Here the most common bony disturbances have been noted. Introduction to mandible bone anatomy.
 Angle Of The Mandible Wikipedia
Angle Of The Mandible Wikipedia
The mandible sits beneath the maxilla.
Mandibular anatomy. Intra and extracapsular condylar fractures are the most frequent mandibular fractures. The lower set of teeth in the mouth is rooted in the lower jaw. These muscles are the masseter the temporalis the medial pterygoid and the lateral pterygoid.
It is the only movable bone of the skull discounting the ossicles of the middle ear. Each of these muscles occurs in pairs with one of each muscle appearing on either side of the skull. Mandible anatomy mental foramen.
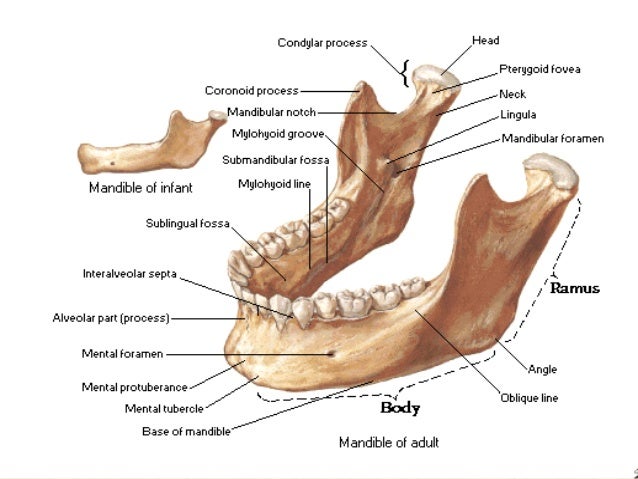
Inferior alveolar nerves and vessels to the lower teeth. It consists of a curved horizontal portion the body and two perpendicular portions the rami which unite with the ends of the body nearly at right angles angle of the jaw. Other mandibular fracture areas include the body the angle the.
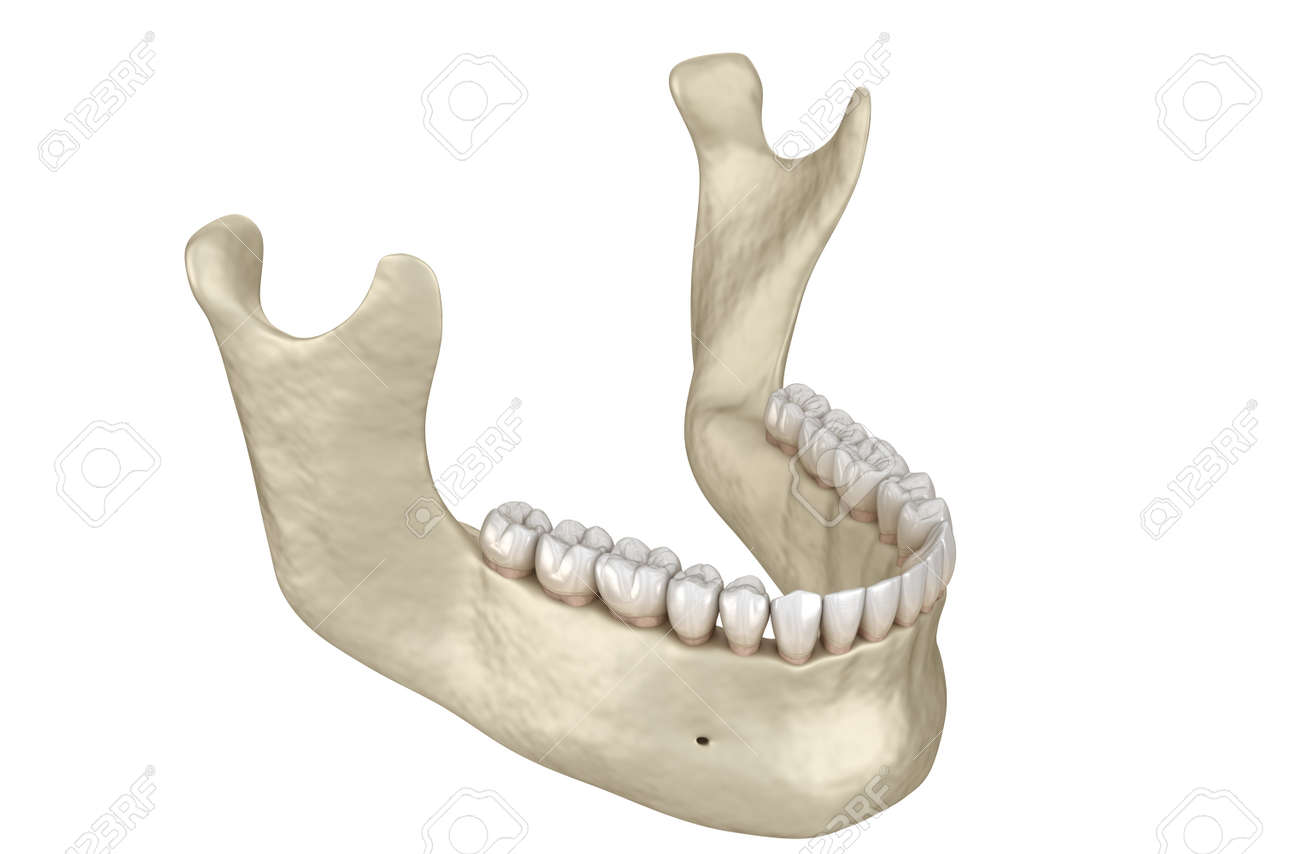
The mandible lower jaw or jawbone is the largest strongest and lowest bone in the human face. There is a lack. Mental nerve and vessels.
External lateral surface mentalis buccinator platysma depressor labii inferioris depressor anguli oris. The mandibles of a nauplius have two branches with a chewing or compressing lobe at the base. The mandible l mandere to chew is the facial bone that forms the lower jaw and contains the lower teeth.
The anterior portion of the mandible called the body is horseshoe shaped and runs horizontally. They also may be used for swimming. Internal medial surface genioglossus geniohyoid mylohyoid and digastric.
It forms the lower jaw and holds the lower teeth in place. It articulates with both temporal bones at the mandibular fossa at the temporomandibular joints tmj. The mandible is the single midline bone of the lower jaw.
Alveolar bone resorption occurs when the teeth are lost. It consists of right and left halves that fuse together early in life. Jaws function by moving in opposition to each other and are used for biting chewing and the handling of food.
Four different muscles connect to the lower jaw to facilitate its movement. Jaw in jaw a movable lower jaw mandible and fixed upper jaw maxilla.
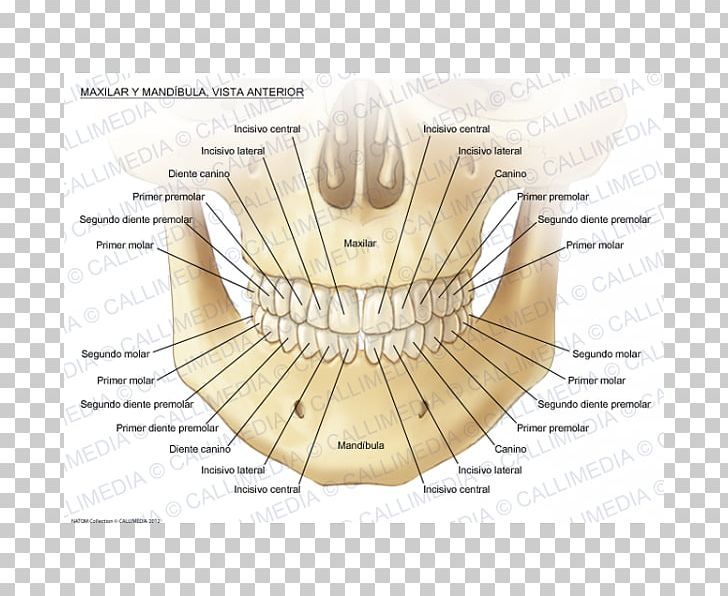 Maxilla Anatomy Mandible Mandibular Nerve Human Body Png
Maxilla Anatomy Mandible Mandibular Nerve Human Body Png
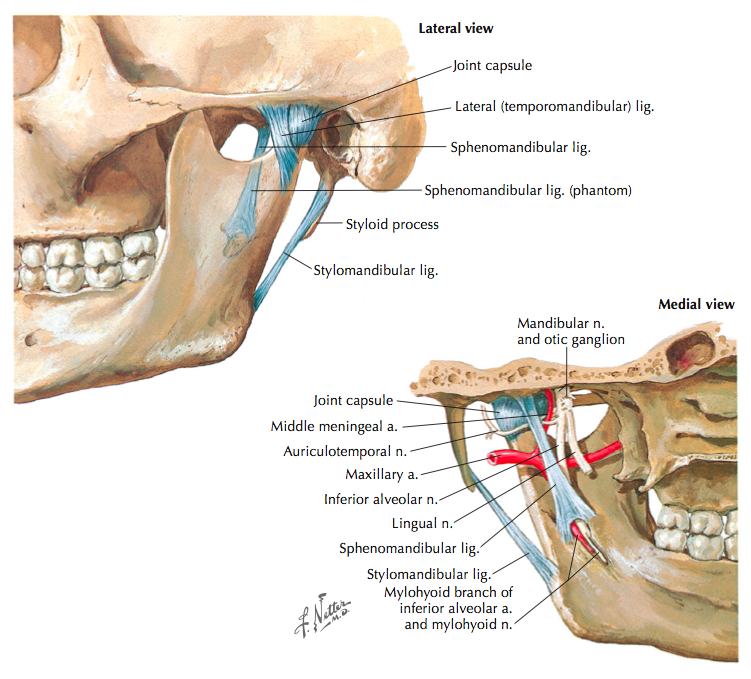 Temporomandibular Joint Disorders Clinical Anatomy
Temporomandibular Joint Disorders Clinical Anatomy
Trigeminal Anatomy The Mandibular Nerve Daily Med Fact
 Detailed Anatomy Of The Mandible And Maxilla Purposegames
Detailed Anatomy Of The Mandible And Maxilla Purposegames
 Real Human Mandibular Jaw Anatomy With Teeth 3d Print Model
Real Human Mandibular Jaw Anatomy With Teeth 3d Print Model
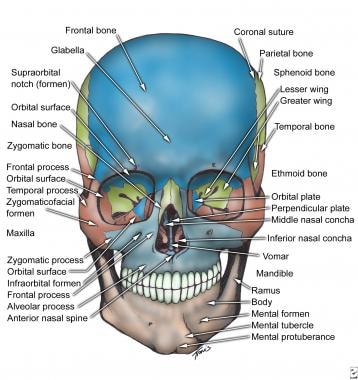 Facial Bone Anatomy Overview Mandible Maxilla
Facial Bone Anatomy Overview Mandible Maxilla
Imaging Mandibular Fractures Wikiradiography
 Figure 6 From An Analysis Of Anterior Mandibular Anatomy
Figure 6 From An Analysis Of Anterior Mandibular Anatomy
 Give Mental Block In The Mental Foramen Mandible Mandible
Give Mental Block In The Mental Foramen Mandible Mandible
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/7639/IkZJJPMujD6IQ2e7r8yiNA_mandible_latin.jpg) The Mandible Anatomy Structures Fractures Kenhub
The Mandible Anatomy Structures Fractures Kenhub
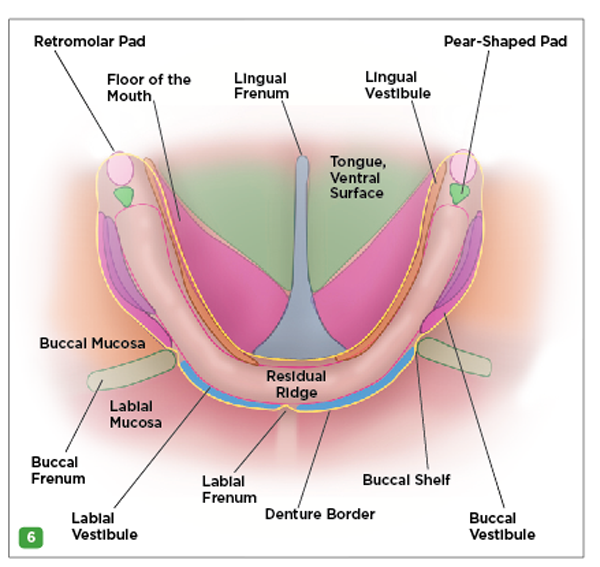
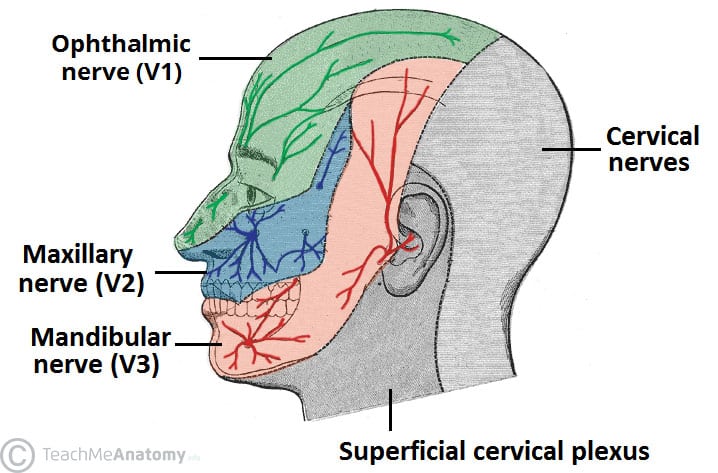 The Mandibular Division Of The Trigeminal Nerve Cnv3
The Mandibular Division Of The Trigeminal Nerve Cnv3
 Oral Cavity Pharynx Atlas Of Anatomy
Oral Cavity Pharynx Atlas Of Anatomy
 Surgical Anatomy Of The Marginal Mandibular Nerve A
Surgical Anatomy Of The Marginal Mandibular Nerve A
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/4972/d2DFbcWqOqSTAXfJrVg3Mg_Foramen_mandibulae_01.png) Mandibular Foramen Anatomy And Contents Kenhub
Mandibular Foramen Anatomy And Contents Kenhub
The Anatomy Of The Laboratory Mouse
Trigeminal Anatomy The Mandibular Nerve Daily Med Fact
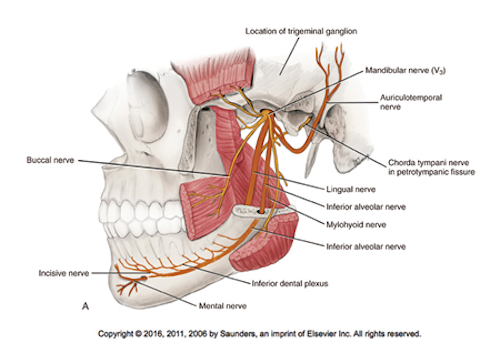 The Underused Block The Vazirani Akinosi Mandibular Block
The Underused Block The Vazirani Akinosi Mandibular Block
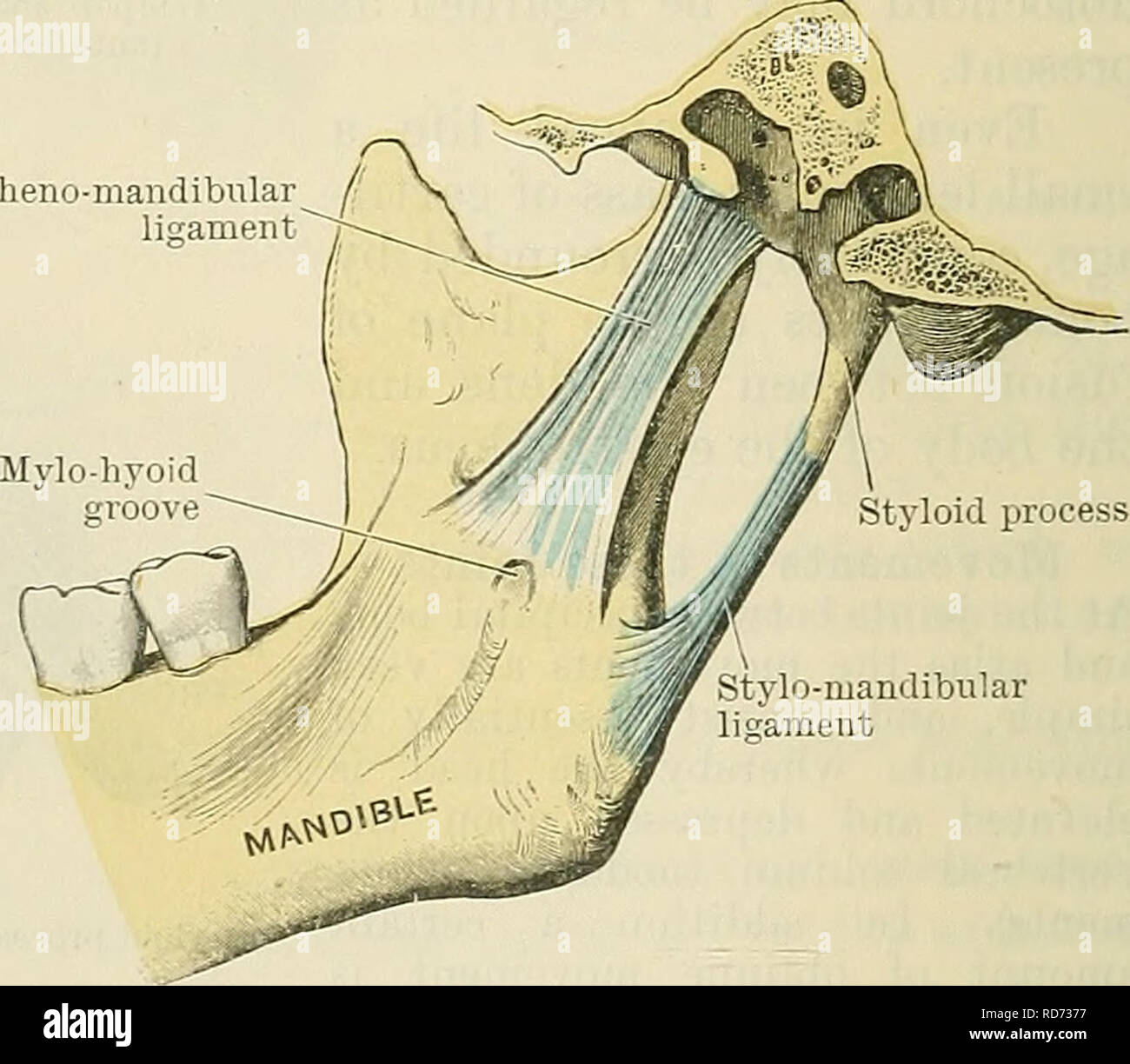 Cunningham S Text Book Of Anatomy Anatomy Fig 299
Cunningham S Text Book Of Anatomy Anatomy Fig 299
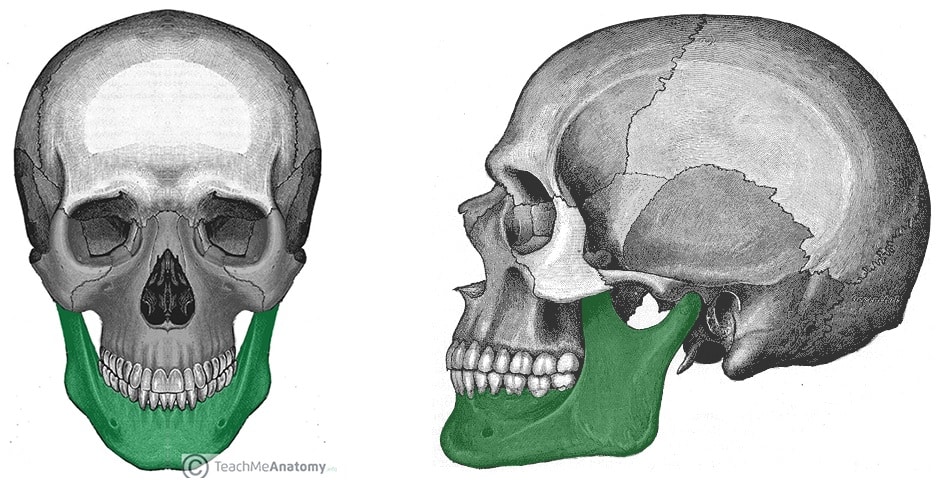 The Mandible Structure Attachments Fractures
The Mandible Structure Attachments Fractures
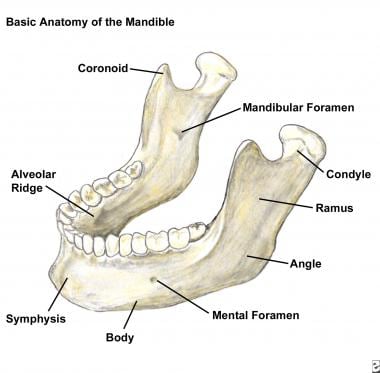 Mandibular Fracture Imaging Practice Essentials
Mandibular Fracture Imaging Practice Essentials
 Oral Cavity Pharynx Atlas Of Anatomy
Oral Cavity Pharynx Atlas Of Anatomy
Dental Malpractice Central Anatomy Of The Lingual Nerve
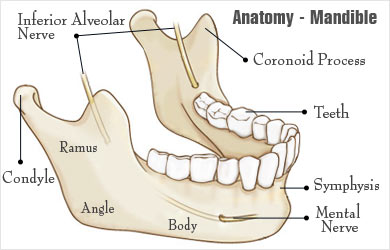 Broken Jaw Mandibular Fracture Types Causes Symptoms
Broken Jaw Mandibular Fracture Types Causes Symptoms
The Skull Anatomy And Physiology Openstax


Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar