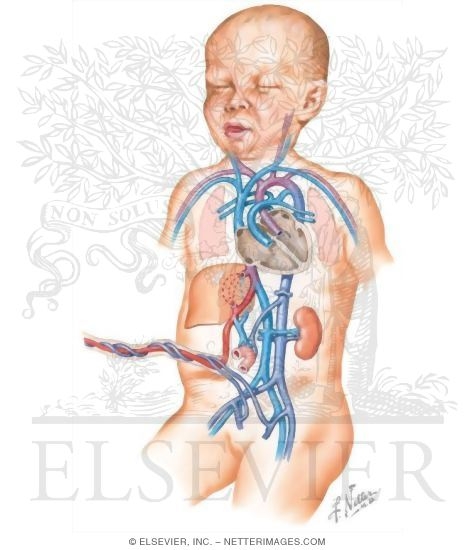
The cord contains one vein and two arteries housed within its protective whartons jelly. The umbilical vein goes all the way to the fetuss liver where it splits into two.
 Amazon Com Wang Fetal Model Baby Blood Circulation With
Amazon Com Wang Fetal Model Baby Blood Circulation With
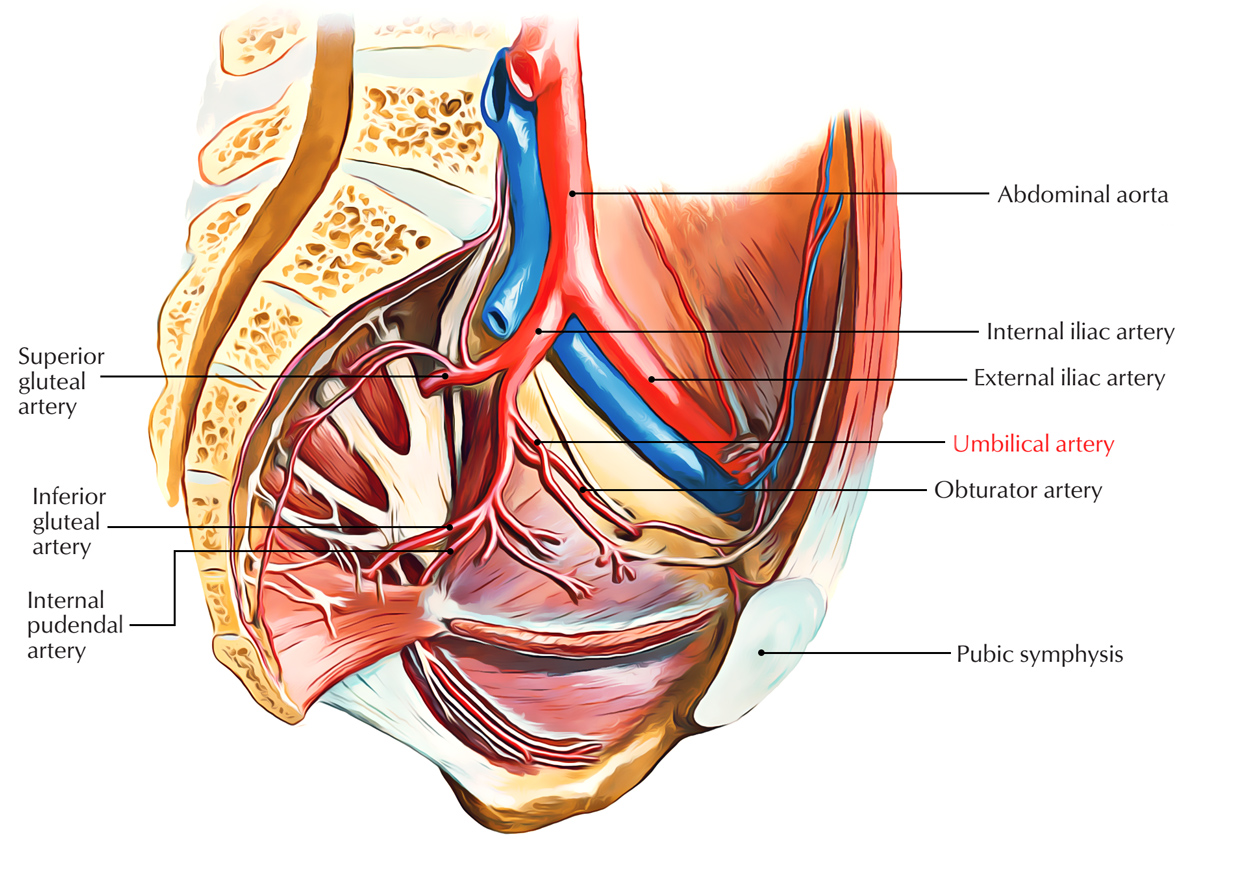
This is the distal part of the umbilical artery.

Umbilical cord anatomy. It is the lifeline of the fetus in the uterus throughout pregnancy. The umbilical cord derives from the primitive umbilical ring which includes the connecting stalk yolk stalk vitelline vessels and a canal between the intraembryonic and extraembryonic cavities. These are not branches but are actually a direct continuation of the umbilical artery.
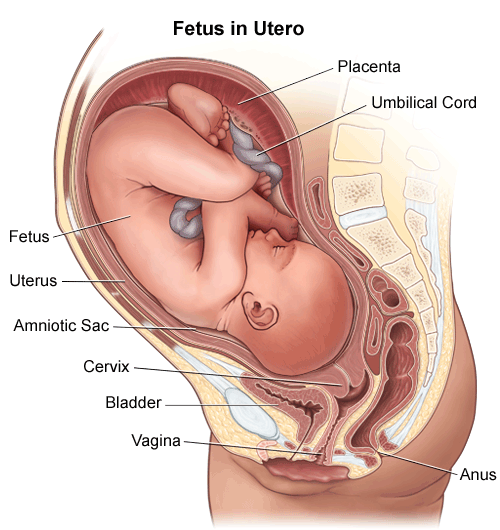
The umbilical cord is a tube like structure that connects a fetus to the mothers placenta. Sources of stem cells in the umbilical cord cells in surrounding cells in cord tissue blood from umbilical vein cells in perivascular regions surrounding umbilical vessels. Umbilical cord the structure that connects the fetus and placenta.
Within the first week of life the remnant umbilical cord stump separates from the neonate creating the umbilicus commonly referred to as the navel. The umbilical arteries are atypical of those of the remainder of the body in that they carry oxygen poor blood lack an internal elastic lamina and have considerable metachromatic ground substance within their. Umbilical cord compression can result from for example entanglement of the cord a knot in the cord or a nuchal cord which is the wrapping of the umbilical cord around the fetal.
A number of abnormalities can affect the umbilical cord which can cause problems that affect both mother and child. The umbilical cord uc is the essential life sustaining connection between fetus and placenta. In the adult there are two vessels which the umbilical artery gives rise to.
The persistent proximal. Plate 13261 umbilical cord. The cord is covered by a simple epithelium of amniotic derivation which becomes stratified in late gestation.
The umbilical cord is made up of a substance called whartons jelly instead of normal connective tissue and skin. The anatomy of the umbilical cord the umbilical cord contains valuable stem cells in the blood tissue and perivascular regions 1 figure 1. It constitutes a stable connection to the fetomaternal interface while allowing fetal mobility that is essential for fetal development in general and neuromotor development in particular.
A placenta is an organ attached to the uterine wall with access to the mothers blood supply. Called also exomphalos and exumbilication. Inside the cord is one vein which contains oxygenated blood and two arteries.
At birth the umbilical cord which provided vascular flow between the fetus and placenta is clamped and cut.
 Doctors Tout Life Saving Benefits Of Umbilical Cord Blood
Doctors Tout Life Saving Benefits Of Umbilical Cord Blood
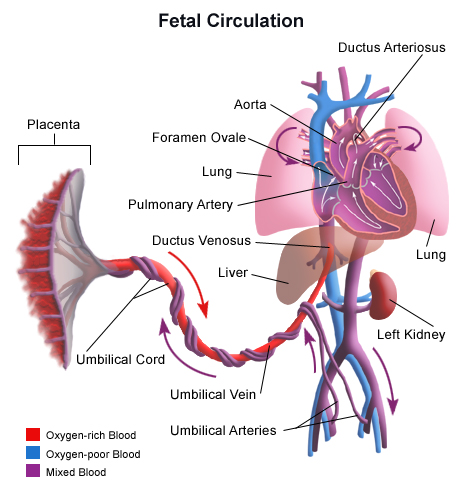
 The Umbilical Cord Anatomy And Physiology Review
The Umbilical Cord Anatomy And Physiology Review
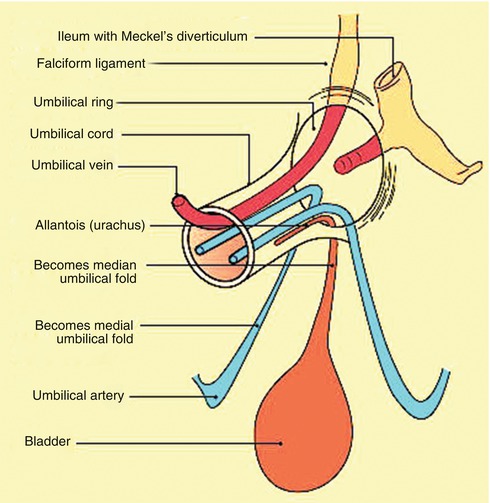 Anatomy And Physiology Of The Umbilicus Springerlink
Anatomy And Physiology Of The Umbilicus Springerlink
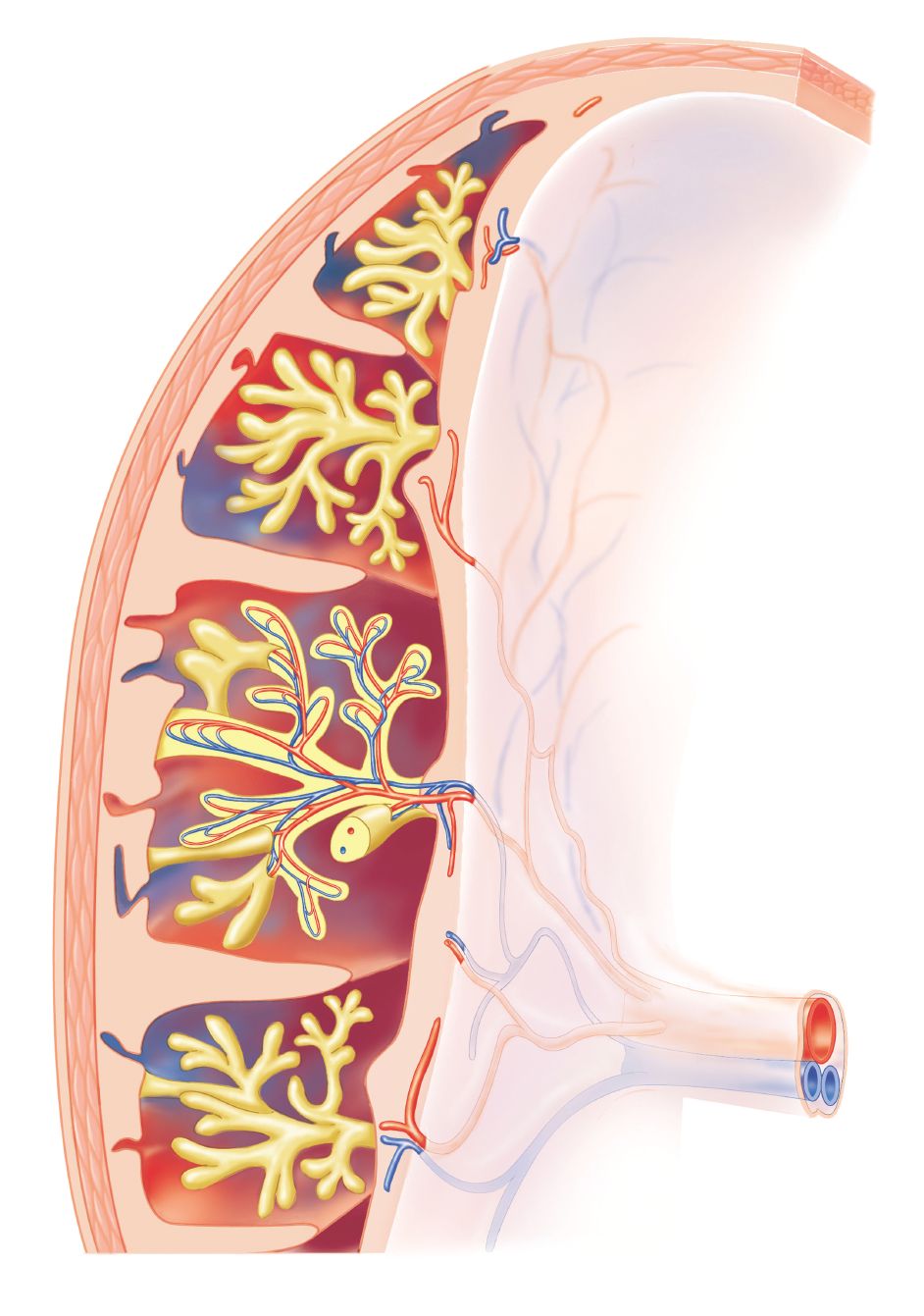 How Umbilical Cords Work How It Works
How Umbilical Cords Work How It Works
 Umbilical Cord Blood Gases Normal Values Babymed Com
Umbilical Cord Blood Gases Normal Values Babymed Com
 Axis Scientific Placenta Model With Removable Umbilical Cord
Axis Scientific Placenta Model With Removable Umbilical Cord
 Anatomy And Cell Biology 3319 Lecture Notes Fall 2017
Anatomy And Cell Biology 3319 Lecture Notes Fall 2017
 Things You Didn T Know About Your Belly Button The Healthy
Things You Didn T Know About Your Belly Button The Healthy
 Umbilical Cord Connected To Placenta Medical Illustration
Umbilical Cord Connected To Placenta Medical Illustration
 Isolation And Characterization Of Mesenchymal Stromal Cells
Isolation And Characterization Of Mesenchymal Stromal Cells
Correlation Between Isolated Sonographic Finding Of
 Histology Of Umbilical Cord In Mammals Intechopen
Histology Of Umbilical Cord In Mammals Intechopen
 Compressed Umbilical Cord Medical Illustration Human
Compressed Umbilical Cord Medical Illustration Human

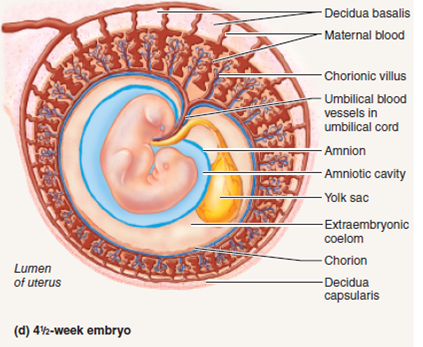 Examining The Stages Of Human Developmentuse Figure 44
Examining The Stages Of Human Developmentuse Figure 44
 Umbilical Cord And Remnants Embryology Medbullets Step 1
Umbilical Cord And Remnants Embryology Medbullets Step 1
 15102 02x Umbilical Cord Compression Anatomy Exhibits
15102 02x Umbilical Cord Compression Anatomy Exhibits




Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar