Anatomy of the jaw in regards to jaw anatomy the major joint in the jaw is the temporomandibular joint tmj which connects the lower jaw to the skull temporal bone under the ear. Lymph nodes line the cervical spine and neck regions as well as along the face and jaw.
 Yoga Anatomy Forward Head Posture Part 1 Yogauonline
Yoga Anatomy Forward Head Posture Part 1 Yogauonline
The anatomy and physiology of the cervical neck spine is explained and sheds light on why movements of the lower jaw mandible affect neck posture and how neck posture affects lower jaw position.
Anatomy of jaw and neck. Primary muscle discomfort is not really common but overuse as in chewing gum or in south africa biltong in association with disc malfunction can commonly causes jaw facial and sometimes neck pain as well as headache. Anatomy of the skull. The tonsils also are lymphatic tissue and help mediate the ingestion of pathogens.
The neck is the thinner portion of the condyloid process that projects from the ramus. There are three kinds of tmj anatomy pain. Some physicians associate disorder in this joint with tiny myofascial trigger points or contractions knots in the overworked or traumatized jaw muscles.
At the angle of the jaw some of the fibres insert into the bone of the mandible. Interestingly this is the only bony insertion. All the bones of the skull except the lower jaw the mandible are fixed to each other by immovable joints called sutures.
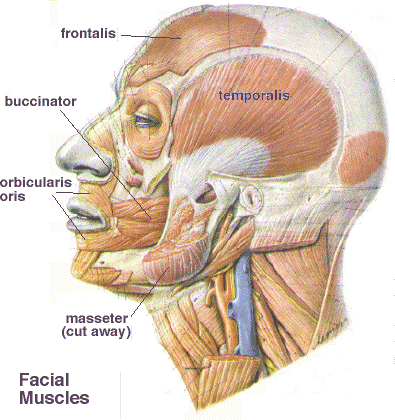
The platysma is a large flat cutaneous muscle which stretches from the upper chest all the way to the mid cheek. It arises from the pectoralis muscle with the fibres ascending upwards. The condyloid process is also located at the superior aspect of the ramus and is divided into two parts the neck and the condyle.
The lymphatic system drains the head and neck of excess interstitial fluid via lymph vessels or capillaries equally into the right lymphatic duct and the thoracic duct. Jaws the upper and lower jaws of the oral cavity supporting the teeth and the tongue and providing the openings for the respiratory tract and the digestive tract. The condyle is the most superior portion and contributes to the temporomandibular junction by articulating with the articular disk.
 Movements Of The Jaw Conscious Movements
Movements Of The Jaw Conscious Movements
 Diagnosis And Treatment Of Temporomandibular Disorders
Diagnosis And Treatment Of Temporomandibular Disorders
 14 Triangles Of The Neck And Root Of The
14 Triangles Of The Neck And Root Of The
 Angle Of The Mandible An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Angle Of The Mandible An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
 Mandibular Nerve An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Mandibular Nerve An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
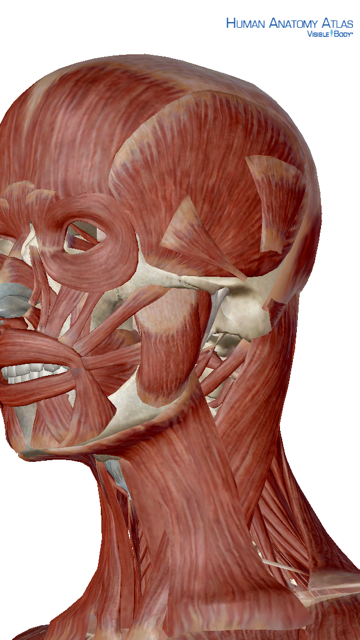
Superficial Muscles Of The Neck Human Anatomy
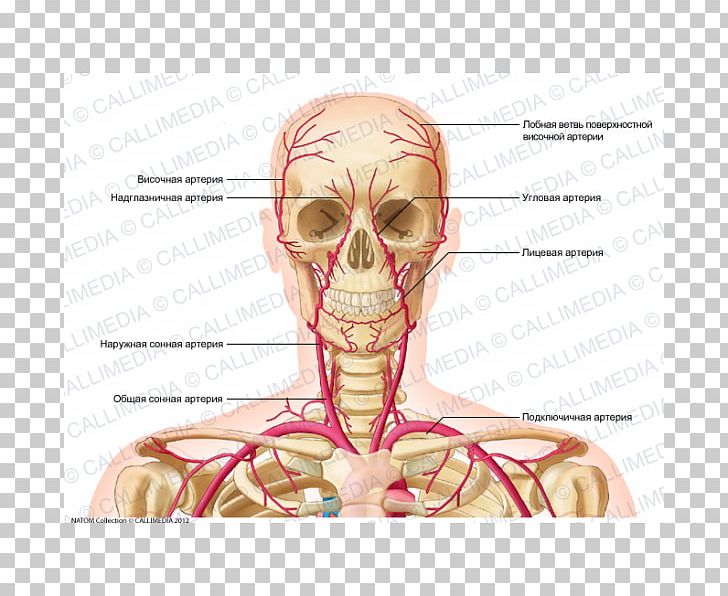 Supratrochlear Artery Head And Neck Anatomy Vein Human Body
Supratrochlear Artery Head And Neck Anatomy Vein Human Body
 The Lymphatics Of The Head Face And Neck Human Anatomy
The Lymphatics Of The Head Face And Neck Human Anatomy
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/12550/HeadCadavar.png) Temporal Muscle Anatomy Function And Innervation Kenhub
Temporal Muscle Anatomy Function And Innervation Kenhub
 Tmd A Pain In The Jaw And Neck Uconn Today
Tmd A Pain In The Jaw And Neck Uconn Today
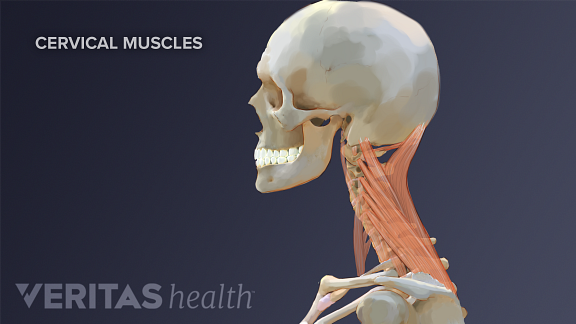 Neck Strain Causes And Remedies
Neck Strain Causes And Remedies
 Head And Neck Muscles Boundless Anatomy And Physiology
Head And Neck Muscles Boundless Anatomy And Physiology
 Neck Cancer Anatomy Headandneckcancerguide Org
Neck Cancer Anatomy Headandneckcancerguide Org
 The Veins Of The Head And Neck Human Anatomy
The Veins Of The Head And Neck Human Anatomy
 What Is Happening When You Have A Swelling Under Your Jaw
What Is Happening When You Have A Swelling Under Your Jaw
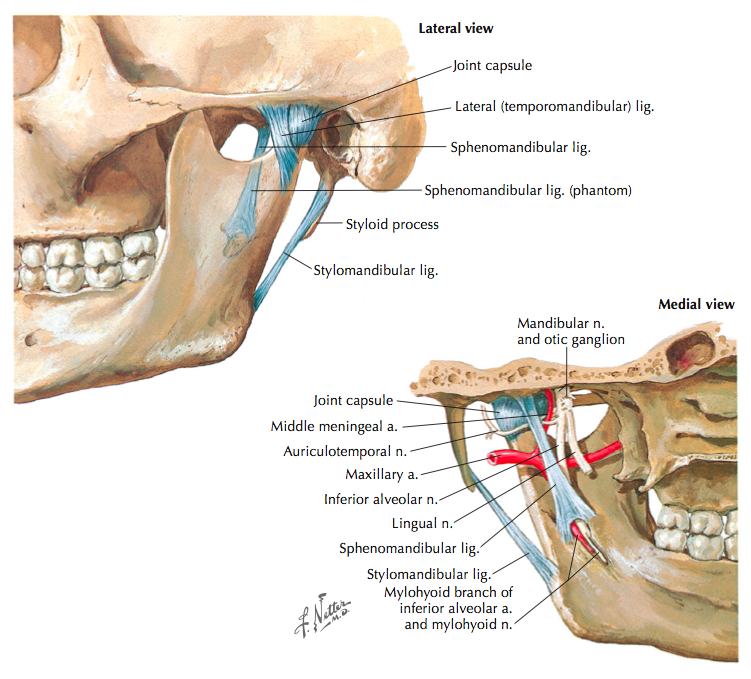 Temporomandibular Joint Disorders Clinical Anatomy
Temporomandibular Joint Disorders Clinical Anatomy
 Normal Anatomy Of The Jaw This Lateral View Of The Skull
Normal Anatomy Of The Jaw This Lateral View Of The Skull
 Details About 1879 Antique Folio Engraving Muscles Of Jaw Back Neck Anatomy Decor Gift
Details About 1879 Antique Folio Engraving Muscles Of Jaw Back Neck Anatomy Decor Gift
 Tmj Jaw Pain T O P S Physical Therapy
Tmj Jaw Pain T O P S Physical Therapy
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/10668/main-bones-of-skull_english__1_.jpg) Head And Neck Anatomy Structures Arteries And Nerves Kenhub
Head And Neck Anatomy Structures Arteries And Nerves Kenhub
 How Meningitis Causes Neck Pain And Stiffness
How Meningitis Causes Neck Pain And Stiffness
 When You Have Temporomandibular Disorder Tmd
When You Have Temporomandibular Disorder Tmd
 Jaw Anatomy Langford Karls Chiropractic Clinic
Jaw Anatomy Langford Karls Chiropractic Clinic
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-670890563-5b6d0e6a46e0fb0050e8b985.jpg) The Hyoid Bone Anatomy Function And Conditions
The Hyoid Bone Anatomy Function And Conditions





Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar