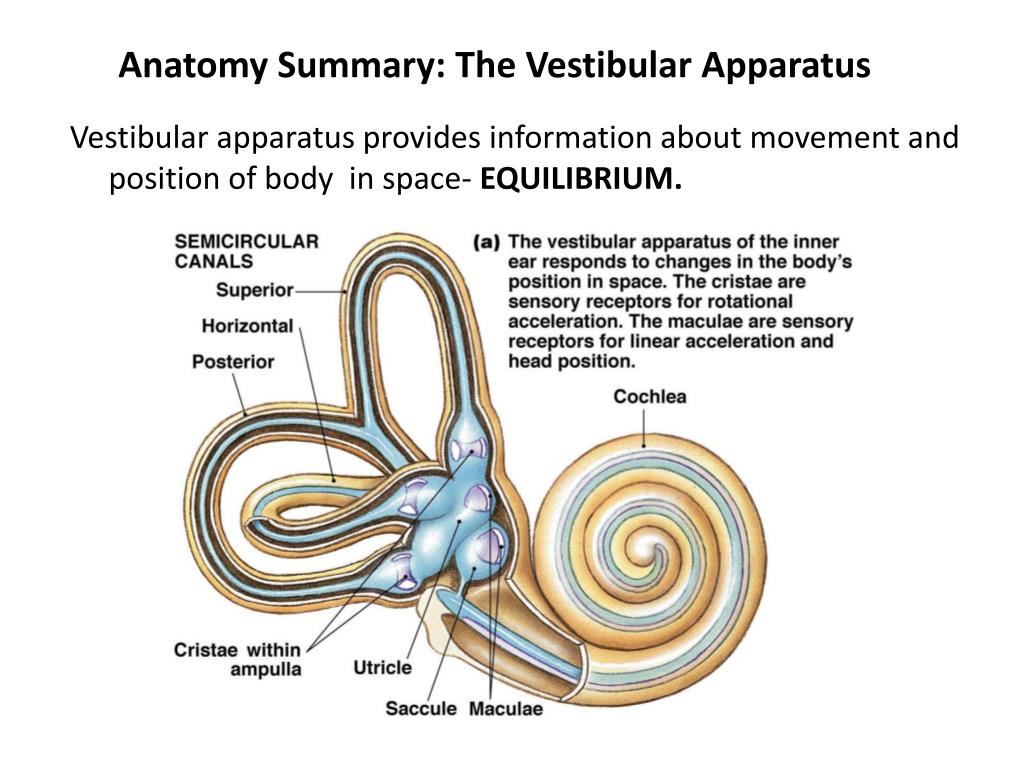
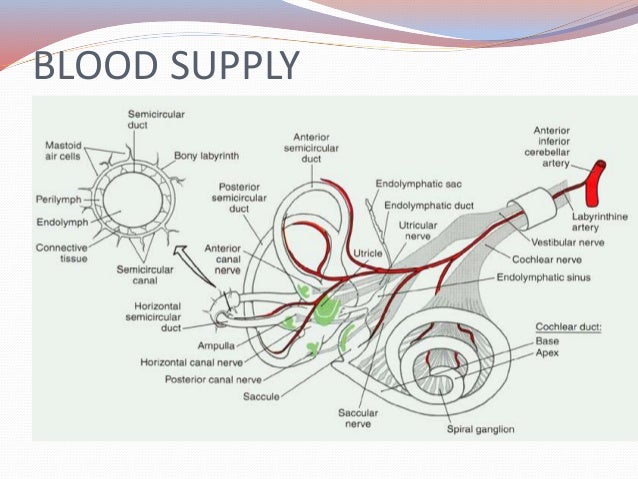
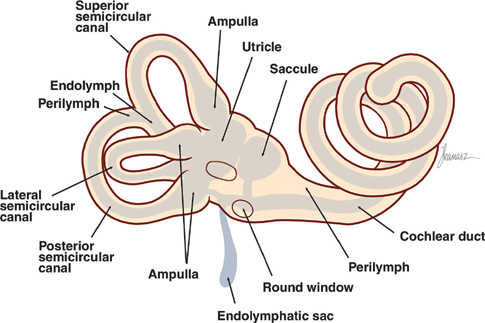
Vestibular system anatomy. The vestibular system monitors the motion and position of the head in space by detecting angular and linear acceleration. Each canal is filled with endolymph and has a swelling at the base termed the ampulla. The peripheral vestibular system is an integral part of the labyrinth that lies in the otic capsule in the petrous portion of the temporal bone.
Vestibulo spinal reflex vsr maintains vertical alignment of the trunk. The 3 semicircular canals in the inner ear detect angular acceleration and are positioned at near right angles to each other. 3 anatomy 1 good balance is often taken for granted.
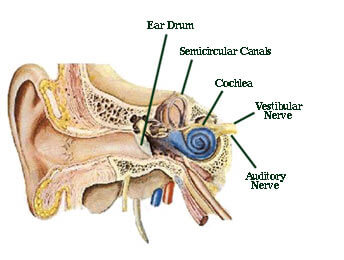
Both halves use the vestibulocochlear nerve which conducts neural signals to the brain for interpretation and integration. 3 semicircular canals that are sensitive to angular accelerations head rotations and 2 otolith organs that are sensitive to linear or straight line accelerations. Anatomy of human inner ear.
This system allows the body to easily change orientation and maintain balance while making different types of movement simultaneously. The vestibular system which is the system of balance consists of 5 distinct end organs. It consists of two structures of the bony labyrinth the vestibule and the semicircular canals and the structures of the membranous labyrinth contained within them.
However with impaired balance such activities can be extremely fatiguing. The vestibular system is a system that enables humans to maintain balance and orientation within its three dimensional environment in relation to gravity. Vestibular system the vestibular system is the apparatus of the inner ear involved in balance.
The brain uses vestibular input to help it stabilize the head and body in space through neck trunk and hip muscle activation.
 Vestibular System Functions Anatomy Structure Nervous
Vestibular System Functions Anatomy Structure Nervous
 Know Your Brain Vestibular System Neuroscientifically
Know Your Brain Vestibular System Neuroscientifically
Chapter 9 Vestibular Functions
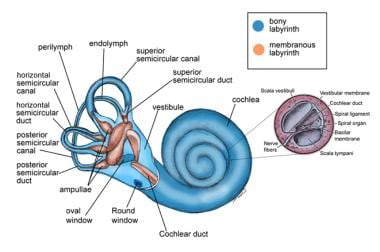 Vestibular System Anatomy Overview Membranous Labyrinth
Vestibular System Anatomy Overview Membranous Labyrinth
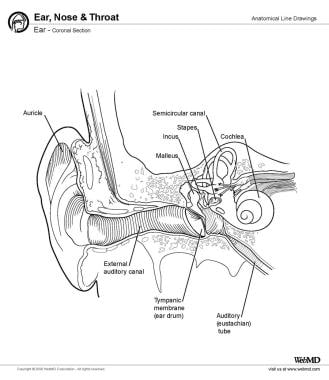 Vestibular System Anatomy Overview Membranous Labyrinth
Vestibular System Anatomy Overview Membranous Labyrinth
 Vestibular System Google Search Inner Ear Anatomy Ear
Vestibular System Google Search Inner Ear Anatomy Ear
Vestibular Apparatus Control Of Posture And Movement
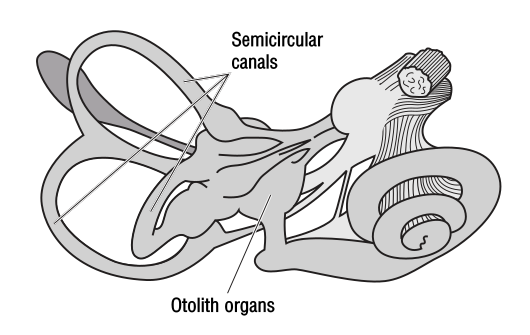 Vestibular System Medical Anatomy Ear Vestibular System
Vestibular System Medical Anatomy Ear Vestibular System
Vestibular Dysfunction Disability Insurance Benefits Claim
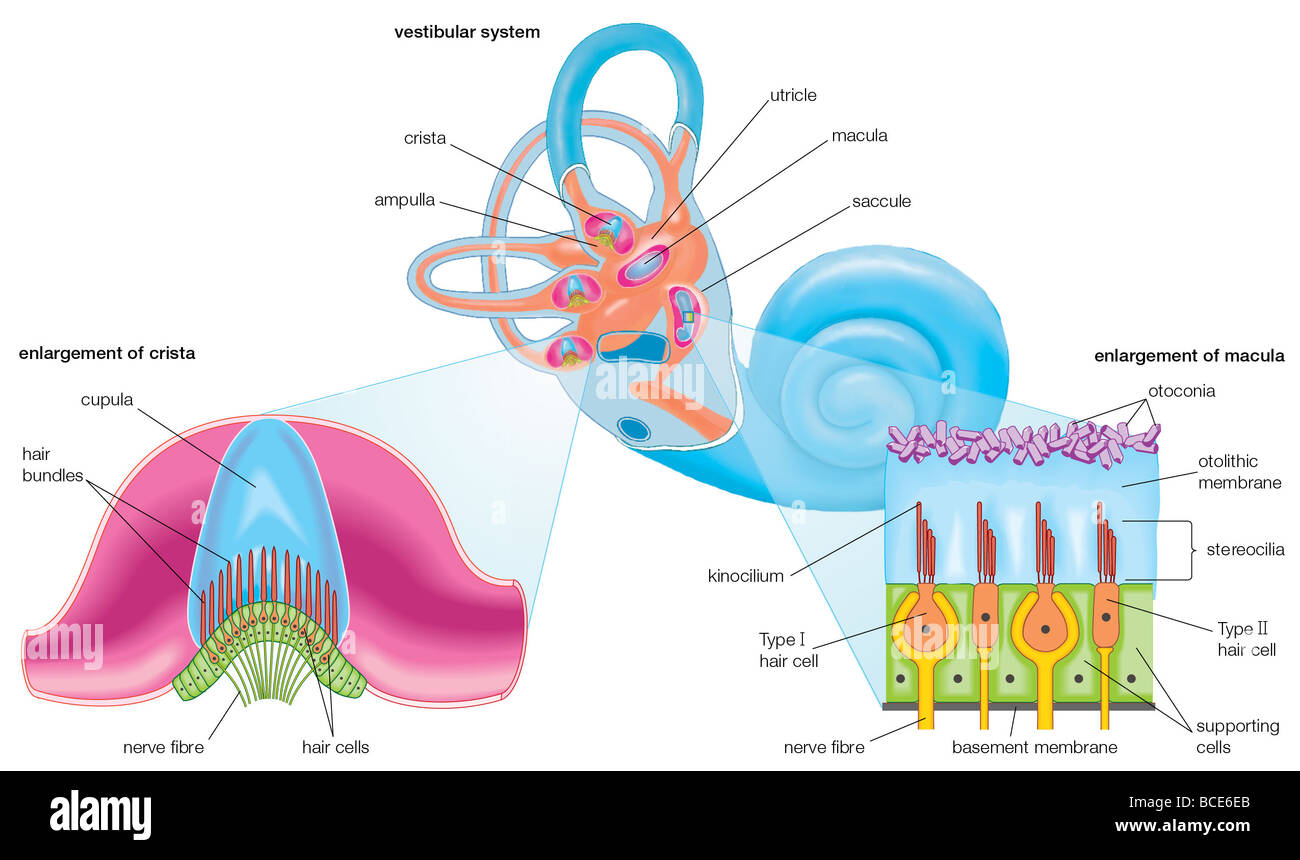 The Membranous Labyrinth Of The Vestibular System Which
The Membranous Labyrinth Of The Vestibular System Which
 Anatomy Physiology Of Vestibular System
Anatomy Physiology Of Vestibular System
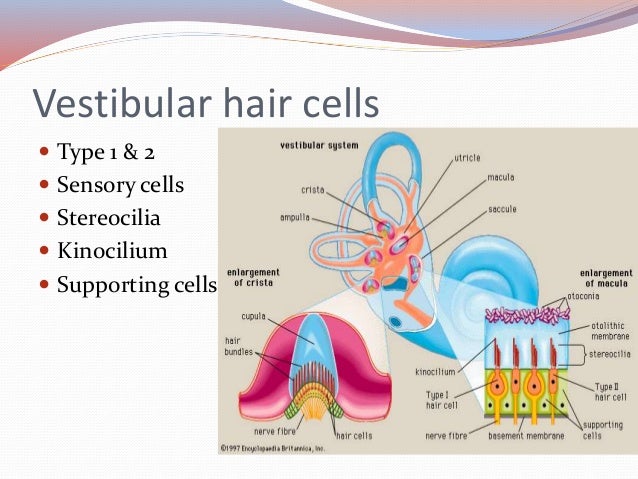 Anatomy Embryology Of Vestibular System
Anatomy Embryology Of Vestibular System
Poop Puke And Pass Out A Guide To Stimulating The
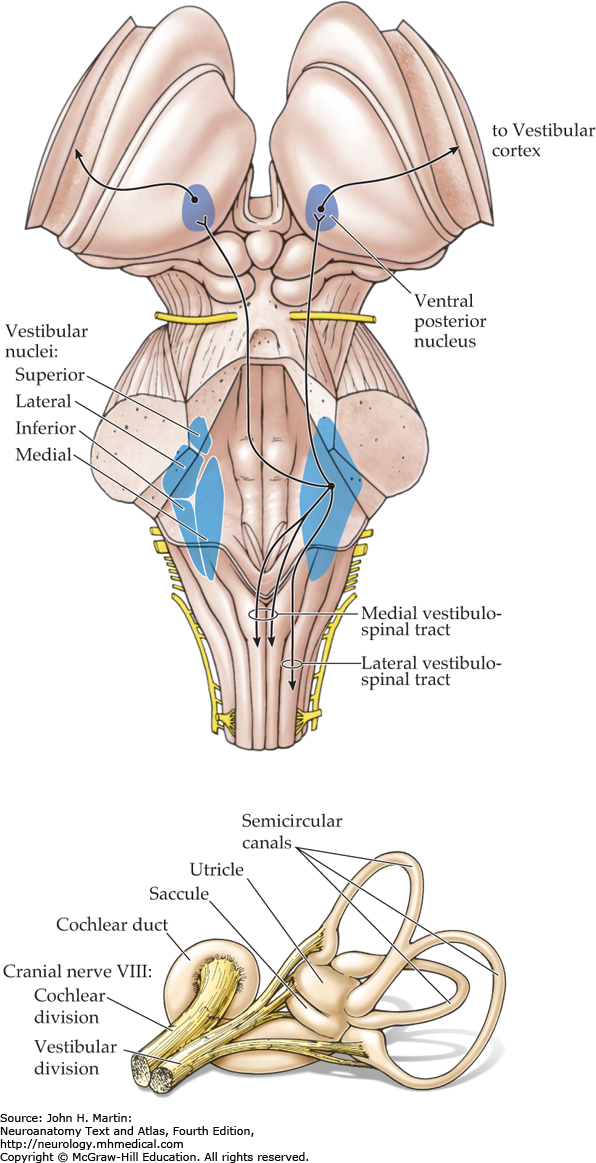 The Vestibular System And Eye Movements Neuroanatomy Text
The Vestibular System And Eye Movements Neuroanatomy Text
 Sensory Systems Vestibular System Wikibooks Open Books
Sensory Systems Vestibular System Wikibooks Open Books
Ch 15 Inner Ear Static Dynamic Equilibrium
 Peripheral Vestibular System Vestibular Disorders Association
Peripheral Vestibular System Vestibular Disorders Association
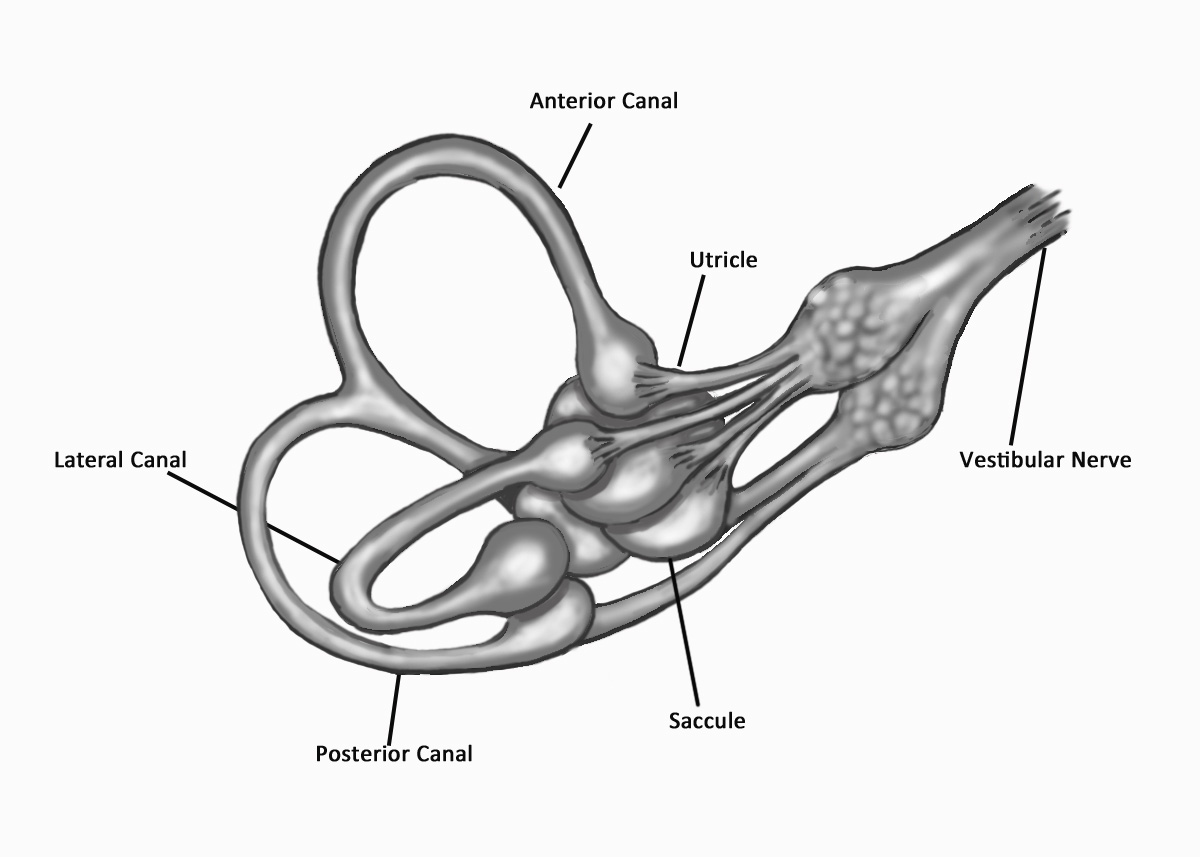 A Patient S Guide To The Vestibular System Vestibular
A Patient S Guide To The Vestibular System Vestibular
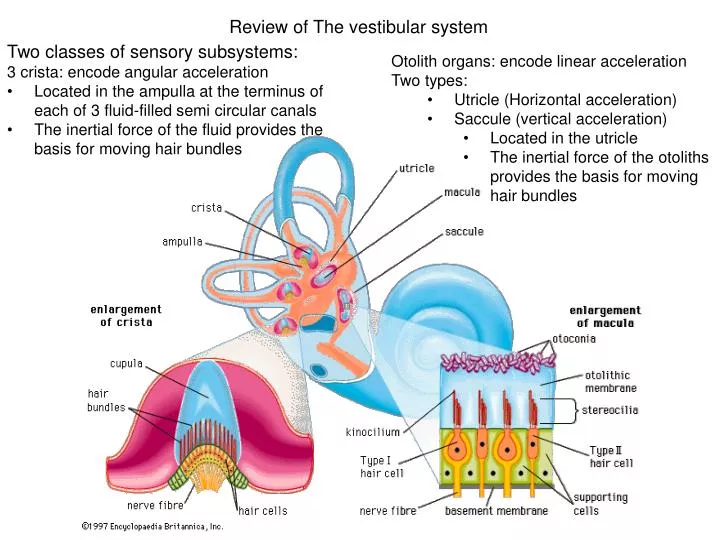 Ppt Review Of The Vestibular System Powerpoint
Ppt Review Of The Vestibular System Powerpoint
 The Vestibular System Definition Anatomy Function
The Vestibular System Definition Anatomy Function
 48 Best Vestibular System Images In 2019 Vestibular System
48 Best Vestibular System Images In 2019 Vestibular System
![]() Vestibular System Icon Vector From Anatomy Collection Thin
Vestibular System Icon Vector From Anatomy Collection Thin
 Ppt Vestibular System Powerpoint Presentation Free
Ppt Vestibular System Powerpoint Presentation Free
 The Inner Ear Anatomy Of The Vestibular System
The Inner Ear Anatomy Of The Vestibular System
 The Vestibular System Anatomy Of The Ear Ampulla Of
The Vestibular System Anatomy Of The Ear Ampulla Of
 Ear Anatomy Inner Ear Cochlea Histology Vestibular System Structure Audiology Canvas Print
Ear Anatomy Inner Ear Cochlea Histology Vestibular System Structure Audiology Canvas Print
 Cochlea Of Inner Ear Anatomy Art Vestibular System Inner Ear Structure Cochlea Cochlea Print Audiology Medical Office Decor
Cochlea Of Inner Ear Anatomy Art Vestibular System Inner Ear Structure Cochlea Cochlea Print Audiology Medical Office Decor

 Schematic Of The Human Vestibular System Showing The Three
Schematic Of The Human Vestibular System Showing The Three
 Hearing And Equilibrium Anatomy And Physiology
Hearing And Equilibrium Anatomy And Physiology
 Anatomy Embryology Of Vestibular System
Anatomy Embryology Of Vestibular System


Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar