Retrolateral refers to the surface of a leg that is closest to the posterior end of an arachnids body. Araneae normally have eight eyes in four pairs.
Often used to indicate the position of one structure relative to another that is nearer the back of the body.
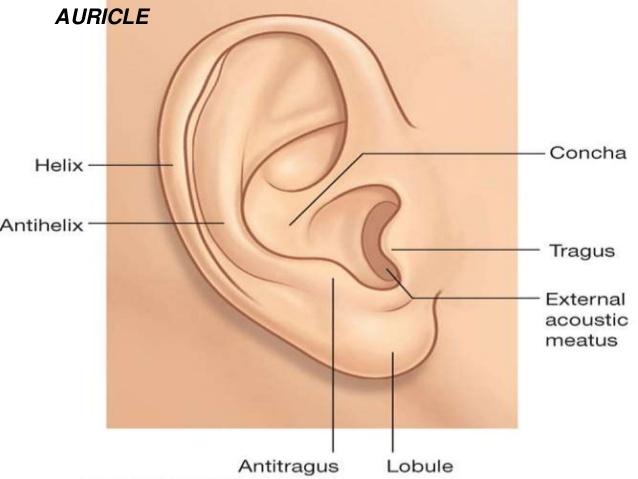
Posterior ear anatomy. Congenital abnormalities of the ear are common and largely affect the shape of the auricle. In some ears a little prominence known as darwins tubercle is seen along the upper posterior portion of the helix. Because of the unusual nature and positions of the eyes of the araneae spiders and their importance in taxonomy evolution and anatomy special terminology with associated abbreviations has become established in arachnology.
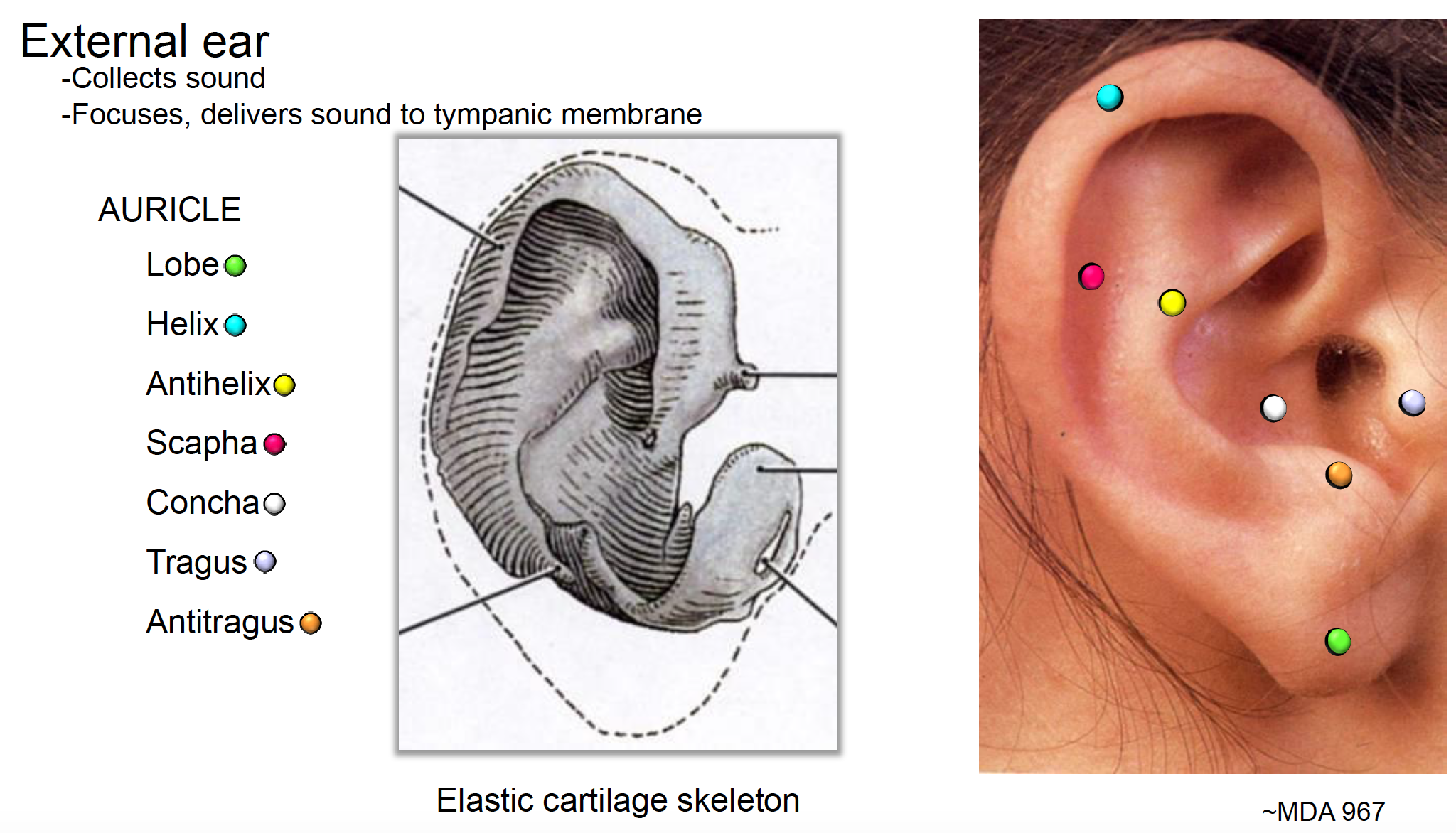
Auricle cartilage covered by skin placed on opposite sides of the head auditory canal also called the ear canal eardrum outer layer also called the tympanic membrane the outer part of the ear collects sound. Venous drainage is via veins following the arteries listed above. Variant anatomy of the external ear can be divided into congenital and acquired entities.
Human anatomy denoting the back surface of the body. The outer ear includes. You will need ear drops but it needs to be prescription.
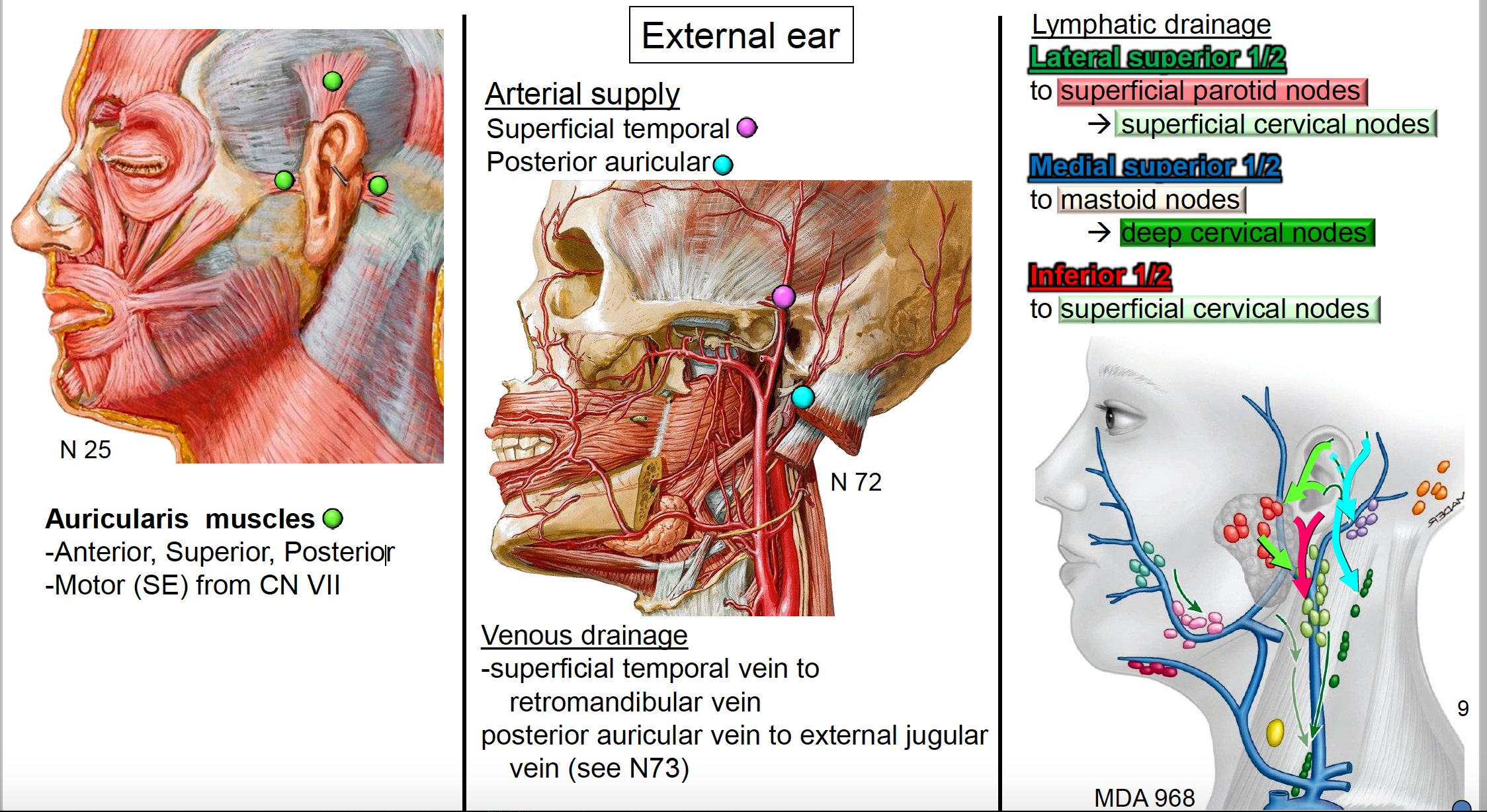
The external ear is supplied by branches of the external carotid artery. The lobule the fleshy lower part of the auricle is the only area of the outer ear that contains no cartilage. Sound travels through the auricle and the auditory canal a short tube that ends at the eardrum.
Acquired entities can further be delineated into intrinsic processes such as cancer and extrinsic processes such as trauma. Dorsalis ta dorsal 2. Helpful trusted answers from doctors.
Maxillary artery deep auricular branch supplies the deep aspect of the external acoustic meatus and tympanic membrane only. Posterior pos tēre or directed toward or situated at the back. It is the vestige of the folded over point of the ear of a remote human ancestor.
Colantino on posterior ear anatomy. The outer ear is called the pinna and is made of ridged cartilage covered by skin. Sound funnels through the pinna into the external auditory canal a short tube that ends at the eardrum tympanic.
Do not use q tips or alcohol.
:watermark(/images/watermark_5000_10percent.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/atlas_overview_image/498/QWbpLPS26Ez5PtJhHuzMQ_structures-of-outer-ear-and-auditory-tube_english.jpg) Ear Anatomy Parts And Functions Kenhub
Ear Anatomy Parts And Functions Kenhub
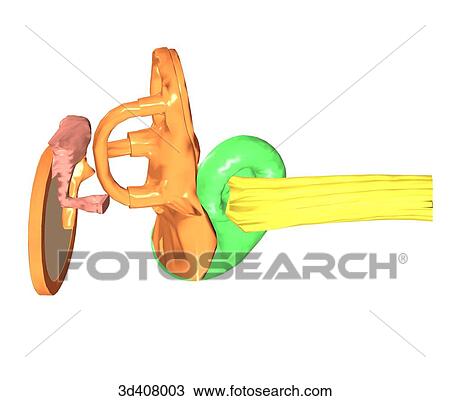 Posterior View Of Inner Ear Anatomy Drawing 3d408003
Posterior View Of Inner Ear Anatomy Drawing 3d408003
 Auricular Haematoma Tidsskrift For Den Norske Legeforening
Auricular Haematoma Tidsskrift For Den Norske Legeforening
 Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo Continuing Professional
Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo Continuing Professional
 Anatomy Of Middle Ear With Clinical Correlation Epomedicine
Anatomy Of Middle Ear With Clinical Correlation Epomedicine
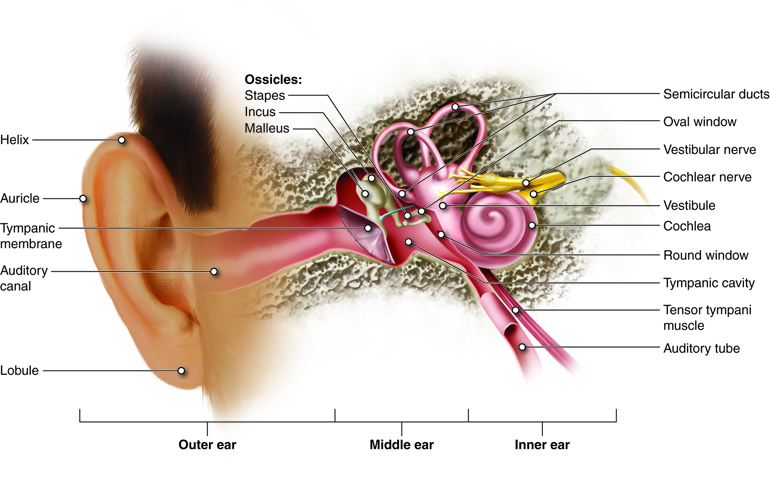 Hearing And Equilibrium Anatomy And Physiology
Hearing And Equilibrium Anatomy And Physiology
 1 Anatomy And Physiopathology Of The Medone Thieme
1 Anatomy And Physiopathology Of The Medone Thieme
 The Eye Ear Special Sense Organs Junqueira S Basic
The Eye Ear Special Sense Organs Junqueira S Basic
Anatomy Of Ear Cochlea Membrane Internal Fig External
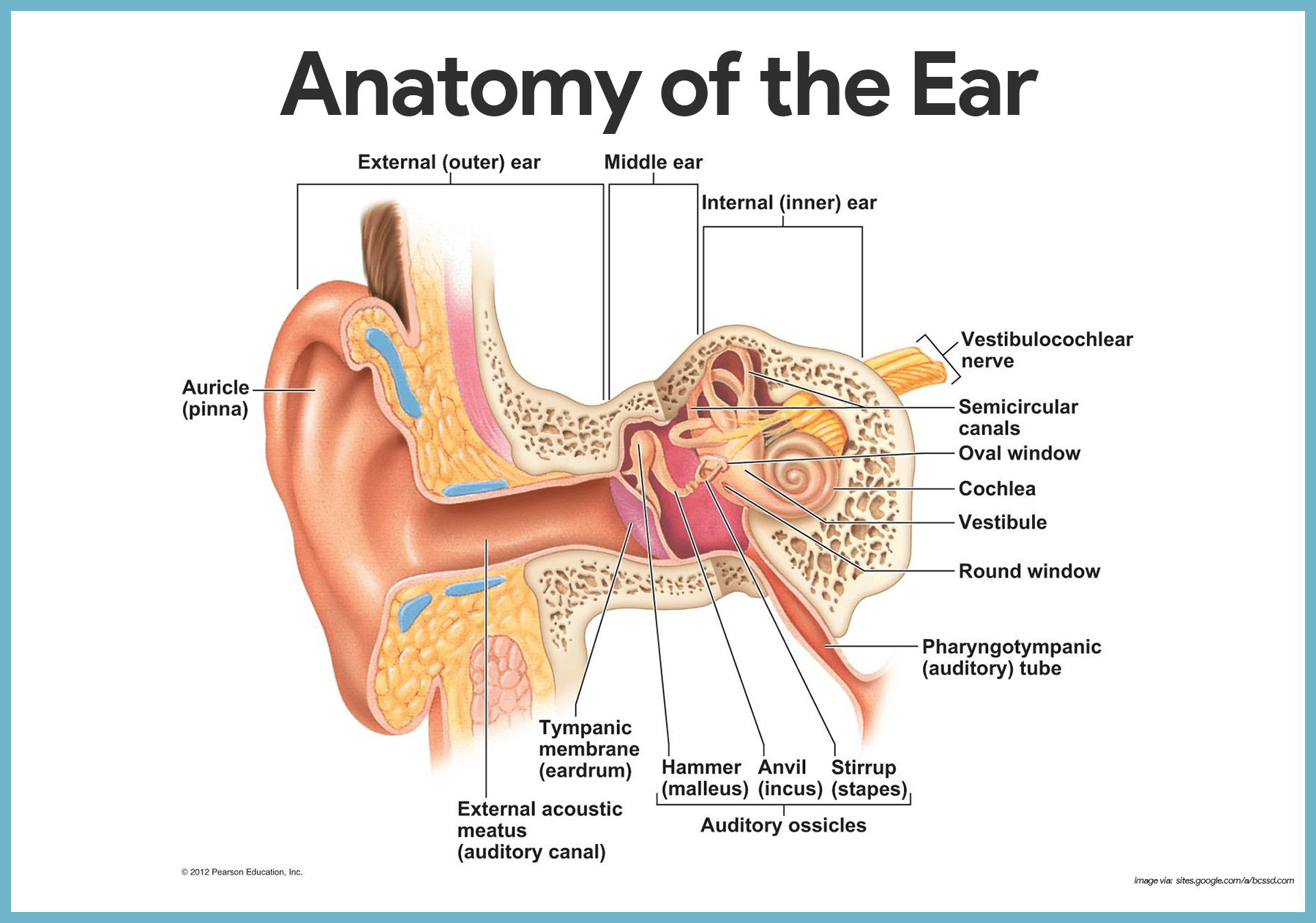 Special Senses Anatomy And Physiology Nurseslabs
Special Senses Anatomy And Physiology Nurseslabs
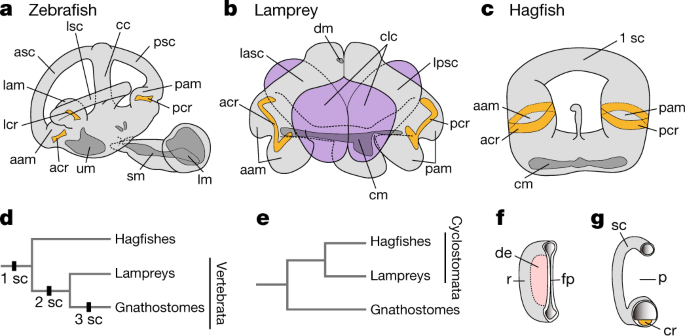 Inner Ear Development In Cyclostomes And Evolution Of The
Inner Ear Development In Cyclostomes And Evolution Of The
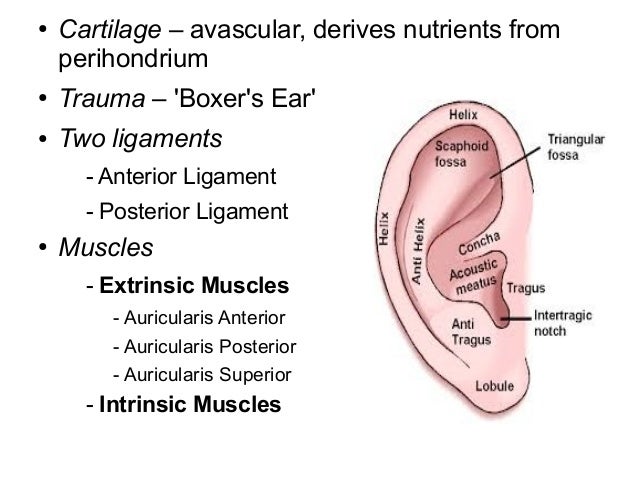 Anatomy Embryology Ext Ear Middle Ear
Anatomy Embryology Ext Ear Middle Ear
 Middle Ear Anatomy Diagram Quizlet
Middle Ear Anatomy Diagram Quizlet
 Disorders Of The Outer Ear Outer Ear Ear Anatomy Piercings
Disorders Of The Outer Ear Outer Ear Ear Anatomy Piercings
 The Association Between Tinnitus The Neck And Tmj
The Association Between Tinnitus The Neck And Tmj
![]() Basic Human Ear Anatomy And Physiology Outer Middle And
Basic Human Ear Anatomy And Physiology Outer Middle And
 Where Are The Major Arteries In Your Ears If You Puncture A
Where Are The Major Arteries In Your Ears If You Puncture A
 Print Ear Anatomy Flashcards Easy Notecards
Print Ear Anatomy Flashcards Easy Notecards
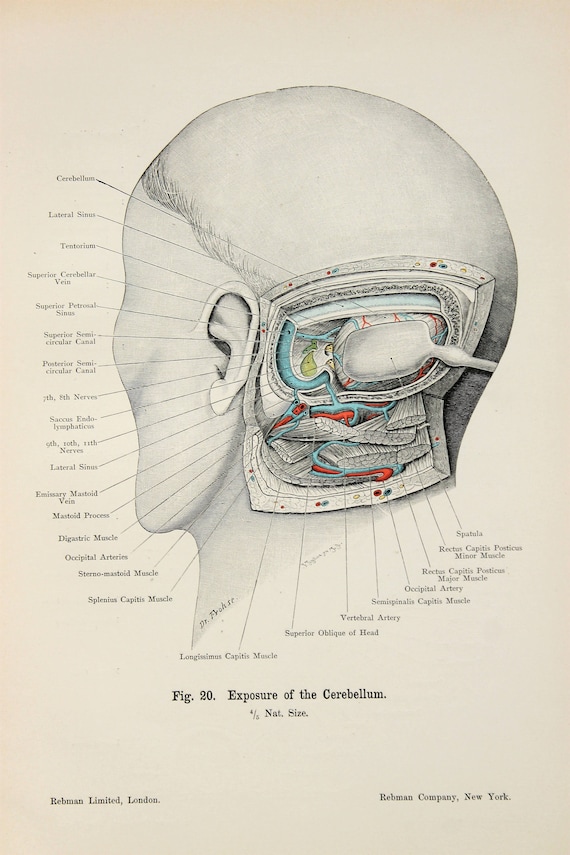 Skull Anatomy Cerebellum Ears Hearing C 1900 Double Sided Antique Anatomy Print Colour Anatomical Print Lithograph
Skull Anatomy Cerebellum Ears Hearing C 1900 Double Sided Antique Anatomy Print Colour Anatomical Print Lithograph
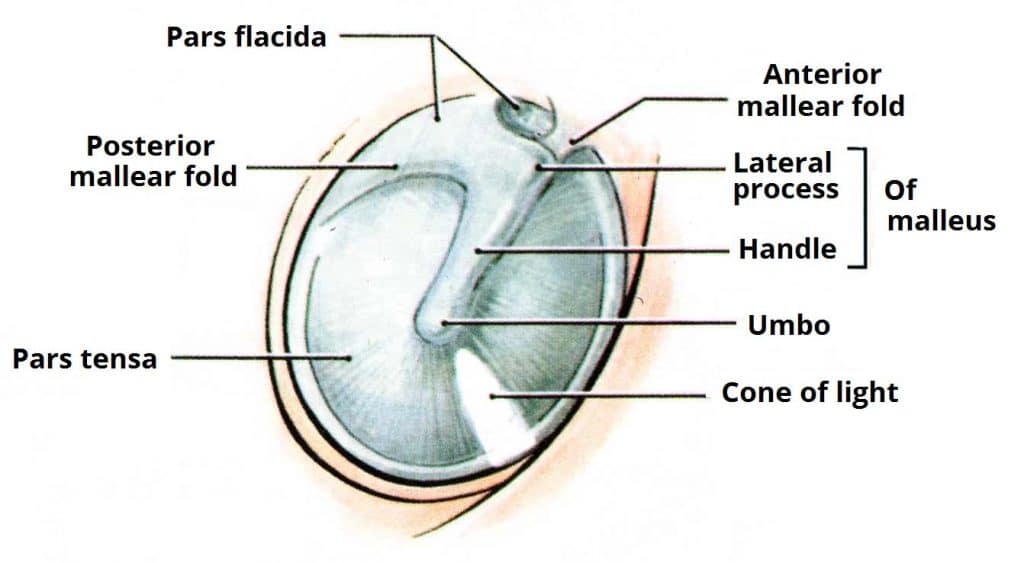 The External Ear Structure Function Innervation
The External Ear Structure Function Innervation
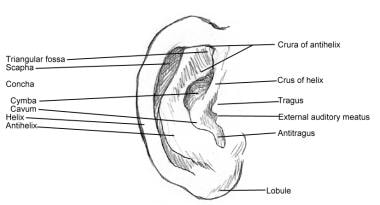 Ear Anatomy Overview Embryology Gross Anatomy
Ear Anatomy Overview Embryology Gross Anatomy
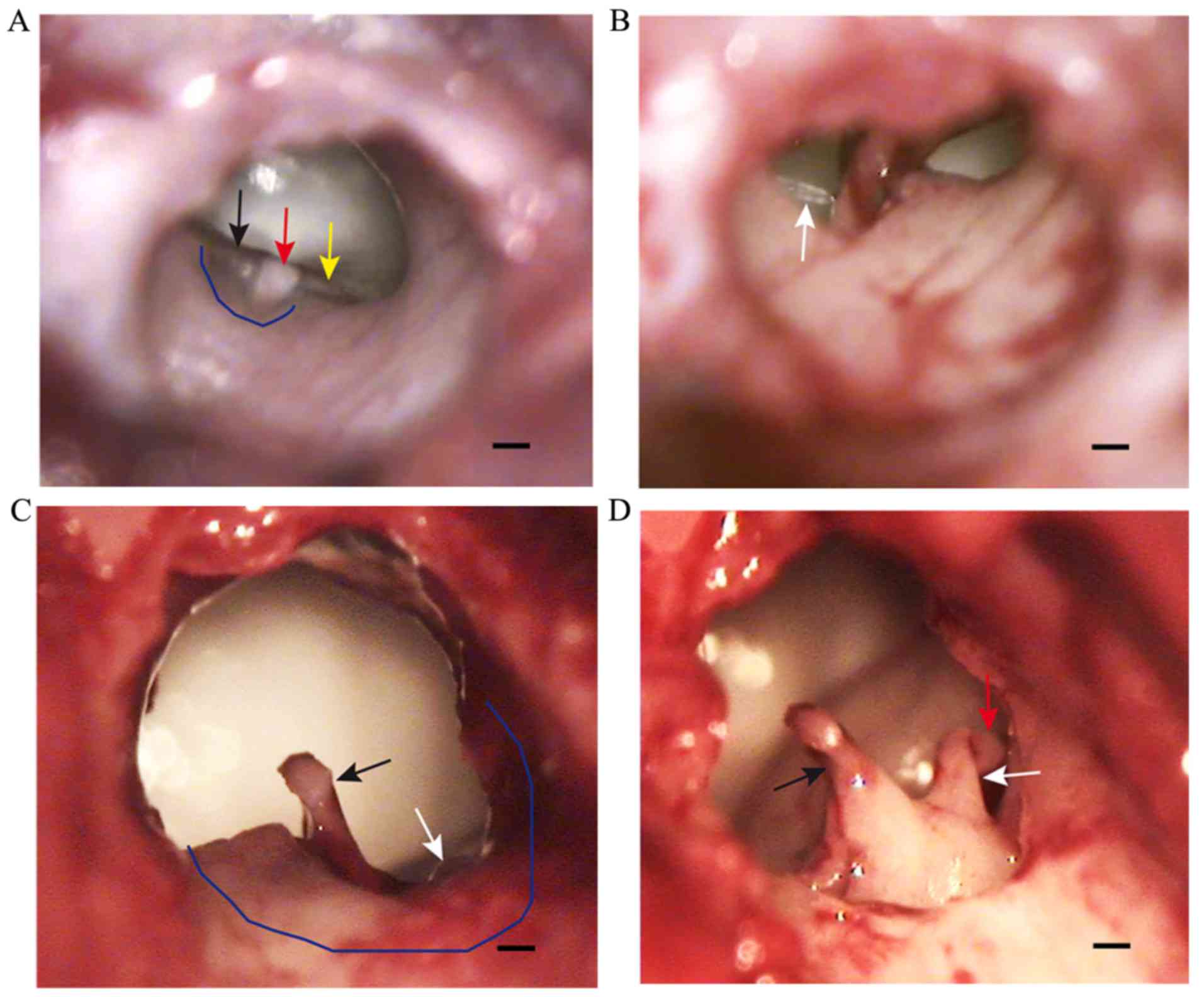 Middle Ear Structure And Transcanal Approach Appropriate For
Middle Ear Structure And Transcanal Approach Appropriate For
 The External Ear Human Anatomy
The External Ear Human Anatomy
:watermark(/images/watermark_only.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/meatus-acusticus-externus-2/cNYVakPkJkzvw8J3mO7HA_Meatus_acusticus_externus_01.png) Ear Anatomy Parts And Functions Kenhub
Ear Anatomy Parts And Functions Kenhub
The Anatomical Terminology Of Auricular Medicine Figure 2 1
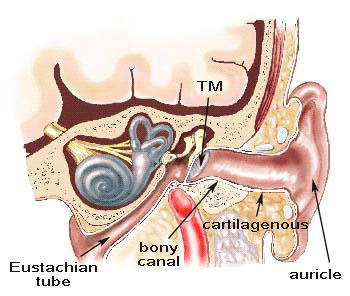
 Where Are The Major Arteries In Your Ears If You Puncture A
Where Are The Major Arteries In Your Ears If You Puncture A
 Human Ear Tympanic Membrane And Middle Ear Britannica
Human Ear Tympanic Membrane And Middle Ear Britannica
 Surgical Management Of Skin Cancer And Trauma Involving The
Surgical Management Of Skin Cancer And Trauma Involving The
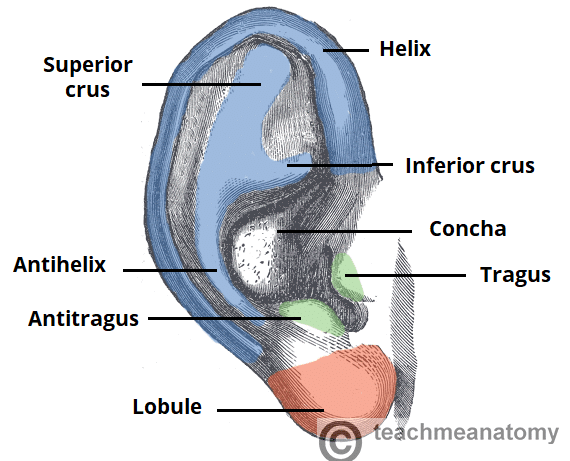 The External Ear Structure Function Innervation
The External Ear Structure Function Innervation

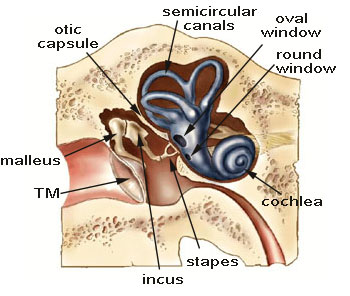
Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar