Anterior rootlets carry motor information out of the spinal cord ie. The anterior ventral root and rootlets contain axons of motor neurons which conduct nerve impulses from the cns to effectors muscles and glands.
 Spinal Cord And Spinal Nerves Physiology And Anatomy
Spinal Cord And Spinal Nerves Physiology And Anatomy
Anatomy and physiology of the spinal cord.
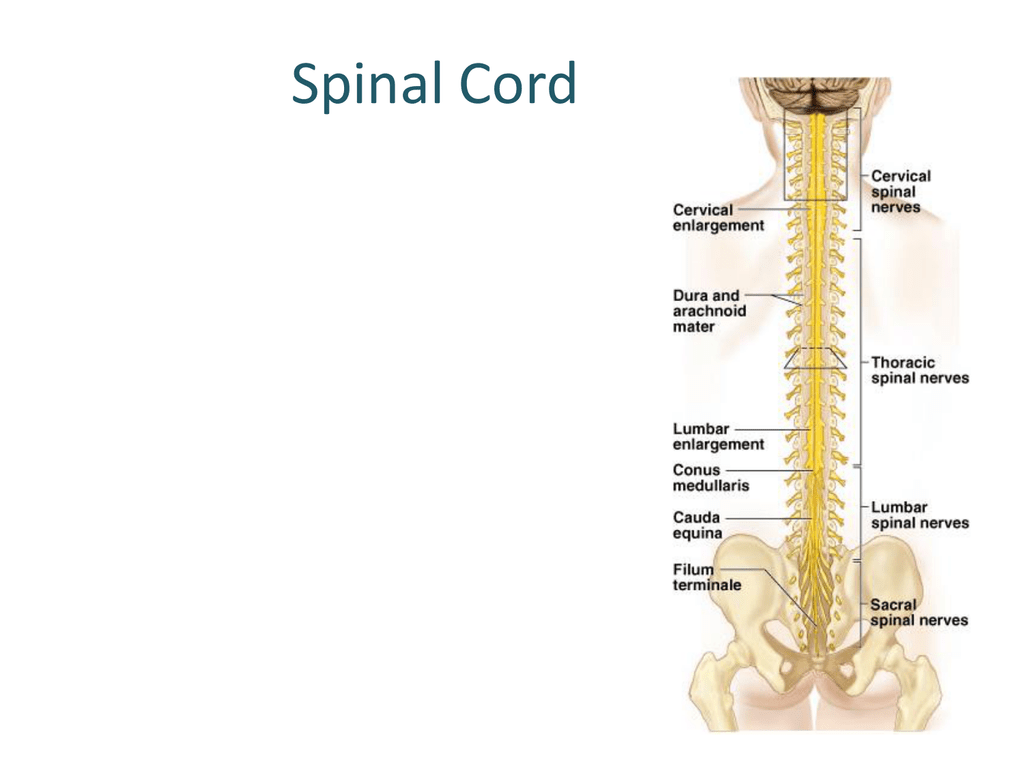
Anatomy and physiology of spinal cord. In an adult the spinal cord ends in the spinal canal in the small of the back around the level of the second lumbar vertebrae l2. Function is precise fine or skilled movements distally. They contain efferent fibers while the posterior rootlets carry sensory information into the spinal cord ie.
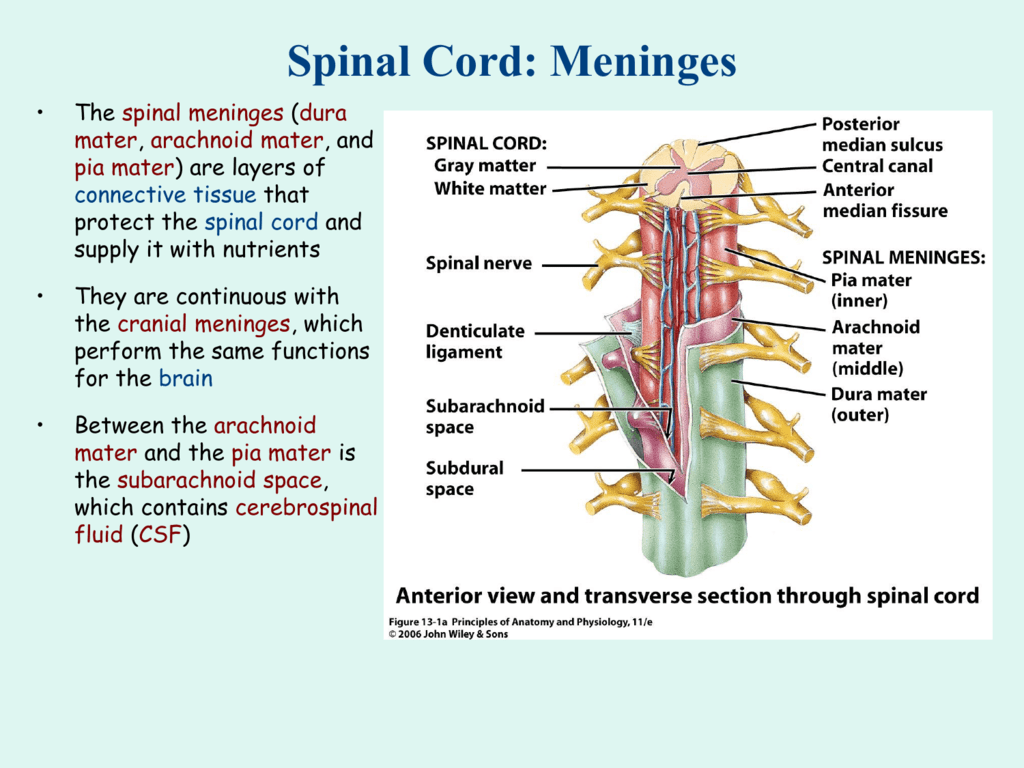
Anatomy and physiology of the spinal cord a guide for patients key points your spinal cord is the connection between your brain and the rest of your body your spinal cord is soft and enclosed in a bony tunnel the spine your brain communicates via the spinal cord to control voluntary functions such as. It is covered by the three membranes of the cns ie the dura mater arachnoid and the innermost pia mater. Origin is cerebral cortex.
Upper motor neuron upper motor neurons tract from brain to spinal cord where neurons synapse with lower motor neurons. The brain and the spinal cord are the central nervous system and they represent the main organs of the nervous system. Its extension goes from the occipital foramen of the skull to approximately the first lumbar vertebra.
The spinal cord is a single structure whereas the adult brain is described in terms of four major regions. 31 spinal nerves are connected along the spinal cord. The spinal cord runs within the spinal canal.
Destination is the spinal cord. The spinal cord is part of the central nervous system cns which extends caudally and is protected by the bony structures of the vertebral column. External anatomy of the spinal cord.
The spinal cord and the spinal canal are of equal lengths before birth. The cerebrum the diencephalon the brain stem and the cerebellum. Each posterior root has a swelling the posterior dorsal root ganglion which contains the cell bodies of sensory neurons.
The spinal cord stops growing earlier than the spinal canal that covers it. They contain afferent fibers. Anatomy and physiology the spinal cord is part of the central nervous system cns along with the encephalon.

 Spinal Cord Function Anatomy Physiology Medisavvy
Spinal Cord Function Anatomy Physiology Medisavvy
 The Spinal Cord Anatomy Vertebral Column Physiology Arm
The Spinal Cord Anatomy Vertebral Column Physiology Arm

 Organization In The Spinal Cord The Anatomy And Physiology
Organization In The Spinal Cord The Anatomy And Physiology
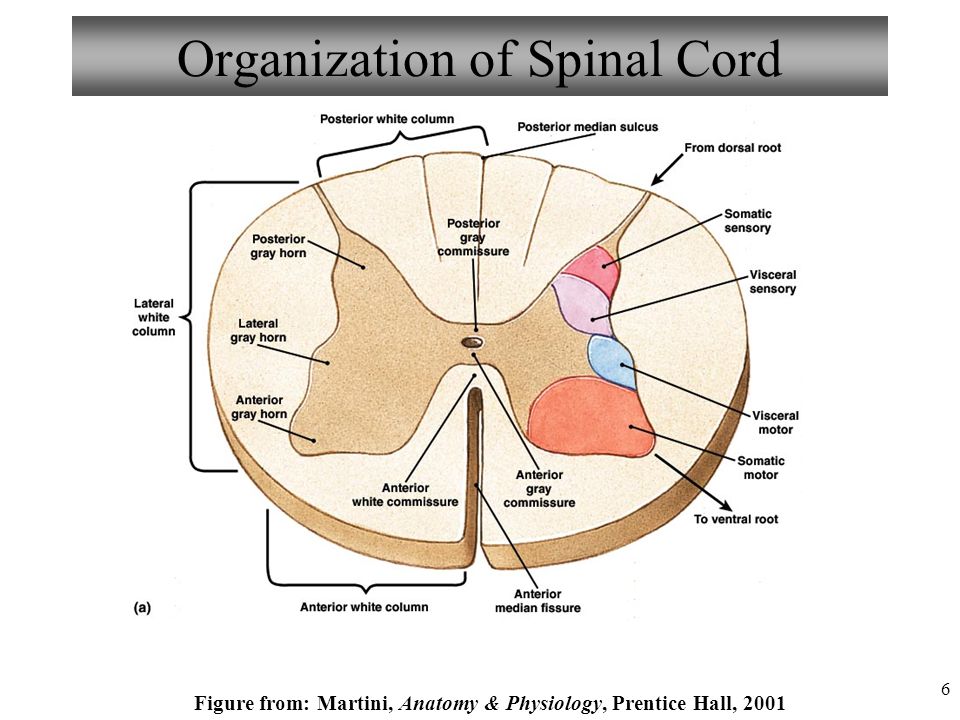 Anatomy And Physiology Ppt Video Online Download
Anatomy And Physiology Ppt Video Online Download
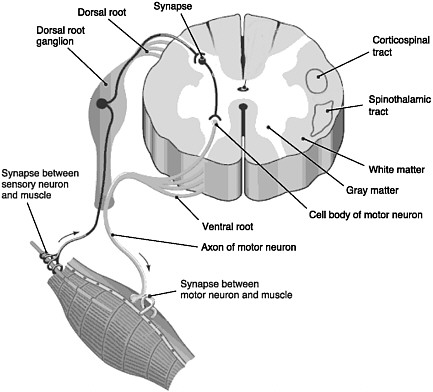 2 Progression Of Spinal Cord Injury Spinal Cord Injury
2 Progression Of Spinal Cord Injury Spinal Cord Injury
 Spinal Cord Anatomy Physiology Pptx Powerpoint
Spinal Cord Anatomy Physiology Pptx Powerpoint
 Spinal Cord Slides Pdf Spinal Cord Anatomy Physiology Nbio
Spinal Cord Slides Pdf Spinal Cord Anatomy Physiology Nbio
 Spinal Cord Anatomy And Physiology Amyl Digimerge Net
Spinal Cord Anatomy And Physiology Amyl Digimerge Net
 Ppt Anatomy And Physiology I Powerpoint Presentation Free
Ppt Anatomy And Physiology I Powerpoint Presentation Free
Injury Profiles Complete Spinal Cord Injury Scriptmedic
 Spinal Cord Anatomy Physiology Wikivet English
Spinal Cord Anatomy Physiology Wikivet English
 Anatomy And Pathophysiology Of Spinal Cord Injury Associated
Anatomy And Pathophysiology Of Spinal Cord Injury Associated
Spinal Cord 091400 Human Anatomy And Physiology Uts
 Spinal Cord And Spinal Nerves Anatomy Physiology 19 With
Spinal Cord And Spinal Nerves Anatomy Physiology 19 With
 The Brain And Spinal Cord Canadian Cancer Society
The Brain And Spinal Cord Canadian Cancer Society
 Anatomy And Physiology Head And Neck Spinal Cord Veins
Anatomy And Physiology Head And Neck Spinal Cord Veins
Chapter 1 Spinal Cord Anatomy Physiology
 The Spinal Cord Boundless Anatomy And Physiology
The Spinal Cord Boundless Anatomy And Physiology
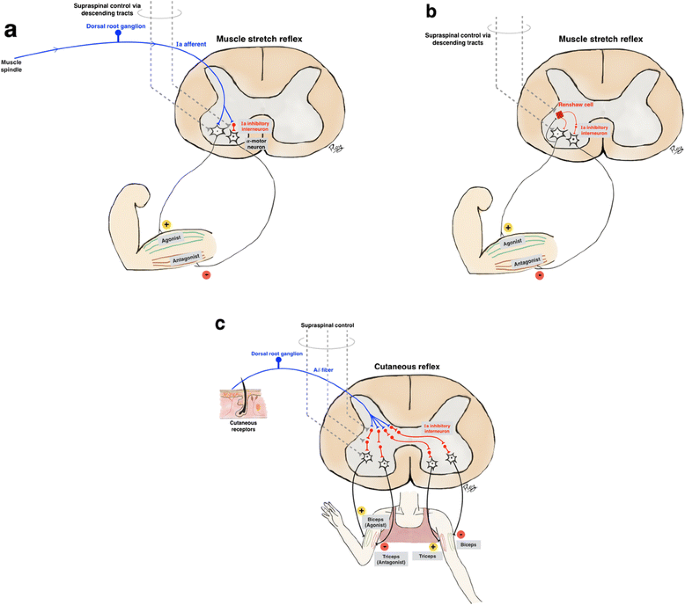 Spinal Generated Movement Disorders A Clinical Review
Spinal Generated Movement Disorders A Clinical Review
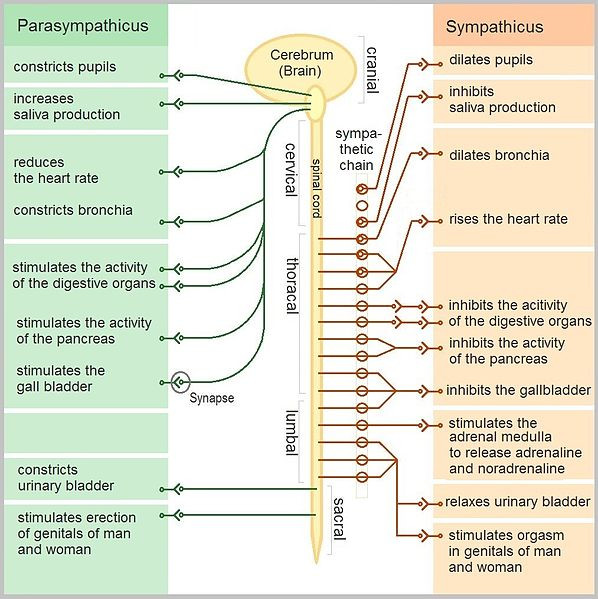
 Introduction To Anatomy And Physiology Online Student
Introduction To Anatomy And Physiology Online Student
Nervous System Anatomy Physiology
 Test Bank For Fundamentals Of Anatomy And Physiology 9th
Test Bank For Fundamentals Of Anatomy And Physiology 9th
 Spinal Cord Function Anatomy Physiology Medisavvy
Spinal Cord Function Anatomy Physiology Medisavvy
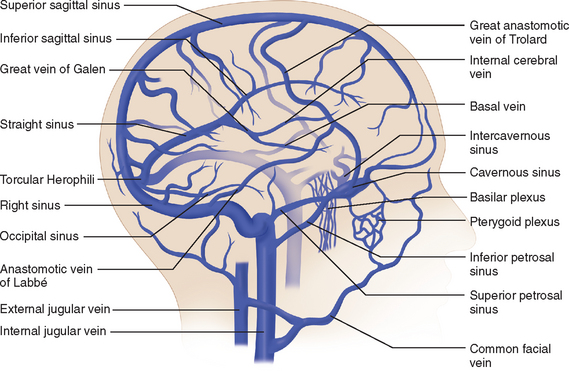 Anatomy And Physiology Of Cerebral And Spinal Cord
Anatomy And Physiology Of Cerebral And Spinal Cord
Anatomy And Physiology Of Animals Nervous System Wikibooks
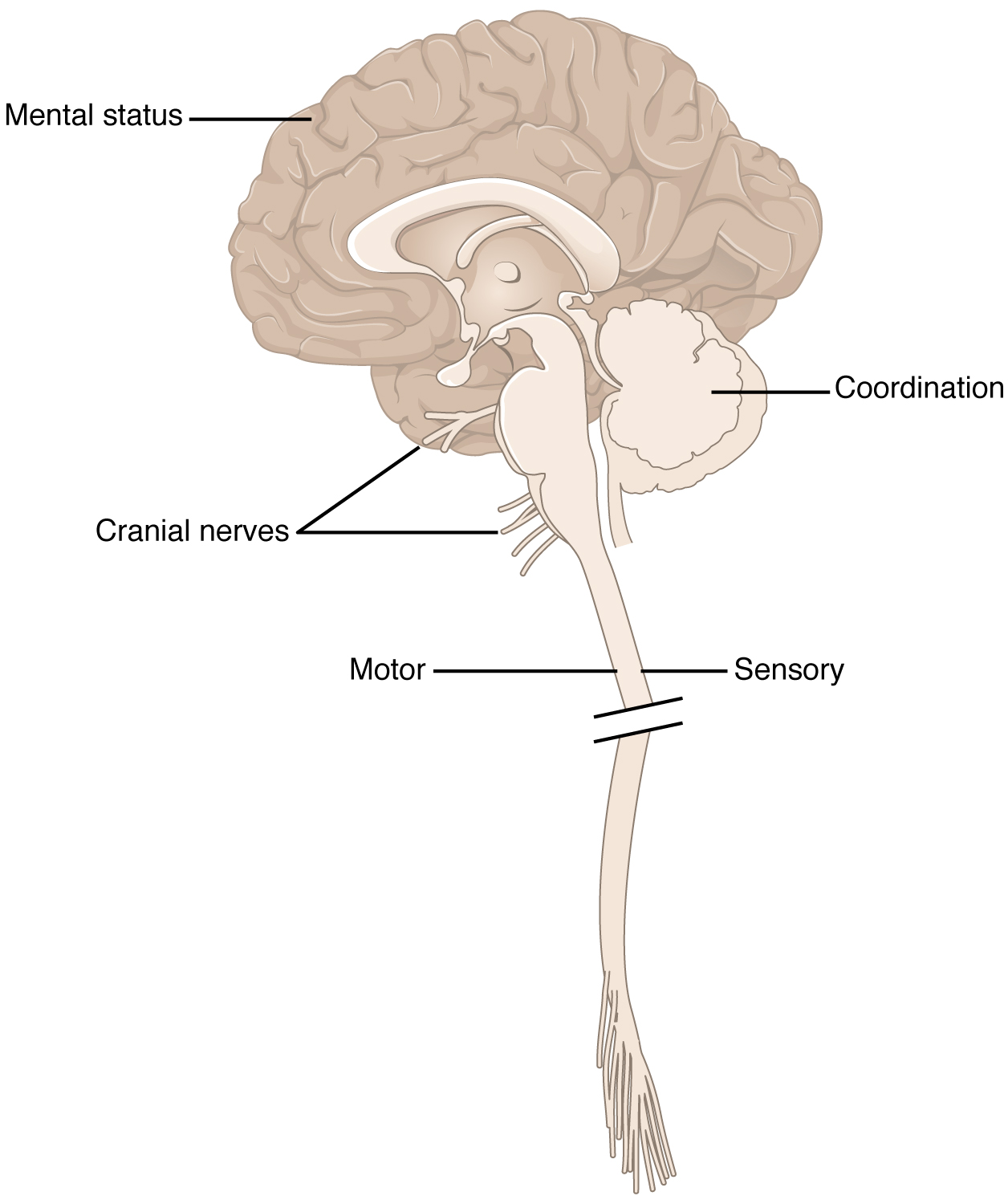 16 1 Overview Of The Neurological Exam Anatomy And Physiology
16 1 Overview Of The Neurological Exam Anatomy And Physiology
 Spinal Cord And Ear Mrs Simmons Anatomy Physiology I Lab
Spinal Cord And Ear Mrs Simmons Anatomy Physiology I Lab

Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar