The thalamus lies at the core of the diencephalon. There are areas of white matter in the thalamus including the stratum zonale that covers the dorsal surface and the external and internal medullary laminae.
 Anatomical Illustrations Chelseacanlas
Anatomical Illustrations Chelseacanlas
The anterior end of the thalamus is rounded and narrow which forms the posterior boundary.
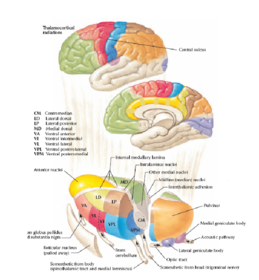
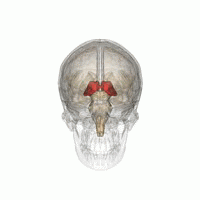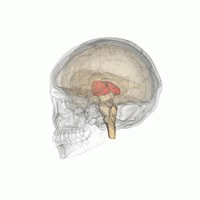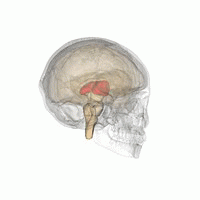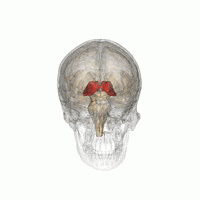
Anatomy of the thalamus. The posterior end of the thalamus is expanded to form the pulvinar. The thalamus separating it into medial and lateral nuclear masses. Thalamus plural thalami either of a pair of large ovoid organs that form most of the lateral walls of the third ventricle of the brain.
The medial surface. The thalamus has four surfaces medial lateral superior and inferior surface and it has two ends or poles anterior and posterior. The thalamus is a limbic system structure and it connects areas of the cerebral cortex that are involved in sensory perception and movement with other parts of the brain and spinal cord that also have a role in sensation and movement.
In addition to the tracts mentioned above. The inferior surface of the thalamus is continuous with the tegmentum of the midbrain. Nuclei in a given pole or surface regulate specific functions or processing of sensory information and maintain particular connections with parts of the nervous and limbic system.
In the rostral part of the thalamus the internal medullary lamina splits to form a partial capsule around the anterior nuclear group. Anatomy of the thalamus the thalamus has two ends the anterior and posterior poles and four surfaces. Medial lateral superior and inferior.
As a regulator of sensory information the thalamus also controls sleep and awake states of consciousness. The external lamina covers the lateral surface and the internal lamina divides the nuclei into anterior medial and lateral groups. In addition to being divided into anterior.
The lateral mass contains the lateral nuclear group and the ventral nuclear group. The medial mass consists of the medial nuclear group. Thalamus anatomy the thalamus a paired structure walnut sized shaped of grey matter found in the forebrain that is superior to the midbrain roughly the middle of the brain.
The thalamus translates neural impulses from various receptors to the cerebral cortex. The thalamus is made up of two symmetrical structures formed from the diencephalon. Anatomy of the thalamus.

Basic Structure Of The Thalamus Interactive Biology With
 Thalamus Anatomy Location Structure Function Physiology
Thalamus Anatomy Location Structure Function Physiology
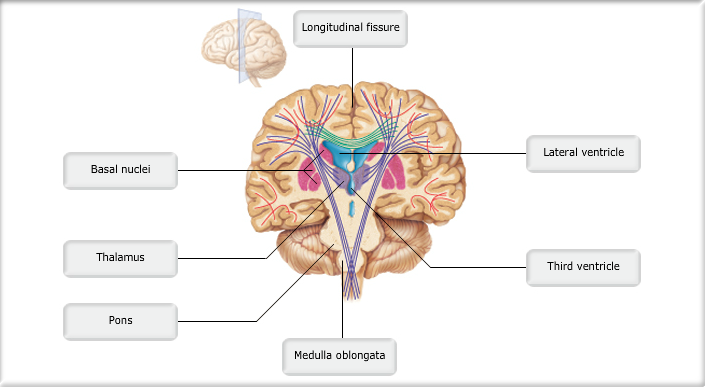 Print Anatomy And Physiology 1 Chapter 12 Flashcards Easy
Print Anatomy And Physiology 1 Chapter 12 Flashcards Easy
 What Is Thalamus And How It Looks Like
What Is Thalamus And How It Looks Like
 2 Minute Neuroscience The Thalamus
2 Minute Neuroscience The Thalamus
:watermark(/images/watermark_only.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/thalamus-2/tzYsVOwqBQl8IeNka2uPpw_Thalamus_01.png) Thalamic Nuclei Connections Functions And Anatomy Kenhub
Thalamic Nuclei Connections Functions And Anatomy Kenhub
 Detailed Anatomy Of The Human Brain Illustration Showing The
Detailed Anatomy Of The Human Brain Illustration Showing The
 Brain Anatomy Thalamus Photos 1 931 Brain Anatomy Stock
Brain Anatomy Thalamus Photos 1 931 Brain Anatomy Stock
 Thalamus Anatomy Physiology Applied Aspects
Thalamus Anatomy Physiology Applied Aspects
 Thalamus Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock
Thalamus Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock
 Thalamus Facts Position In Brain Summary Function
Thalamus Facts Position In Brain Summary Function
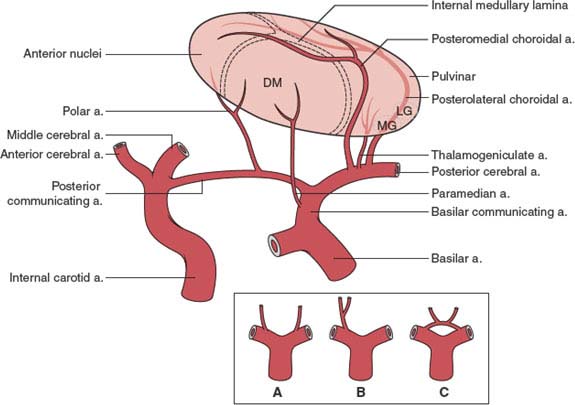 The Anatomic Localization Of Lesions In The Thalamus
The Anatomic Localization Of Lesions In The Thalamus
 Thalamus Hypothalamus Flashcards
Thalamus Hypothalamus Flashcards
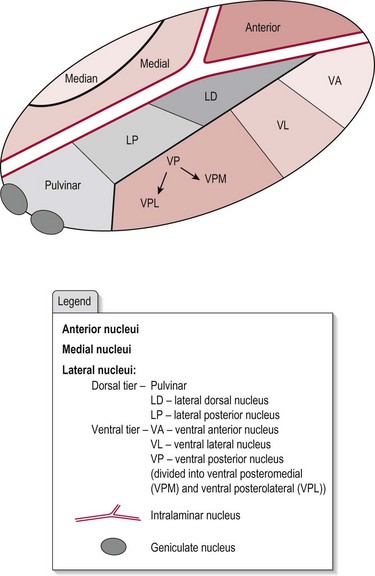 Thalamus And Limbic System Neupsy Key
Thalamus And Limbic System Neupsy Key
 Brain Anatomy Stroke Emergency Care And Rehabilitation
Brain Anatomy Stroke Emergency Care And Rehabilitation
:watermark(/images/watermark_5000_10percent.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/atlas_overview_image/130/rbUGADBqRfwtHiT9LRPSmw_coronal-section-brain-thalamus-level_english__1_.jpg) Diagram Pictures Coronal Section Of The Brain At The
Diagram Pictures Coronal Section Of The Brain At The
 Median Section Of Human Brain Anatomical Structure
Median Section Of Human Brain Anatomical Structure
 Anatomy Of The Intralaminar And Medial Thalamic Nuclei And
Anatomy Of The Intralaminar And Medial Thalamic Nuclei And



Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar