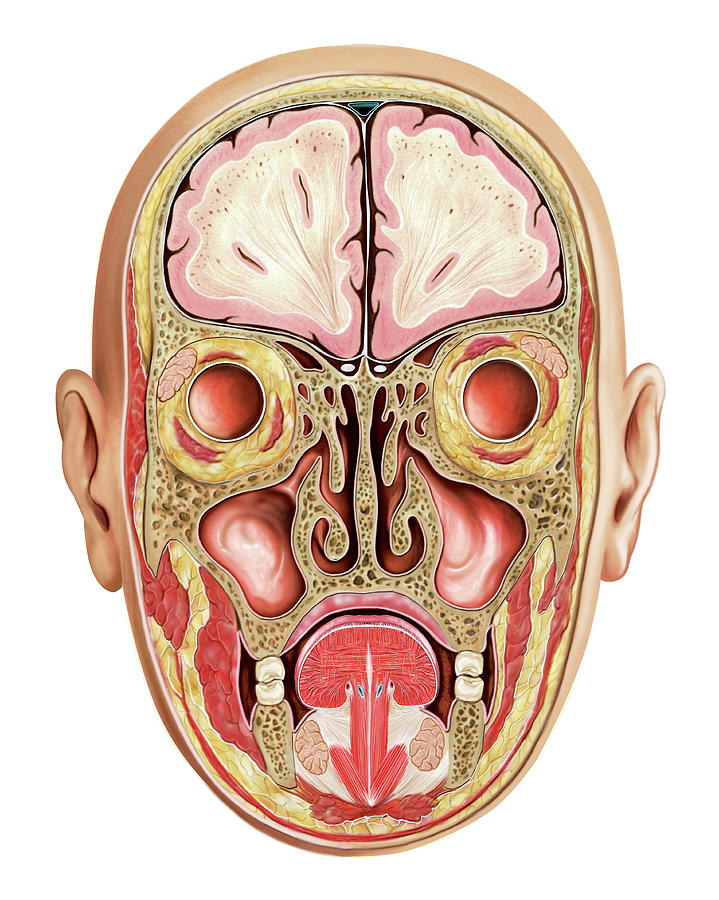
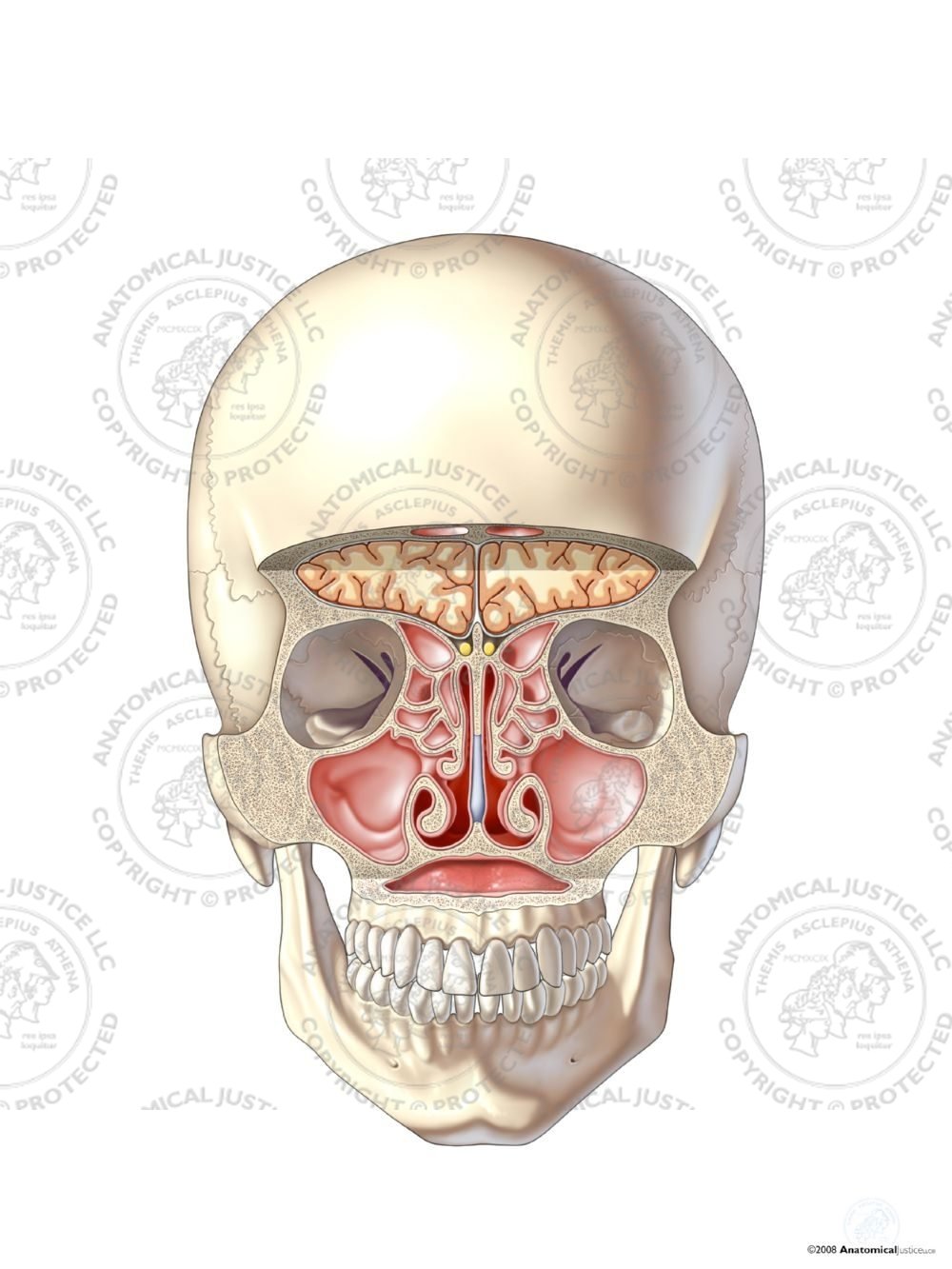
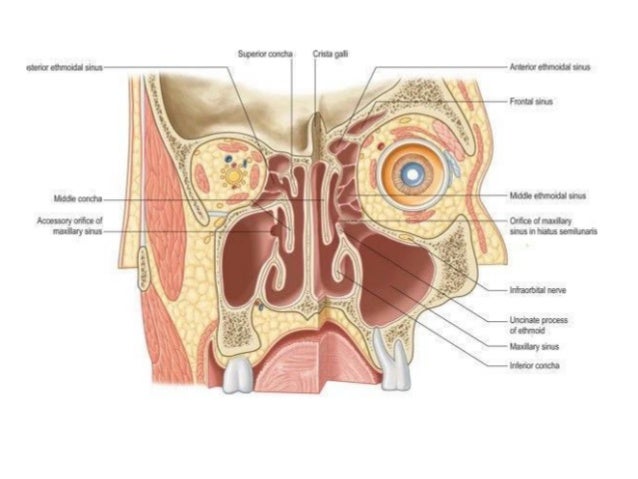
Ethmoid air cells sinuses. Humans possess four paired paranasal sinuses divided into subgroups that are named according to the bones within which the sinuses lie.
 Anatomy And Diagnostic Imaging Of The Equine Paranasal
Anatomy And Diagnostic Imaging Of The Equine Paranasal
Protection of internal cranial structures maintaining structural strength without a significant increase in weight augmenting vocalisation.

Paranasal sinus anatomy. External nose it is pyramidal in shape with its root up and the base directed downwards nares external opening of nose choanae open into the nasopharynx 1. Your cheekbones hold your maxillary sinuses the. Where are the paranasal sinuses situated.
The maxillary sinuses are the largest of the all the paranasal sinuses. Sphenoid sinus within the sphenoid bones. Histology of the nose and paranasal sinuses.
What are the paranasal sinuses a formation from. Anatomy of the equine paranasal sinuses. If more than one sinus is affected it is called pansinusitis.
The most posterior of all the paranasal sinuses these are located behind the ethmoid sinuses near the pituitary gland and optic nerves 8. They have thin walls which are often penetrated by the long roots of the posterior maxillary teeth. Paranasal sinuses frontal sinuses.
Posterior 13rd is bony 1. The nasal cavity and all paranasal sinuses are lined by respiratory pseudostratified epithelium except areas of the roof of the cavity most superior part of nasal septum and the medial part of superior turbinate are lined by mucosa that contains receptors for the smell sensation known as olfactory area. The nasal septum separates the left and right maxillary sinuses 9.
From the nasal mucosa and their continued communication with the nasal fossae. External nose internal nose musculature of nose vascular supply nervous innervation and lymphatic drainage paranasal sinuses 3. The largest sinus cavities are about an inch across.
In the frontal ethmoid and sphenoid of the cranium and the maxillary bones of the face. The frontal sinuses superior to the eyes in the frontal bone. The paranasal sinuses of mammals form complex air filled structures and probably exist for a variety of functions including but not exhaustively.
The maxillary sinuses the largest of the paranasal sinuses are under the eyes. Others are much smaller. As the paranasal sinuses are continuous with the nasal cavity an upper respiratory tract infection can spread to the sinuses.
Infection of the sinuses causes inflammation particularly pain and swelling of the mucosa and is known as sinusitis. The superior border of this sinus is the bony orbit the inferior is the maxillary alveolar bone and corresponding tooth roots. The sinuses are a connected system of hollow cavities in the skull.
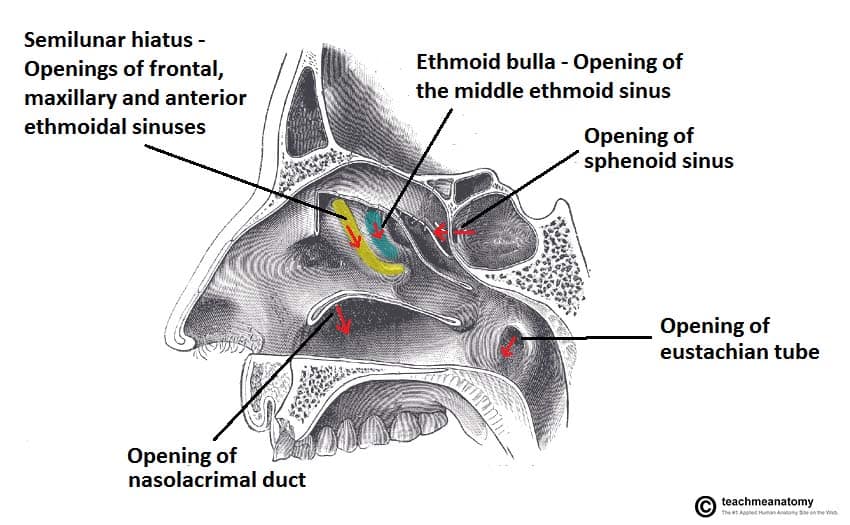 The Nasal Cavity Structure Vasculature Innervation
The Nasal Cavity Structure Vasculature Innervation
 Paranasal Sinus Anatomy What The Surgeon Needs To Know
Paranasal Sinus Anatomy What The Surgeon Needs To Know
 Nose And Paranasal Sinuses Clinical Gate
Nose And Paranasal Sinuses Clinical Gate

 Acute Sinusitis A Cost Effective Approach To Diagnosis And
Acute Sinusitis A Cost Effective Approach To Diagnosis And
 Paranasal Sinus An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Paranasal Sinus An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
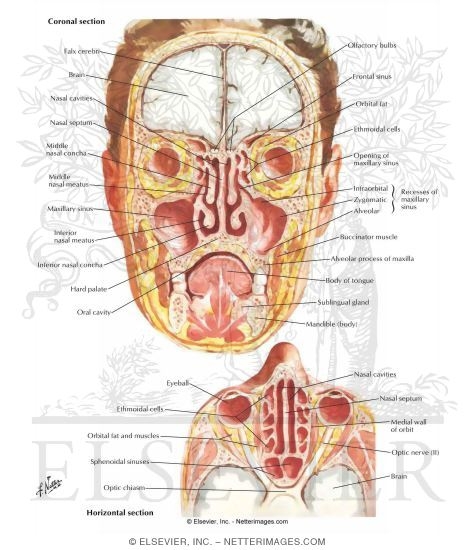 Paranasal Sinuses Nasal Allergy
Paranasal Sinuses Nasal Allergy
 Anatomy Of The Paranasal Sinuses
Anatomy Of The Paranasal Sinuses
 Human Anatomy Sinus Diagram Anatomy Of The Nose Nasal Cavity
Human Anatomy Sinus Diagram Anatomy Of The Nose Nasal Cavity
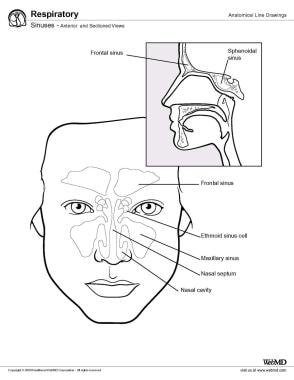 Paranasal Sinus Anatomy Overview Gross Anatomy
Paranasal Sinus Anatomy Overview Gross Anatomy
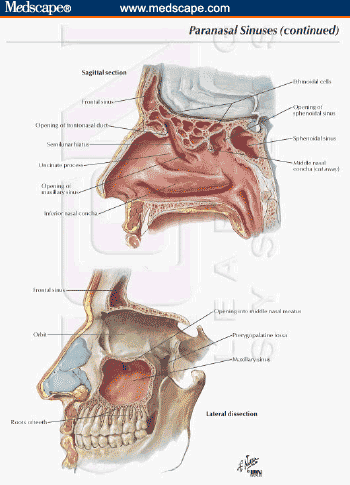 A Practical Approach To The Patient With Sinusitis
A Practical Approach To The Patient With Sinusitis
 The Hidden Anatomy Of Paranasal Sinuses Reveals
The Hidden Anatomy Of Paranasal Sinuses Reveals
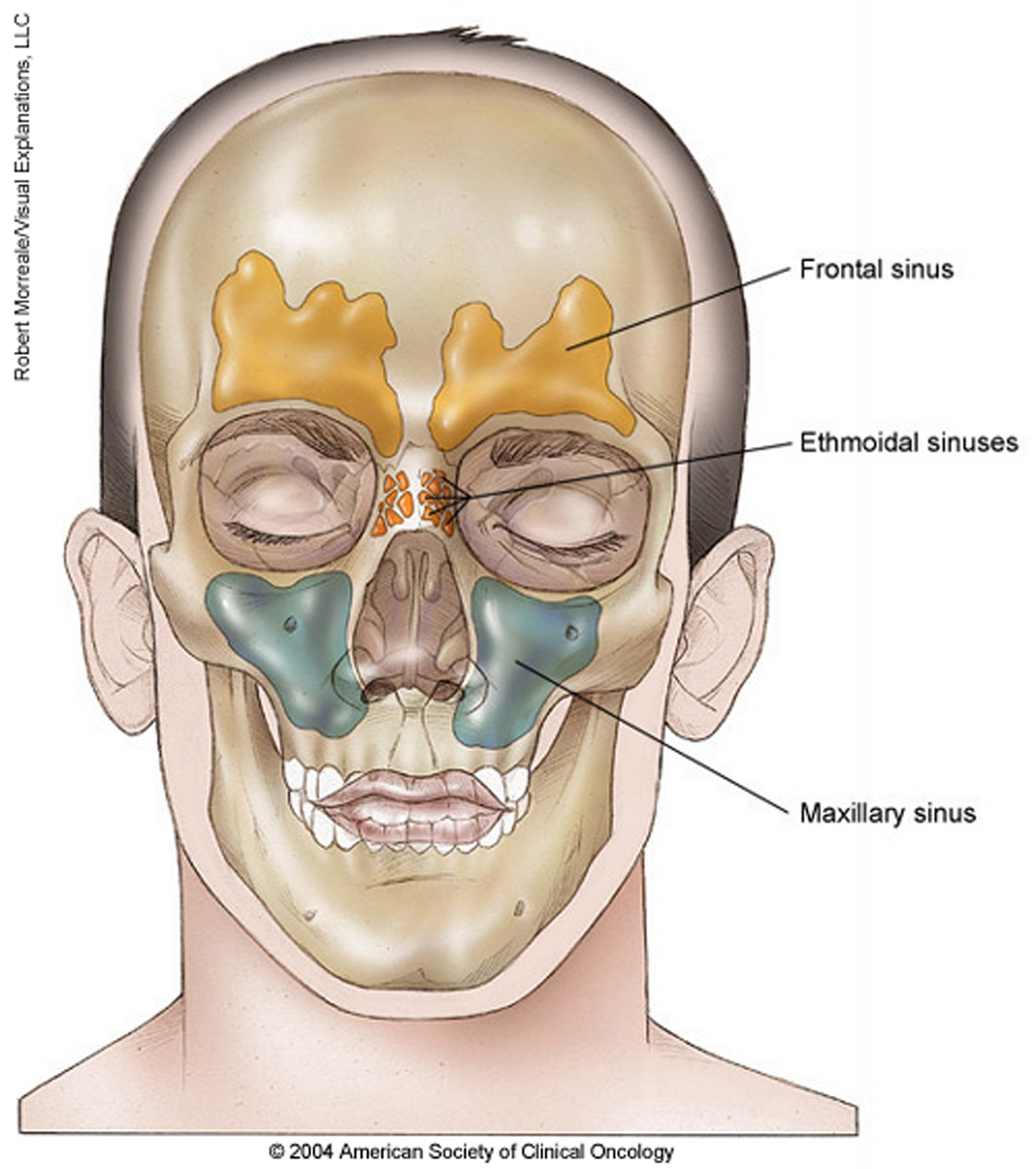 Nasal Cavity And Paranasal Sinus Cancer Cancer Net
Nasal Cavity And Paranasal Sinus Cancer Cancer Net
 Chapter 23 Nasal Cavity The Big Picture Gross Anatomy
Chapter 23 Nasal Cavity The Big Picture Gross Anatomy
 Alison Burke Anatomy Of Paranasal Sinuses And Nasal Passages
Alison Burke Anatomy Of Paranasal Sinuses And Nasal Passages
 Staging Of Nasal Cavity And Paranasal Sinus Cancer
Staging Of Nasal Cavity And Paranasal Sinus Cancer
 Figure Anatomy Of The Paranasal Sinuses Spaces Between The
Figure Anatomy Of The Paranasal Sinuses Spaces Between The
 Paranasal Sinus Cavities Acland S Video Atlas Of Human Anatomy
Paranasal Sinus Cavities Acland S Video Atlas Of Human Anatomy
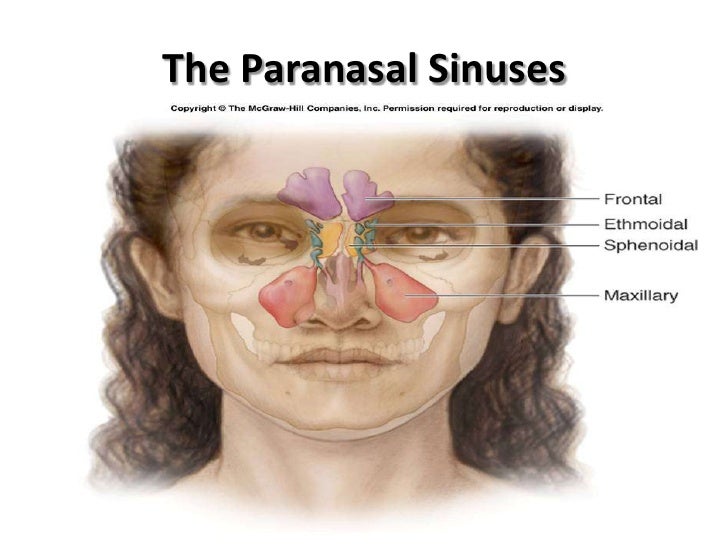 Anatomy Of Nose And Paranasal Sinus
Anatomy Of Nose And Paranasal Sinus
 Nose Anatomy Model With Paranasal Sinuses
Nose Anatomy Model With Paranasal Sinuses
 Surgical Anatomy Of The Paranasal Sinus Ento Key
Surgical Anatomy Of The Paranasal Sinus Ento Key

:watermark(/images/watermark_only.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/maxillary-sinus/TRlfyyApMhY8iJdinFDaA_maxillary_sinus.png) Paranasal Sinuses Anatomy And Clinical Aspects Kenhub
Paranasal Sinuses Anatomy And Clinical Aspects Kenhub
Paranasal Sinuses Human Anatomy Organs


Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar