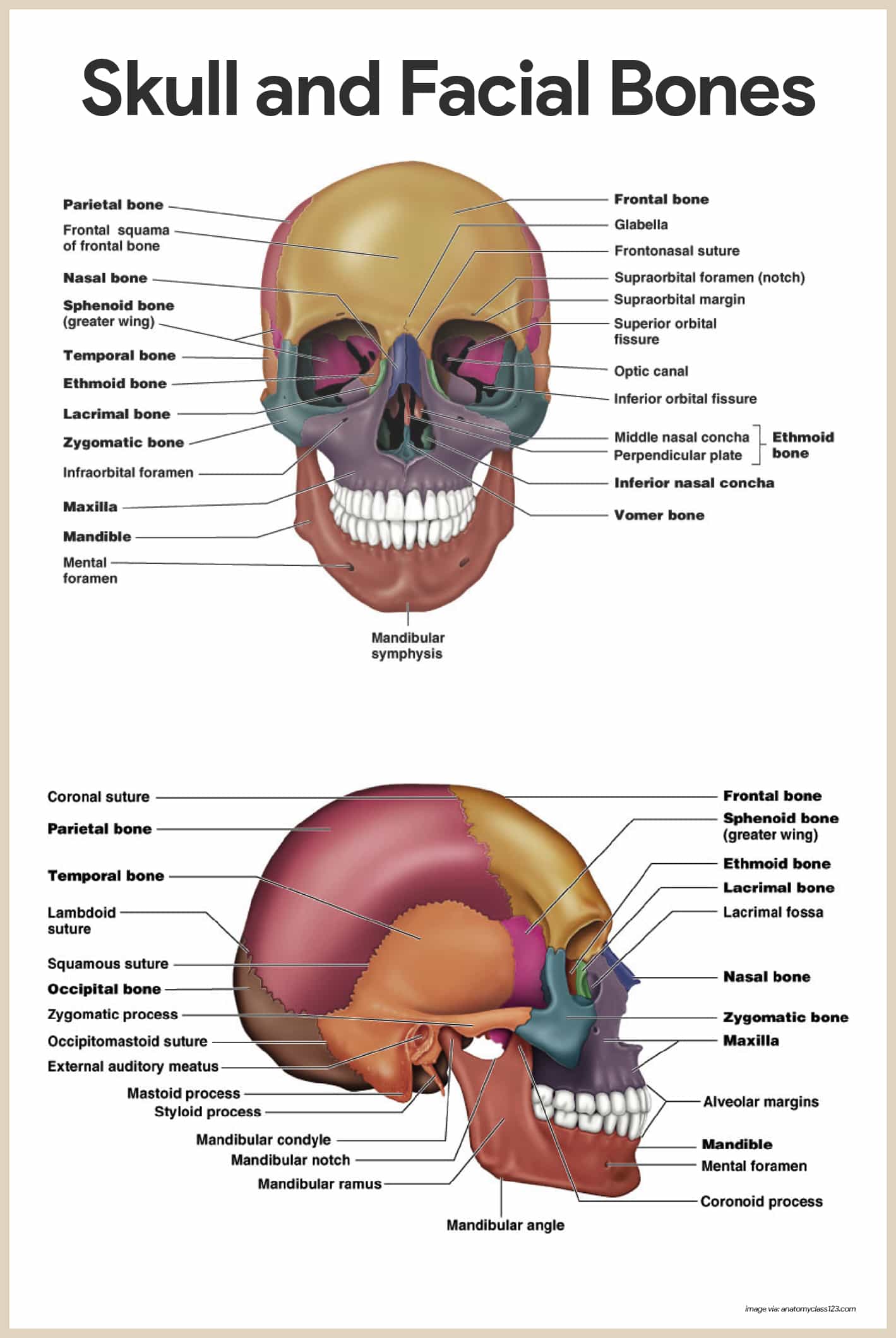
The orbital apex refers to the posterior confluence of the orbit where the optic canal. If you have found anatomyzone useful and you would like to support our aim of providing the best free online anatomy resource please consider using the form below to make a contribution towards our development.
The bony orbit refers to the bones that constitute the margins of the orbits that is the roof medial and lateral walls and floor.

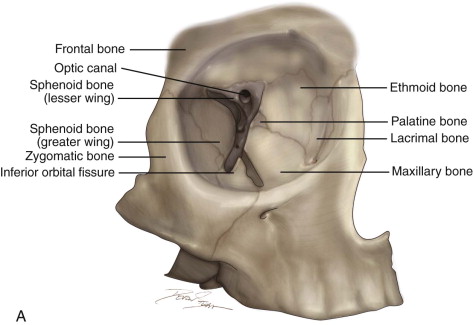
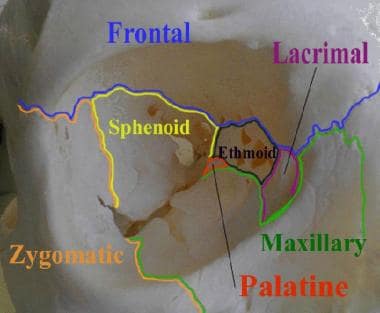
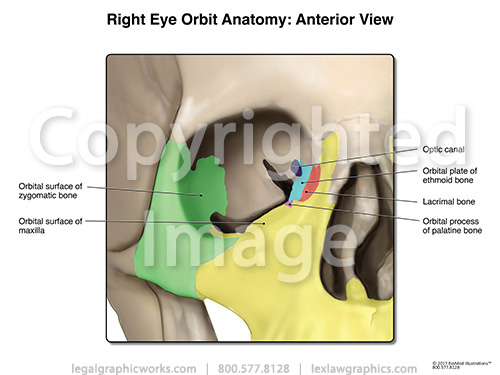
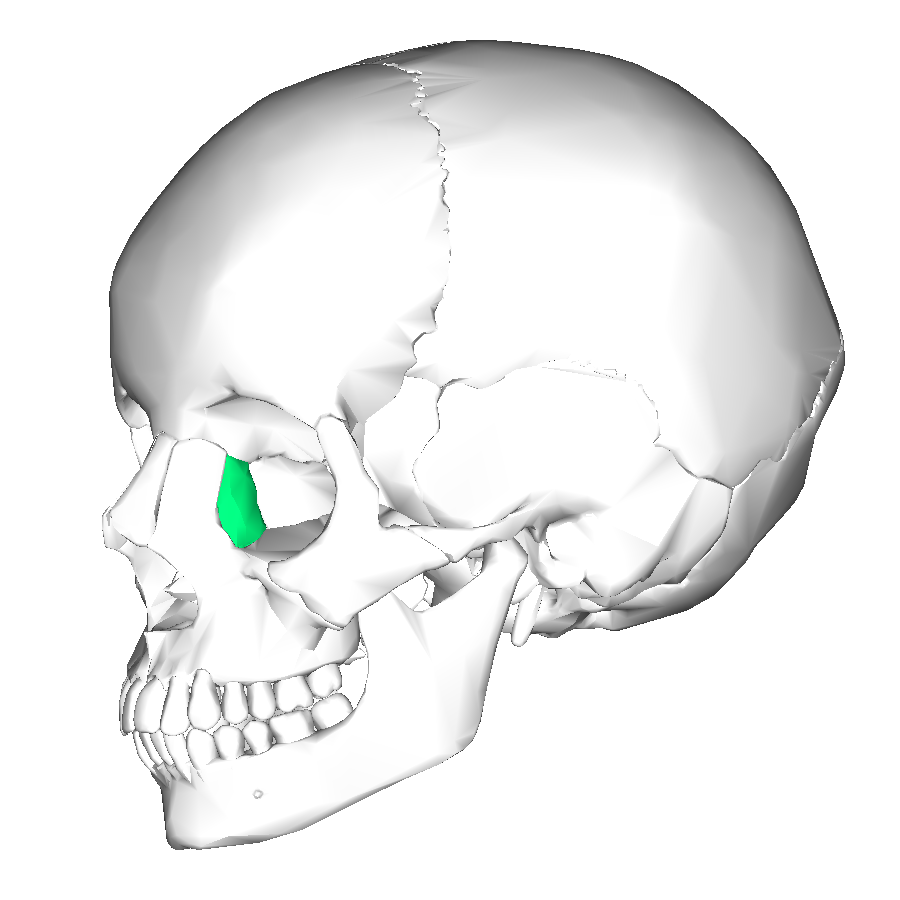
Orbital bone anatomy. Base and apex the apex of the orbit is the optic foramen canal bound medially by the body of the sphenoid bone and laterally by the lesser wing of the sphenoid bone. The bone of this wall separates the anterior cranial fossa from the orbit. The lesser wing of the sphenoid 2 in tan is most posterior and is joined to the ethmoid bone 3 in dark green moving anteriorly to the lacrimal bone 4 in light red and then to the maxillary bone 5 in light green.
Sphenoid ethmoid lacrimal and maxillary bone. Orbital process of the frontal bone orbital process of the zygomatic bone. Orbit can refer to the bony socket or it can also be used to imply the contents.
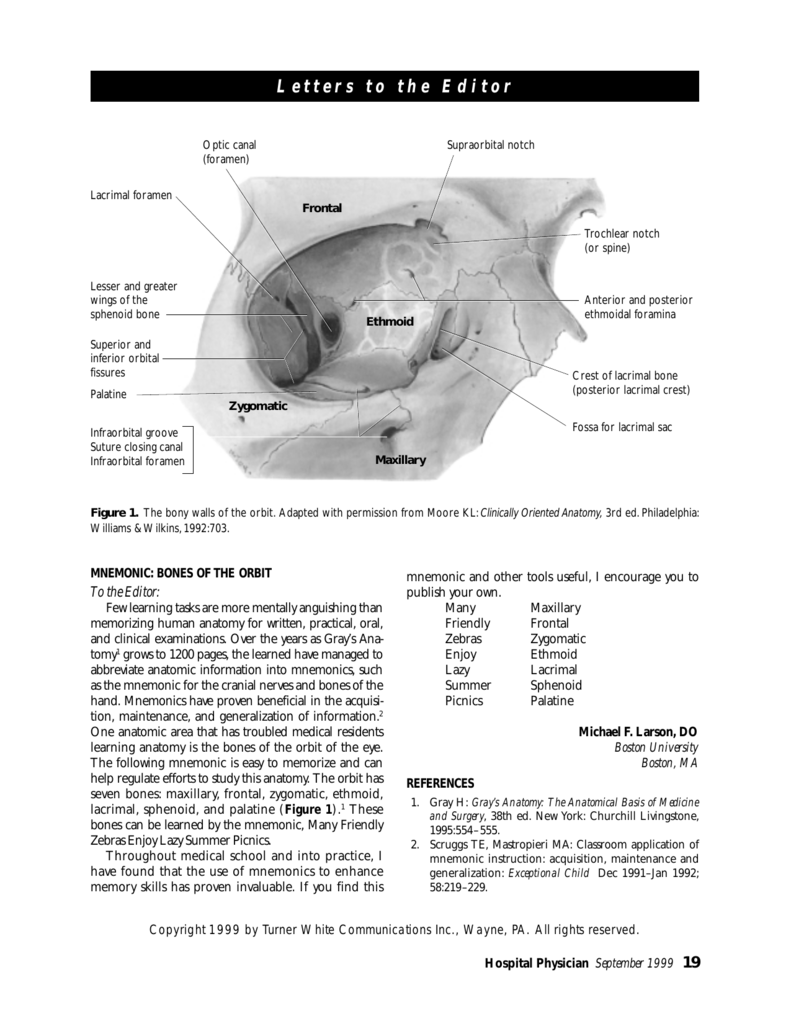
In the adult human the volume of the orbit is 30 millilitres 106 imp fl oz. Fig 12 the major openings into the orbit. Sometimes this notch is calcified and forms a distinct foramen.
Orbital anatomy the orbital cavities are large bony sockets that house the eyeballs with associated muscles nerves blood vessels and fat. Pathways into the orbit. Inferior orbital fissure lies between.
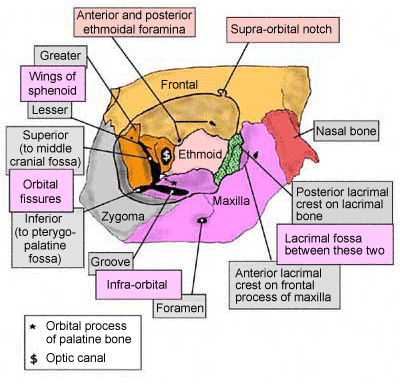
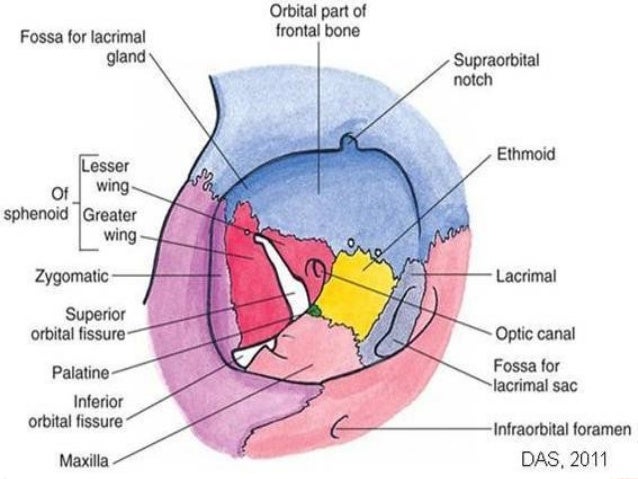
Fig 11 diagram of the arterial supply to the eye. The medial wall of the orbit is composed of 4 bones. Superior orbital fissure lies between the lesser and the greater wing of sphenoid.
The bony orbit borders and anatomical relations. The orbital margin or rim refers to the anterior circular margin of the orbit. It is generally thin and becomes thinner with age.
The orbit can be thought of as a pyramidal structure. Orbit anatomy in anatomy the orbit is the cavity or socket of the skull in which the eye and its appendages are situated. 101 us fl oz.
Orbit bones eye. Each orbit is pear shaped with the optic nerve representing the stem. This fissure allows the passage to the nerves iii iv vi branches of the v1 and ophthalmic veins.
The bones of the orbit are lined with periosteum called periorbita. The superior orbital rim has a notch on the medial third through which the supraorbital nerve runs and supplies sensation to the forehead.
 Superior Orbital Fissure An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Superior Orbital Fissure An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
 The Orbit And Eye Pocket Dentistry
The Orbit And Eye Pocket Dentistry
 Which Bone Contributes To The Lateral And Inferior Borders
Which Bone Contributes To The Lateral And Inferior Borders
 Orbital Fractures Images Bmj Best Practice
Orbital Fractures Images Bmj Best Practice
 Orbit Anatomy Osteology Lacrimal System Connective Tissue
Orbit Anatomy Osteology Lacrimal System Connective Tissue
 Human Anatomy Skeletal System Unit 8 Skull Diagram Quizlet
Human Anatomy Skeletal System Unit 8 Skull Diagram Quizlet
 Orbital Bone Stock Photos Orbital Bone Stock Images Alamy
Orbital Bone Stock Photos Orbital Bone Stock Images Alamy
 Orbital Bone Anatomy Eye Anatomy Facial Anatomy
Orbital Bone Anatomy Eye Anatomy Facial Anatomy
 Orbital Bones Ophthalmology Review
Orbital Bones Ophthalmology Review
/HEAD%20AND%20NECK%20(SEGMENT%20I%20-%20FACE,%20CRANIAL%20CAVITY,%20ORBIT%20DISSECTIONS)_files/image001.jpg) Electronic Dissection Manual Head And Neck Part 1
Electronic Dissection Manual Head And Neck Part 1
 Lab Anatomy Physiology 2010 With Scallion At Dyersburg
Lab Anatomy Physiology 2010 With Scallion At Dyersburg
 Skeletal System Anatomy And Physiology Nurseslabs
Skeletal System Anatomy And Physiology Nurseslabs
 Boundaries Of Bony Orbit Lateral Wall Diagram Quizlet
Boundaries Of Bony Orbit Lateral Wall Diagram Quizlet
 Bones Of The Orbit Purposegames
Bones Of The Orbit Purposegames
 Orbital Tumor Eye Socket Cancer Anatomy
Orbital Tumor Eye Socket Cancer Anatomy
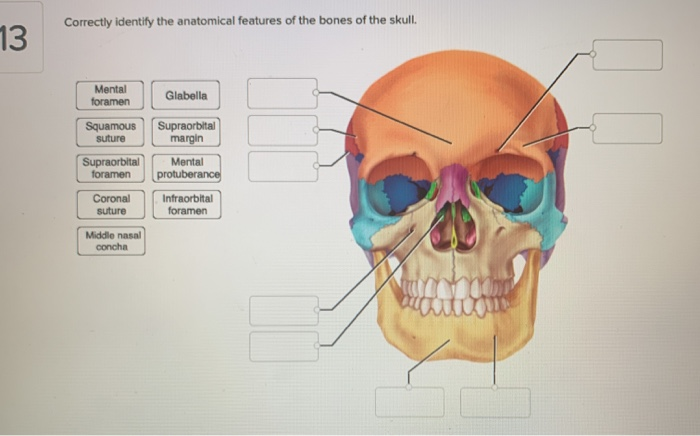 Solved Correctly Label The Anatomical Features Of The Eth
Solved Correctly Label The Anatomical Features Of The Eth
Orbital Bones Ophthalmology Review
:watermark(/images/watermark_only.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/orbital-roof/47sVDgpA7y6NNFAR4Fhrg_Orbital_roof_01.png) Bones Of The Orbit Anatomy Foramina Walls And Diagram
Bones Of The Orbit Anatomy Foramina Walls And Diagram
 Orbital Bone Medical Anatomy Anatomy Physiology Axial
Orbital Bone Medical Anatomy Anatomy Physiology Axial


Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar