For diffusion to occur there must be a concentration gradient. These proteins can move another substrate at the same time without regard to the concentration gradient.
T lymphocytes and their functional types.

Diffusion definition anatomy. Diffusion as a transport mechanism. In summary diffusion is the process of a substance moving from a high concentration to a low concentration until the system is in equilibrium. However over large distances diffusion is very slow.
Diffusion is the net passive movement of molecules or particles from regions of higher to regions of lower concentration. Cell membrane from a region of higher concentration of water to a lower conc. In facilitated diffusion a molecule is transported across a membrane with the help of a carrier protein.
214 the adaptive immune response. 213 the adaptive immune response. 212 barrier defenses and the innate immune response.
Diffusion is the passive movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. Its rate is proportional to the concentrations of the substances and it increases with the temperature. As such it is used in a variety of body systems where gradients and membranes suited to it are found.
Diffusion is very efficient over short distances and does not require energy. Simple diffusion definition simple diffusion is the process by which solutes are moved along a concentration gradient in a solution or across a semipermeable membrane. Of water until equilibrium of water is reach in an attempt to dilute a particular solute.
215 the immune response against pathogens. The movement does not require energy. One substrates concentration gradient provides the driving force and the other one gets a free ride.
Diffusion of only water molecules through the globular protein channels or pores of the cell membrane ie. The spontaneous mixing of the molecules or ions of two or more substances resulting from random thermal motion. Diffusion definition diffusion is a physical process that refers to the net movement of molecules from a region of high concentration to one of lower concentration.
Diffusion happens all the time and does not need. The dissimilarity in the amounts of solutes particles or molecules between two regions will cause them to move between the two regions. Simple diffusion is carried out by the actions of hydrogen bonds forming between water molecules and solutes.
Anatomy physiology diffusion osmosis it moves a specific substrate down its concentration gradient. 211 anatomy of the lymphatic and immune systems. In the body fluids the molecules of water gases and the ions of substances in solution are in constant motion.
The material that diffuses could be a solid liquid or gas. Passive diffusion is the movement of molecules across a membrane such as a cell membrane.
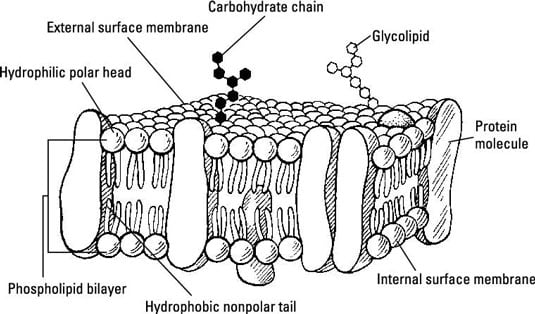 The Cell Membrane Diffusion Osmosis And Active Transport
The Cell Membrane Diffusion Osmosis And Active Transport
 Human Anatomy And Physiology Diffusion And Transport
Human Anatomy And Physiology Diffusion And Transport
 Simple Diffusion Definition And Examples Biology Dictionary
Simple Diffusion Definition And Examples Biology Dictionary
 Facilitated Diffusion Definition Process Examples
Facilitated Diffusion Definition Process Examples
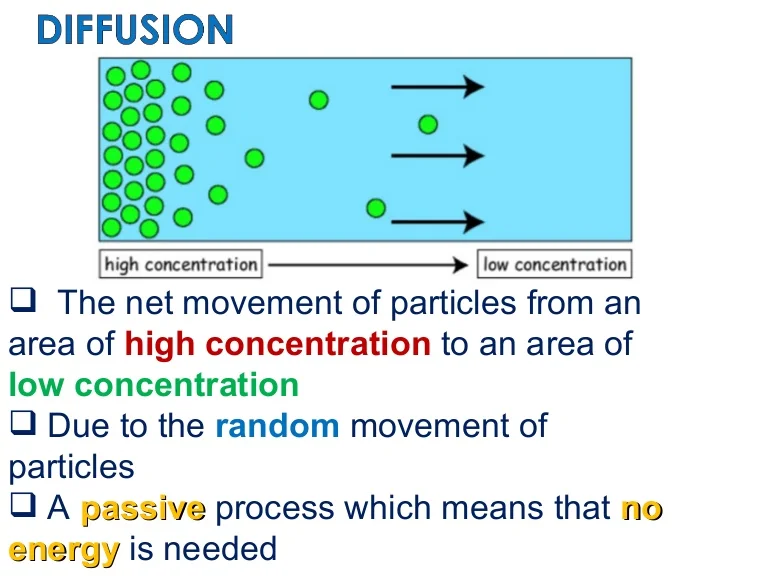 Biological Examples Of Diffusion
Biological Examples Of Diffusion
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/facilitated_diffusion-56cdd5033df78cfb37a3460c.jpg) Diffusion Passive Transport And Facilitated Diffusion
Diffusion Passive Transport And Facilitated Diffusion
 Gas Exchange Anatomy And Physiology Ii
Gas Exchange Anatomy And Physiology Ii
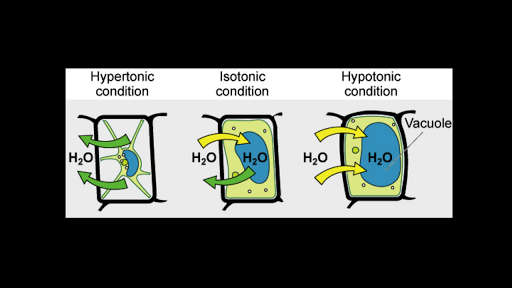
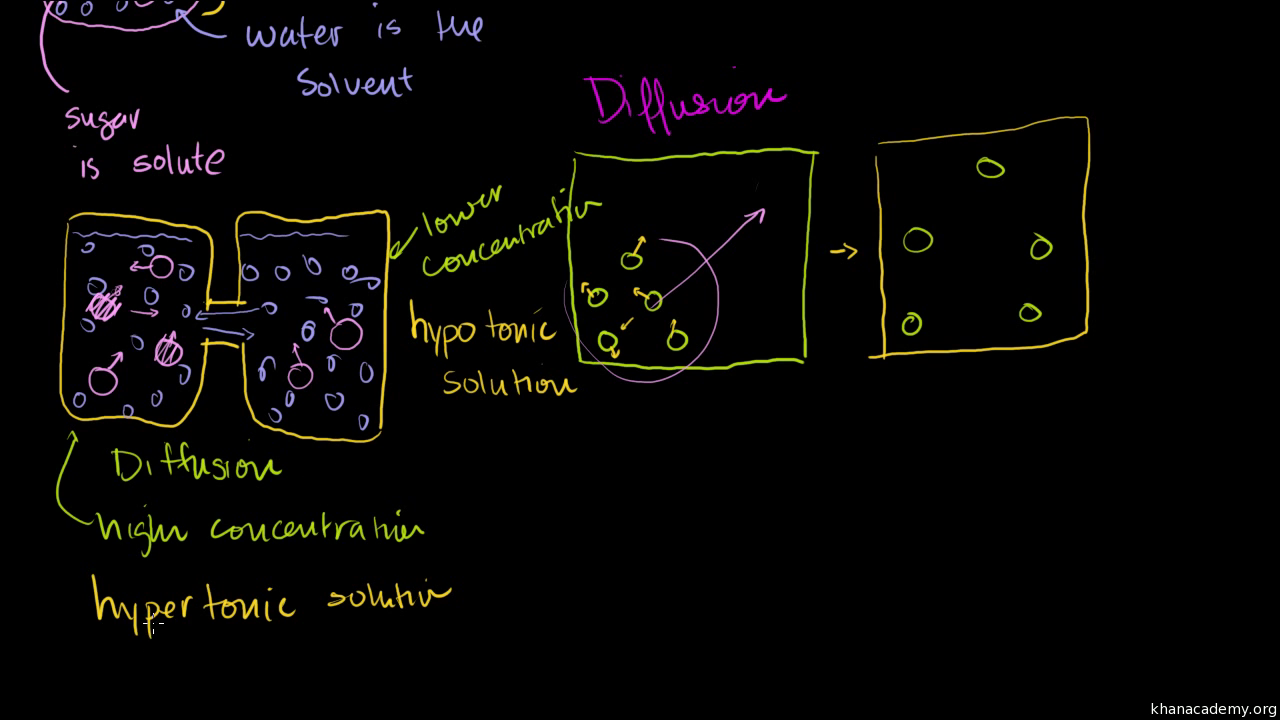
 Isotonic Vs Hypotonic Vs Hypertonic Solution Biology
Isotonic Vs Hypotonic Vs Hypertonic Solution Biology
 Carrier Protein Definition Function And Examples
Carrier Protein Definition Function And Examples
 Diffusion Definition Examples And Types Biology Dictionary
Diffusion Definition Examples And Types Biology Dictionary
 Anatomy And Physiology I Biology 65c With Carr At Harvard
Anatomy And Physiology I Biology 65c With Carr At Harvard
 Diffusion Cell Transport Mrs Paez Anatomy Physiology
Diffusion Cell Transport Mrs Paez Anatomy Physiology
What Is The Difference Between Osmosis And Diffusion Socratic
 Ch 3 Anatomy Flashcards Quizlet
Ch 3 Anatomy Flashcards Quizlet

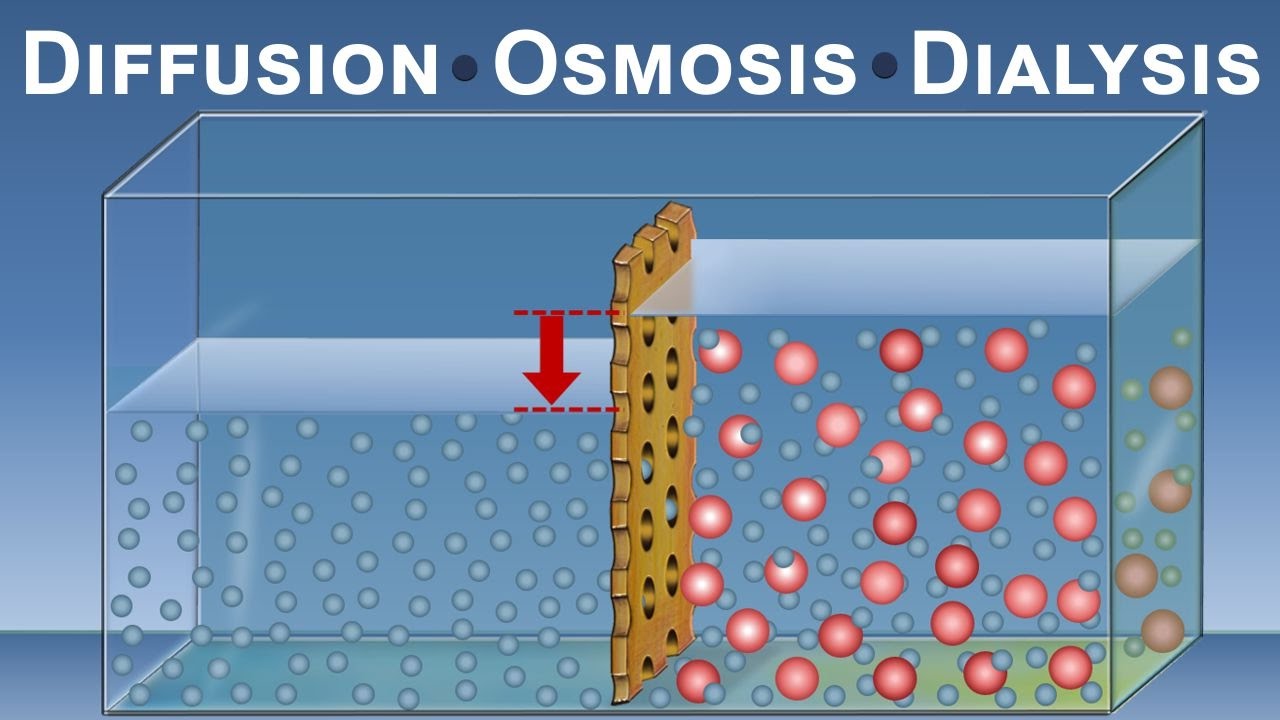 Diffusion Osmosis And Dialysis Iqog Csic
Diffusion Osmosis And Dialysis Iqog Csic
 What Is The Definition Of Diffusion Socratic
What Is The Definition Of Diffusion Socratic
 Passive Transport Anatomy And Physiology I
Passive Transport Anatomy And Physiology I
 What Are The Two Main Types Of Diffusion Osmosis
What Are The Two Main Types Of Diffusion Osmosis
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-112706652-58980a3c5f9b5874eed738d1.jpg) Defining Active And Passive Transport
Defining Active And Passive Transport
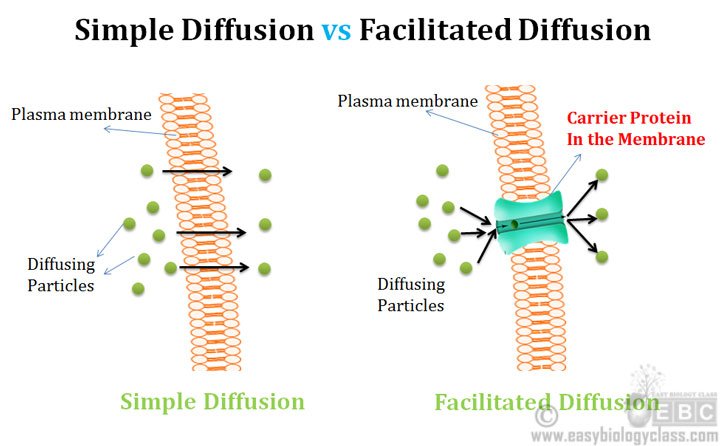 Difference Between Simple And Facilitated Diffusion
Difference Between Simple And Facilitated Diffusion
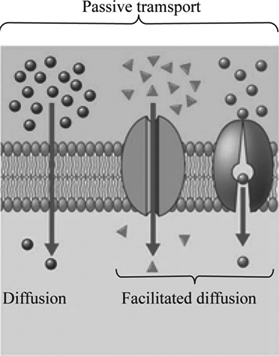 Definition Of Facilitated Diffusion Chegg Com
Definition Of Facilitated Diffusion Chegg Com


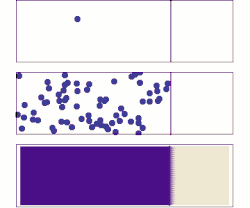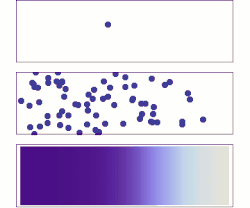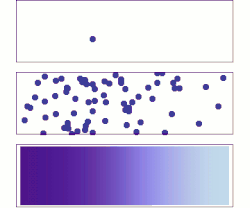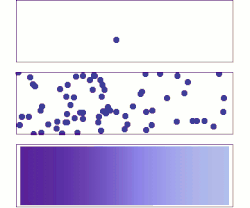
/diffusion-58e6ad0a5f9b58ef7e0e1a60.jpg)
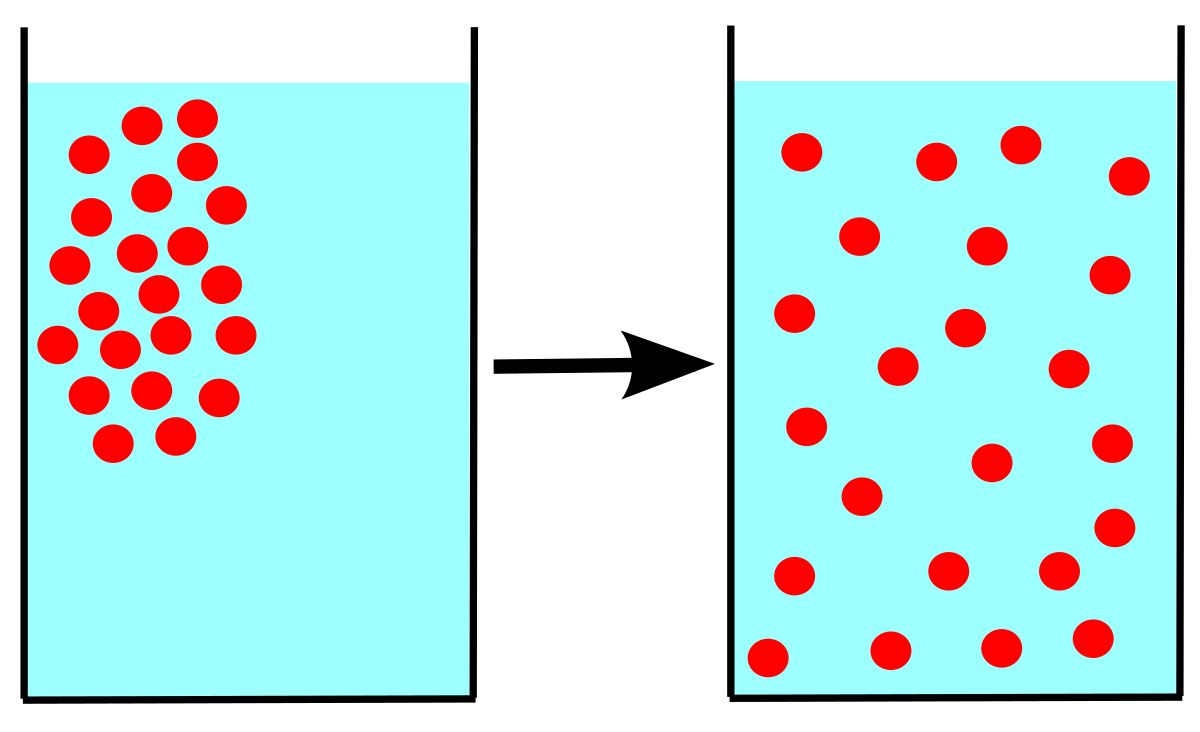

Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar