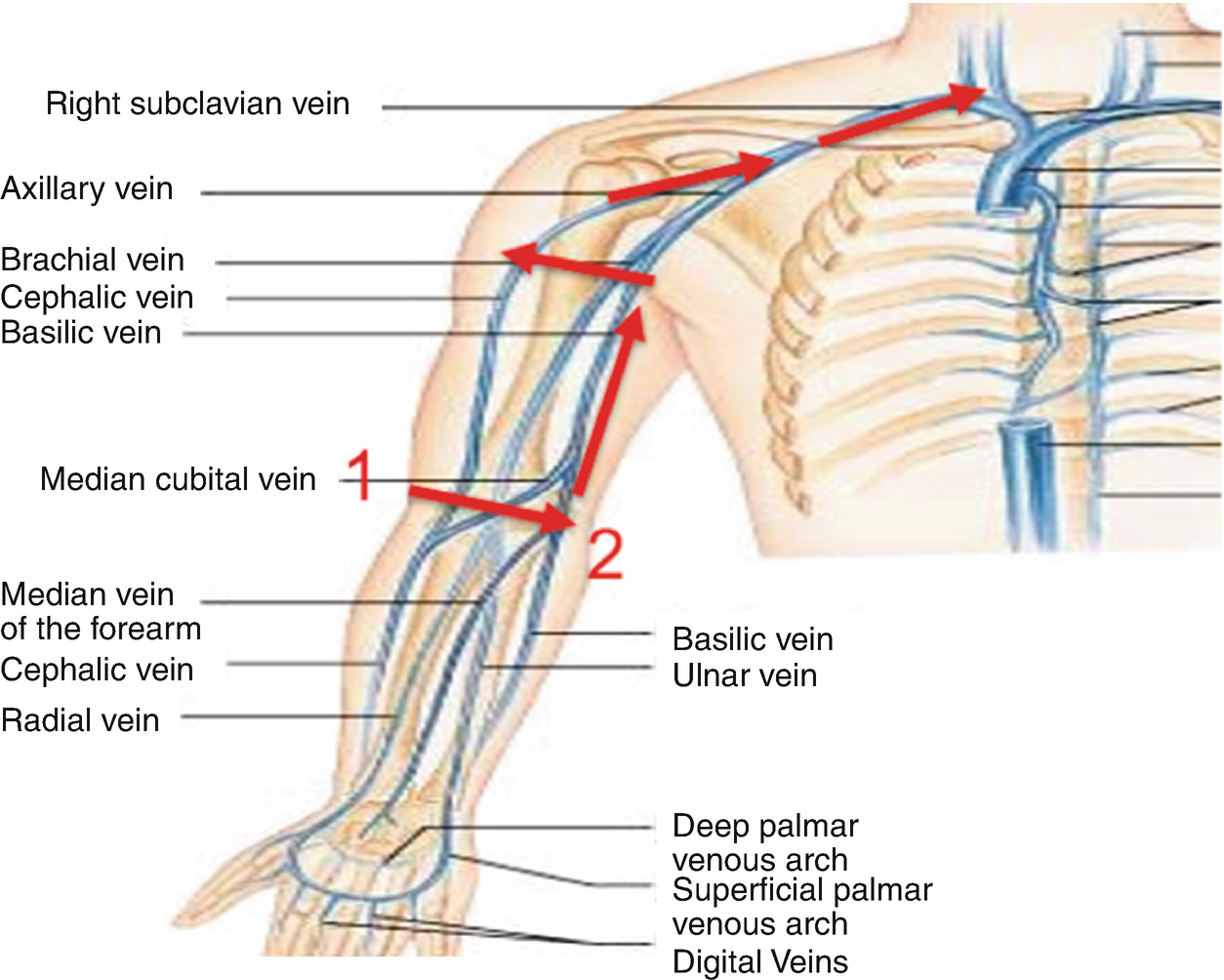
The basilic vein is typically larger than the. In the upper arm the basilic and cephalic veins are the major routes for superficial venous drainage with ultimate runoff into the deep system figs.
 Names Of Veins In The Arm Anatomy And Physiology Medical
Names Of Veins In The Arm Anatomy And Physiology Medical
Deep veins and superficial veins.

Venous arm anatomy. It can anatomically be divided into the superficial veins and the deep veins. Anatomy physiology module provides a broad spectrum of adult male and female normal anatomy cases with varying body morphologies to maximize training efficacy. Upper arm veins brachial basilic the basilic vein is the larger and is more superficial.
The venous system of the upper limb drains deoxygenated blood from the arm forearm and hand. As you reach the proximal arm the axillary vein will divide into the basilic and brachial veins. Each individual hands on training case is accompanied by image window specific expert instruction and probe positioning guidance.
Within the venaecomitantes are both radian and ulnar veins with the ulnar veins typically existing as larger in size while the radial veins interact with the dorsal metacarpal veins. The arteries deliver freshly oxygenated blood to muscles and bone. The vessels of the arms are part of the circulatory system which provides nutrients to the tissues.
Chapter 77 venous anatomy of the extremities. There are three parts of the axillary vein the first distal part into which the cephalic vein enters at a point just superior to the pectoralis minor muscle and the second and third parts which give off branches corresponding to the tributaries off the axillary artery. The venae comitantes of the brachial artery ie the deep veins of the arm or brachial veins are joined by the basilic vein above the lower border of the posterior wall of the axilla to form the axillary vein.
And the other into the cephalic median cephalic vein. On the other hand the ulnar veins interact more with tributaries that deal with deep volar venous arches causing them to have more to do with the wrist area of a human being. The primary venous return from the arm is through the axillary vein which continues centrally as the subclavian and brachiocephalic innominate veins before emptying into the superior vena cava.
The veins of the arm may be divided into two groups.
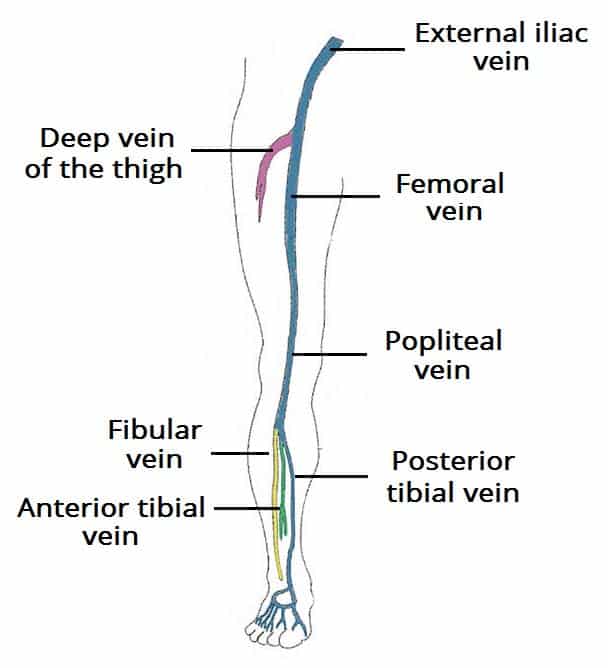
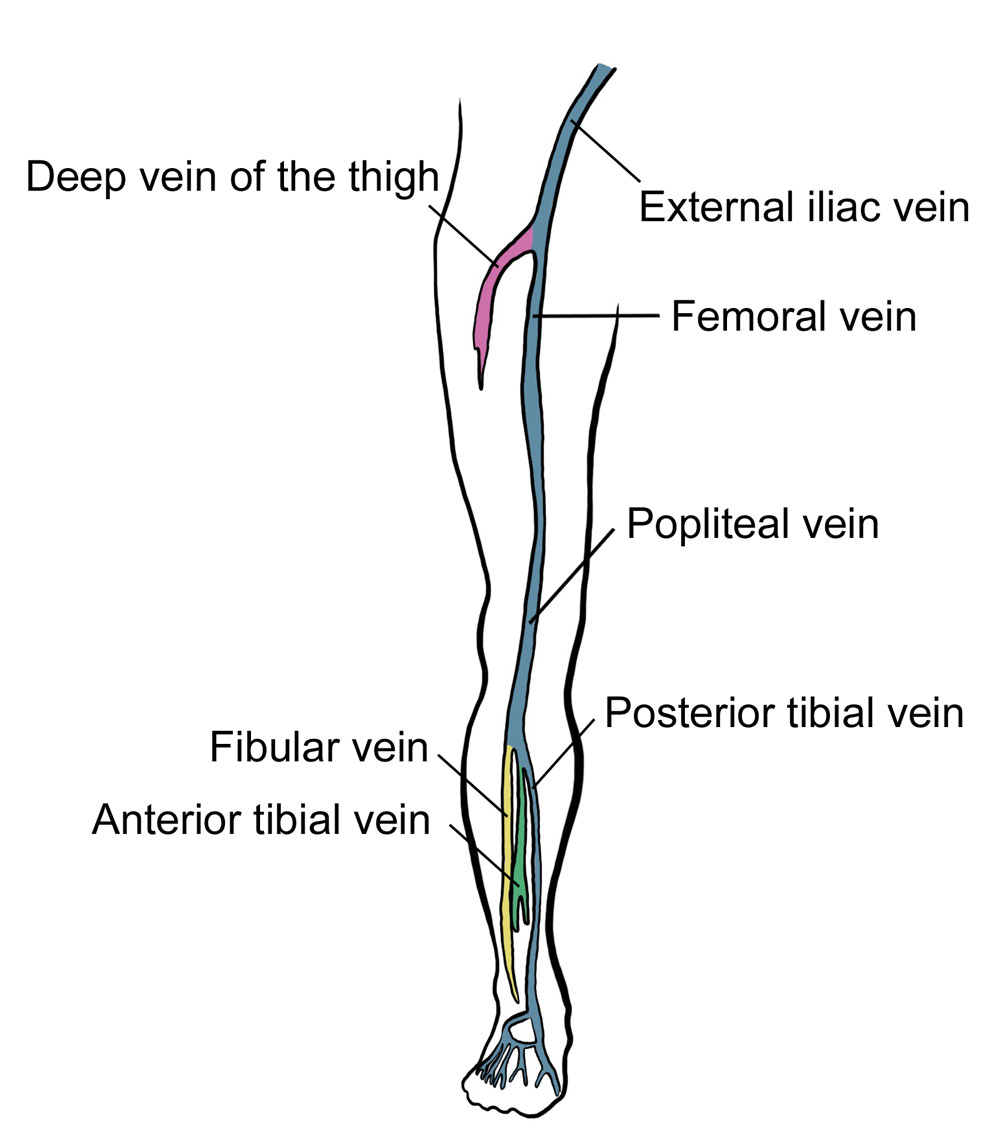
 Pdf Lower Extremity Venous Anatomy Semantic Scholar
Pdf Lower Extremity Venous Anatomy Semantic Scholar
 Right Assessment And Vein Selection Springerlink
Right Assessment And Vein Selection Springerlink
 Venous Drainage Of The Lower Limb Teachmeanatomy
Venous Drainage Of The Lower Limb Teachmeanatomy
 Department Of Surgery Vascular Access For Hemodialysis
Department Of Surgery Vascular Access For Hemodialysis
 Superior Vena Cava And The Azygos System Clinical Anatomy Svc Obstruction Oncology Emergency
Superior Vena Cava And The Azygos System Clinical Anatomy Svc Obstruction Oncology Emergency
 Deep Vein Thrombosis Rcemlearning
Deep Vein Thrombosis Rcemlearning
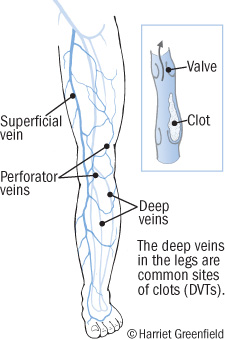 Deep Vein Thrombosis Blood Clots In Your Veins Harvard Health
Deep Vein Thrombosis Blood Clots In Your Veins Harvard Health
 F0 Pngfuel Com Png 705 706 Circulatory System Vein
F0 Pngfuel Com Png 705 706 Circulatory System Vein
:watermark(/images/watermark_5000_10percent.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/atlas_overview_image/753/zYaciDBmAmMJ1T31dwPhog_hand-nerves-vessels_english__1_.jpg) Veins Of The Upper Limb Anatomy Kenhub
Veins Of The Upper Limb Anatomy Kenhub
 Dentistry And Medicine Blood Supply Venous Drainage
Dentistry And Medicine Blood Supply Venous Drainage
 Does The Ring Finger Of The Left Hand Have A Vein That
Does The Ring Finger Of The Left Hand Have A Vein That
 The Cardiovascular System Of The Upper Limbs Anatomy Of
The Cardiovascular System Of The Upper Limbs Anatomy Of
 Cardiovascular System Human Veins Arteries Heart
Cardiovascular System Human Veins Arteries Heart
 Cardiovascular System Of The Arm And Hand
Cardiovascular System Of The Arm And Hand
Catheter Interventions For Hemodialysis Fistulas And Grafts
:watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/cephalic-vein-of-the-forearm/nA2JBRh6FusVKzTaChI3tQ_JufzsJz8pH_Vena_cephalica_antebrachii_2.png) Veins Of The Upper Limb Anatomy Kenhub
Veins Of The Upper Limb Anatomy Kenhub
 Clinical Education Intravenous Therapy Skills
Clinical Education Intravenous Therapy Skills
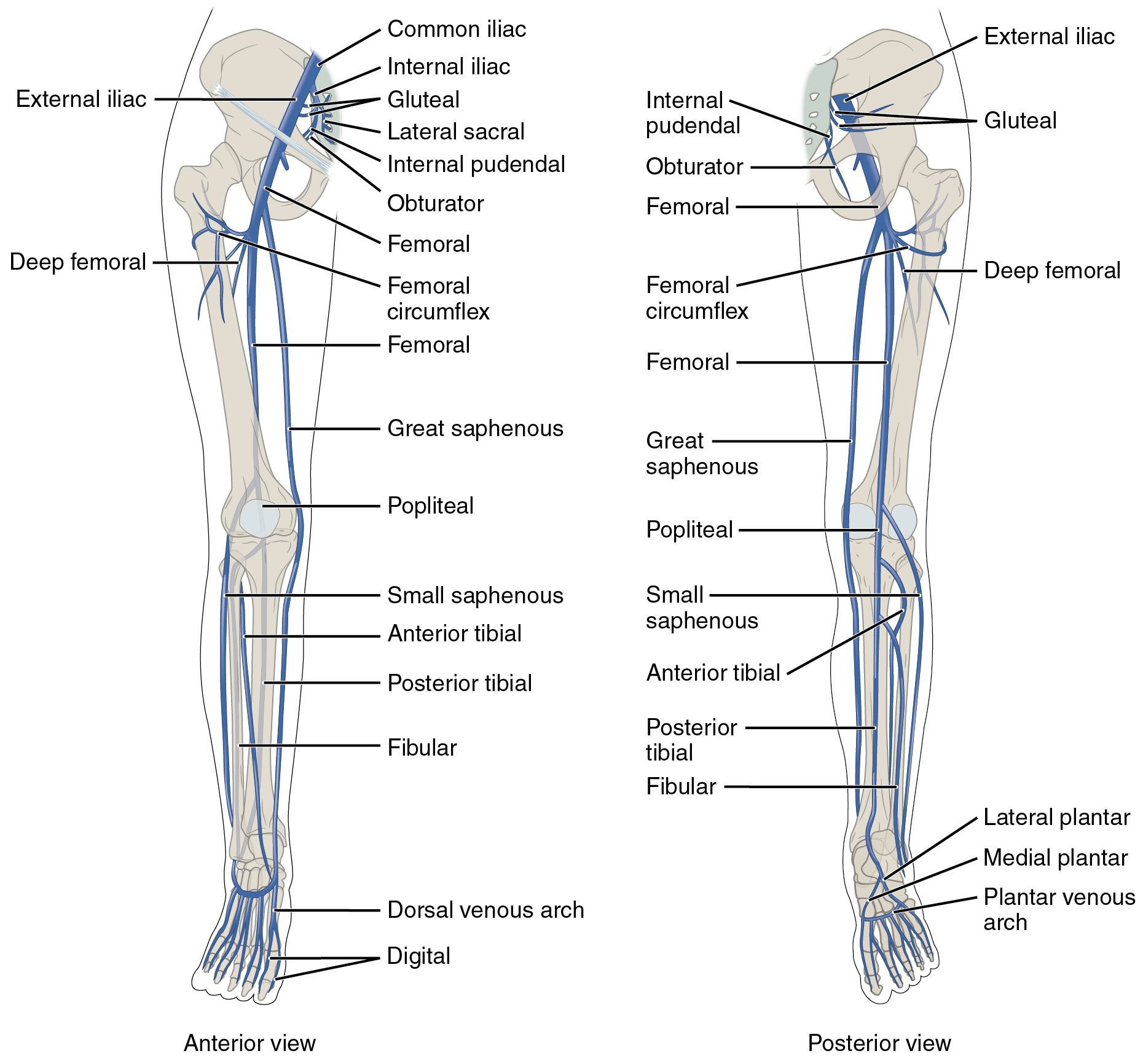 20 5 Circulatory Pathways Anatomy And Physiology
20 5 Circulatory Pathways Anatomy And Physiology
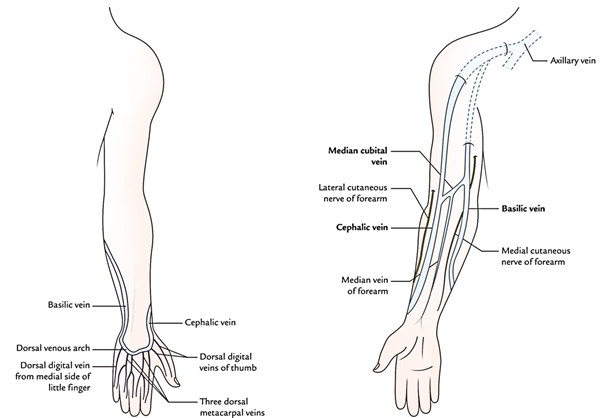 Easy Notes On Venous Drainage Of The Upper Limb
Easy Notes On Venous Drainage Of The Upper Limb



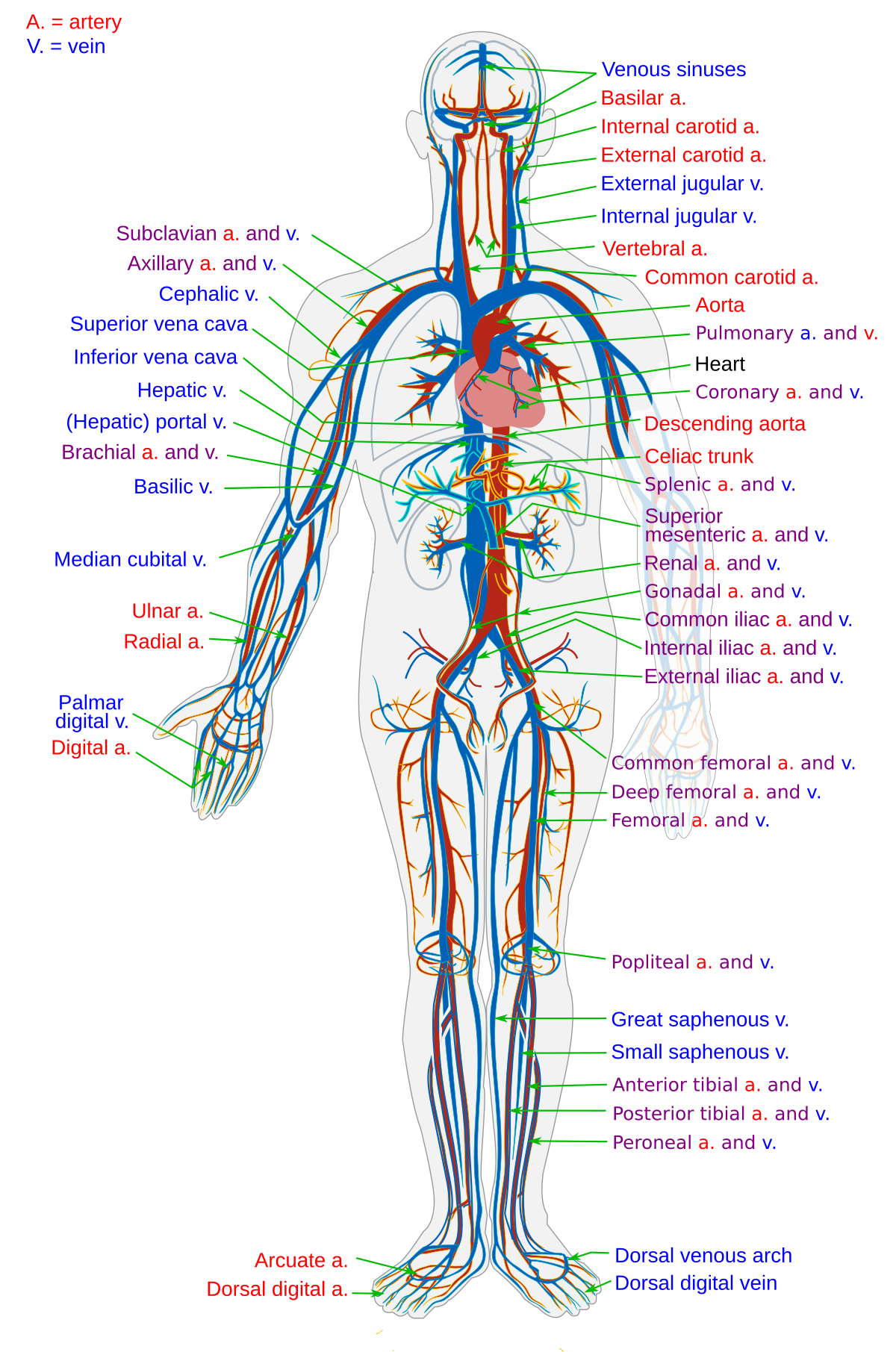
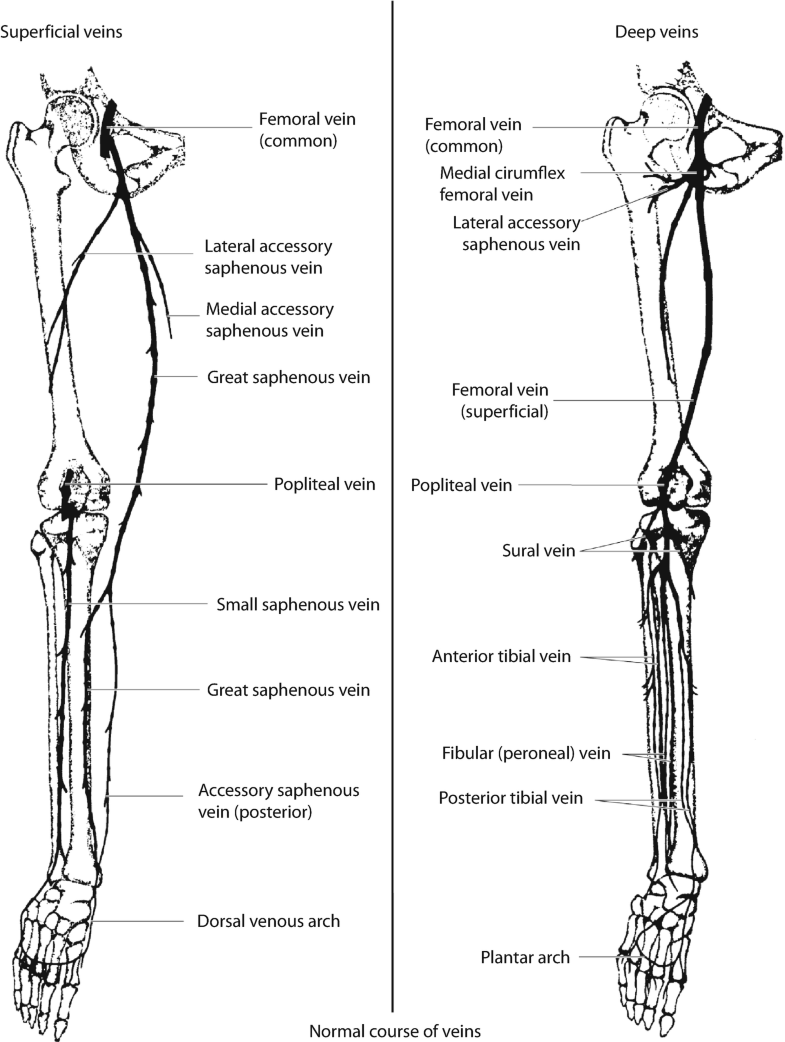

Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar