Orbit anatomy in anatomy the orbit is the cavity or socket of the skull in which the eye and its appendages are situated. In general the globe and orbital contents are supplied from the extensions of the internal carotid via the ophthalmic artery.
 Anatomy And Pathology Of The Orbits
Anatomy And Pathology Of The Orbits
The orbit which protects supports and maximizes the function of the eye.

The orbit anatomy. The orbit and its contents have a rich blood supply coming from both the internal and the external carotid systems. Bones of the orbit by definition the orbit bony orbit or orbital cavity is a skeletal cavity comprised of seven bones situated within the skull. Pathways into the orbit.
Inferior orbital fissure lies between. If you continue browsing the site you agree to the use of cookies on this website. Fig 11 diagram of the arterial supply to the eye.
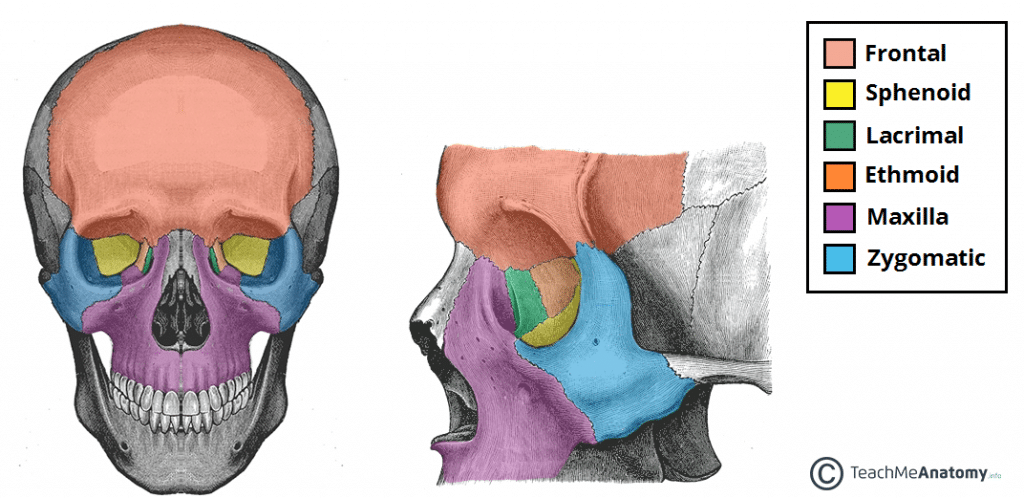
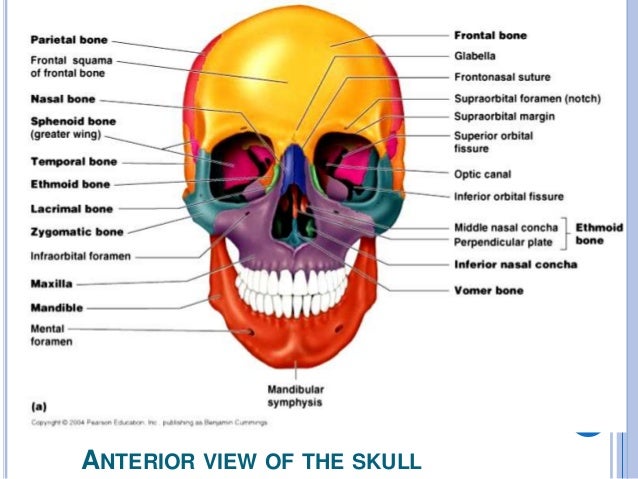
The cranium is the major portion and it consists of three unpaired bones the sphenoid occipital and ethmoid bones and three paired bones the frontal parietal and temporal bones. In the adult human the volume of the orbit is 30 millilitres 106 imp fl oz. The contents of the orbit are separated and supported by multiple.
A clinical perspective in conjunction with anatomy of orbit a clinical perspective in conjunction with anatomy of orbit slideshare uses cookies to improve functionality and performance and to provide you with relevant advertising. Orbital process of the frontal bone orbital process of the zygomatic bone. Orbit can refer to the bony socket or it can also be used to imply the contents.
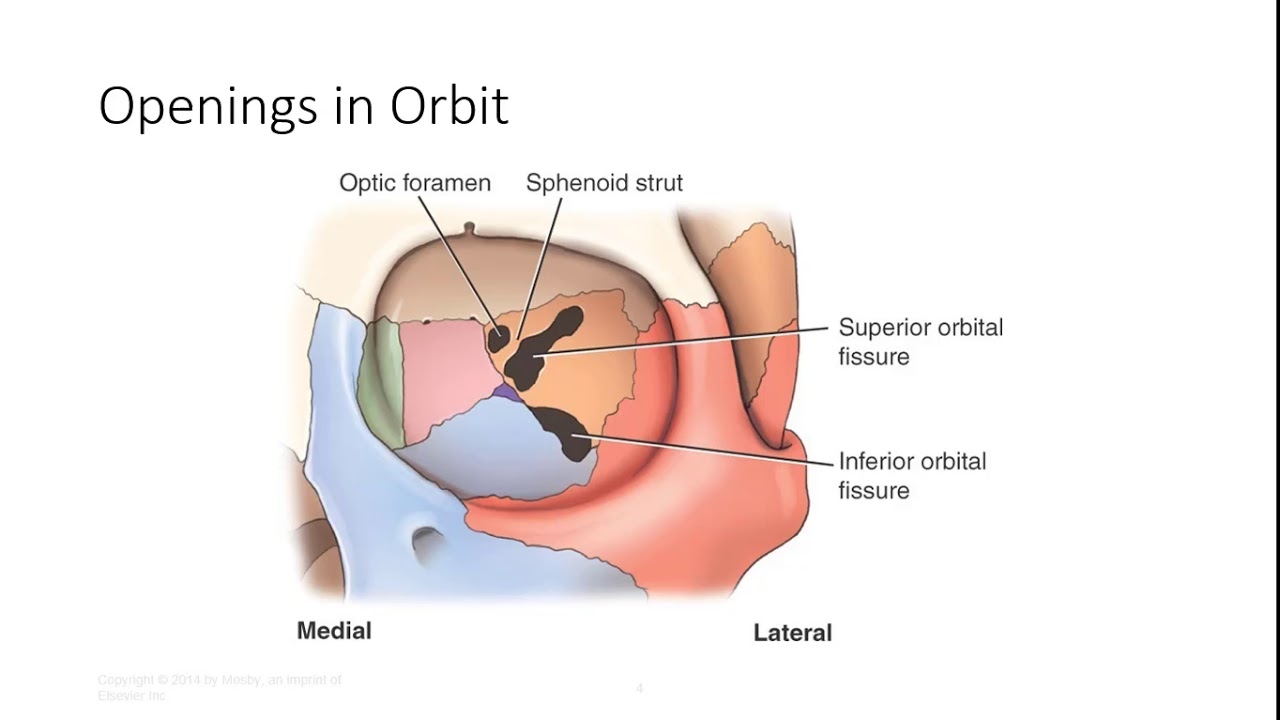
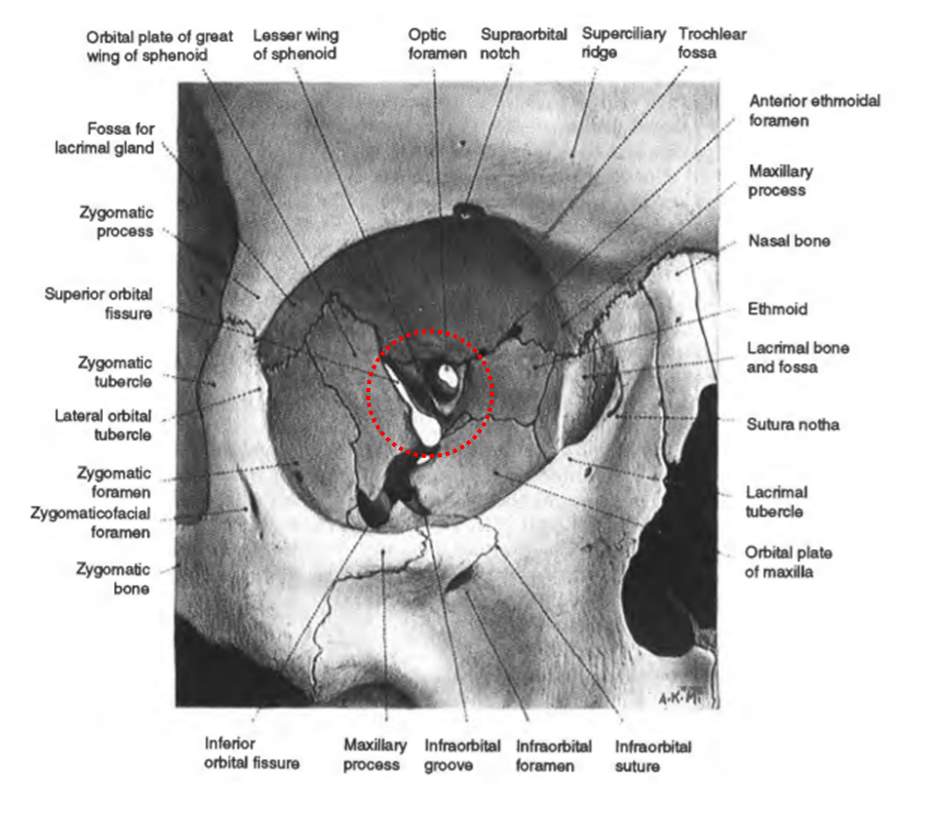
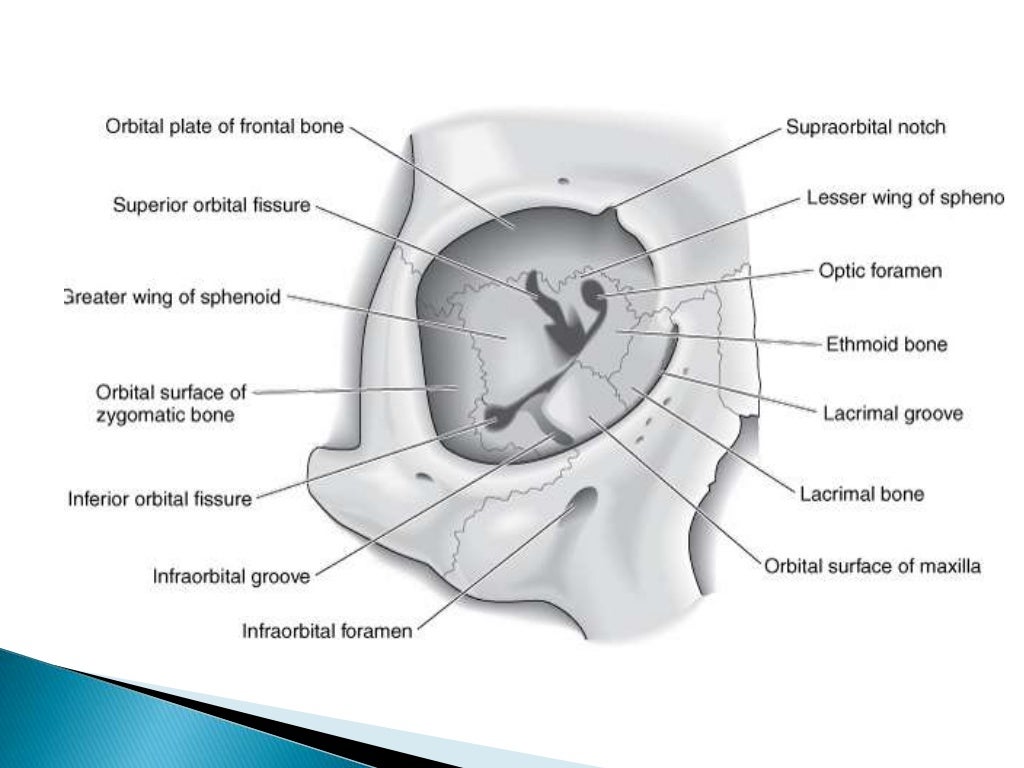
The orbit can be thought of as a pyramidal structure. Superior orbital fissure lies between the lesser and the greater wing of sphenoid. This fissure allows the passage to the nerves iii iv vi branches of the v1 and ophthalmic veins.
The bony orbit borders and anatomical relations. The cavity surrounds and provides mechanical protection for the eye and soft tissue structures related to it. Anatomy of the orbit the skull is composed of two segments the cranium and the face.
Fig 12 the major openings into the orbit. Orbit to ophthalmic veins that communicate facial vein to the cavernous sinus drainage of the eyelid is to the parotid nodes and some to the submandibular nodes. 101 us fl oz.
The lacrimal system produces distributes and drains tears.
 Figure 4 From Surgical Orbital Anatomy Semantic Scholar
Figure 4 From Surgical Orbital Anatomy Semantic Scholar
 Regional Anatomy The Orbit At Texas Woman S University
Regional Anatomy The Orbit At Texas Woman S University
 The Orbital Complex Of The Skull Orbit Anatomy Body
The Orbital Complex Of The Skull Orbit Anatomy Body

Anatomy 9 Vasculature Of Orbit Anatomy 9 Orbit And Its
 Normal Orbital Anatomy Axial Computed Tomographic Ct
Normal Orbital Anatomy Axial Computed Tomographic Ct
 Anatomy Of The Orbit Illustration By Jennifer Thomson Phd
Anatomy Of The Orbit Illustration By Jennifer Thomson Phd
 Figure 1 From Surgical Orbital Anatomy Semantic Scholar
Figure 1 From Surgical Orbital Anatomy Semantic Scholar
Orbital Compartment Syndrome Curriculum
 The Bony Orbit Borders Contents Fractures Teachmeanatomy
The Bony Orbit Borders Contents Fractures Teachmeanatomy
 The Anatomy Of The Orbit Ppt Download
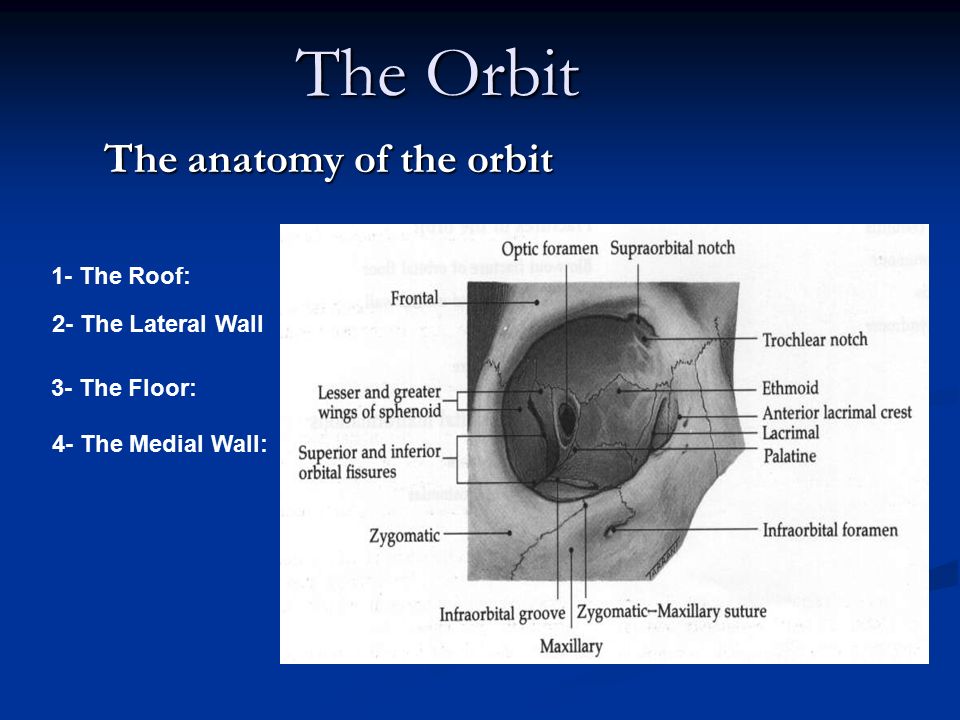
The Anatomy Of The Orbit Ppt Download
Anatomy Of Orbit And Clinical Aspect Of Orbital Disease
 Orbits And Eyes Anatomical Illustrations
Orbits And Eyes Anatomical Illustrations
Anatomy Of Orbit And Clinical Aspect Of Orbital Disease
 Ppt Anatomy And Diseases Of The Orbit Powerpoint
Ppt Anatomy And Diseases Of The Orbit Powerpoint
 Anatomy Of The Orbit Vessels And Nerves
Anatomy Of The Orbit Vessels And Nerves
 The Orbit Anatomy Flashcards Quizlet
The Orbit Anatomy Flashcards Quizlet
 Anatomy Of The Posterior Orbit And Orbital Apex
Anatomy Of The Posterior Orbit And Orbital Apex
 Vision Anatomy And Physiology I
Vision Anatomy And Physiology I
 Microsurgical Anatomy Of The Orbit The Rule Of Seven Figure 8
Microsurgical Anatomy Of The Orbit The Rule Of Seven Figure 8
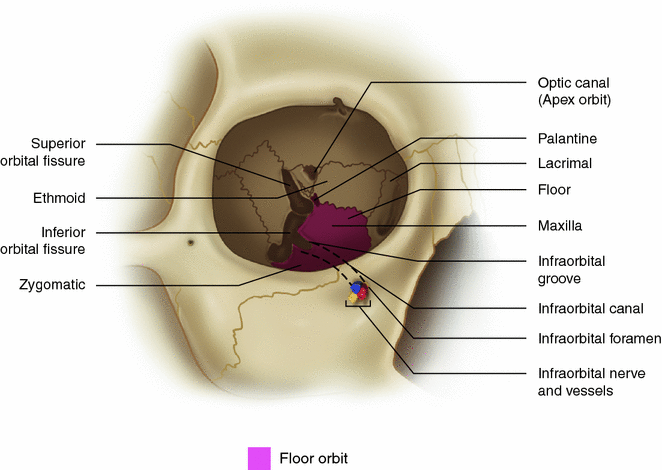 Anatomy Of The Orbit Springerlink
Anatomy Of The Orbit Springerlink
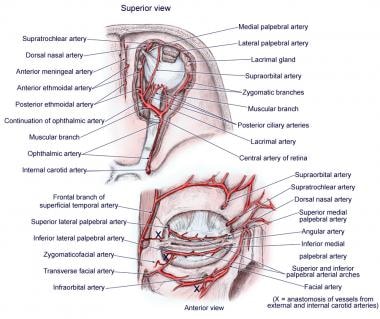 Orbit Arterial Supply Overview The Arterial System The
Orbit Arterial Supply Overview The Arterial System The



Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar