The rectum is a continuation of the sigmoid colon and connects to the anus. An endoscope is inserted into the anus and the entire colon is viewed to look.
 Cross Section Rectum Anal Canal Showing Royalty Free Stock
Cross Section Rectum Anal Canal Showing Royalty Free Stock
Structure the upper 23 has longitudinal folds or elevations of tunica mucosa.
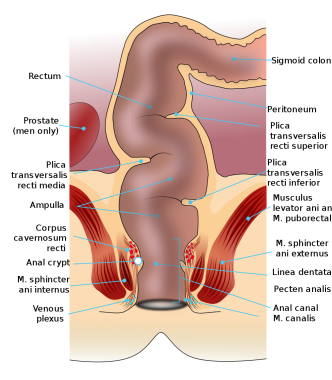
Anus anatomy. The lower 13 of the anal canal is lined by stratified squamous epithelium that blends with the skin. Gross anatomy at the level of the s3 vertebral body the sigmoid colon loses its mesentery and becomes the rectum. Its mucosa is lined by simple columnar epithelium.
The anal canal is the most terminal part of the lower gi tractlarge intestine which lies between the anal verge anal orifice anus in the perineum below and the rectum above. The description in this topic is from below upwards as that is how this region is usually examined in clinical practice. The rectum is the most distal segment of the large intestine and has an important role as a temporary store of faeces.
In this article we will discuss the anatomy of the rectum its structure anatomical relationships and clinical relevance. It is also sinuous with three alternating bends when viewed anteriorly. The lower third of the anal canal is supplied by.
As the rectum passes in front of the sacrum it takes an ap concave shape. Anus tests physical examination. The rectum is continuous with the sigmoid colon and extends 13 to 15 cm 5 to 6 inches to the anus.
Rectum terminal segment of the digestive system in which feces accumulate just prior to discharge. The anus is the opening to the lower gastrointestinal gi tract and connects to the rectum which connects to the colon which traveling backwards connects to the small intestine then the stomach then the esophagus and finally the mouth. Anatomy of the anus.
Structures of the human large intestine rectum and anusthe mucosa of the large intestine is punctuated with numerous crypts that absorb water and are lined with mucus secreting goblet cells. A doctor may inspect the outside of the anus. Anus terminal opening of the anal canal the portion of the digestive tract through which fecal material is excreted.
An endoscope flexible tube with a lighted camera on its tip is inserted into. It is continuous proximally with the sigmoid colon and terminates into the anal canal. The rectum is the final segment of the large intestine that connects the colon to the anus.
The rectum is a hollow muscular tube about 8 inches 20 cm in length and 25 inches in diameter at its widest point. The anus is approximately 2 to 3 inches long and composed of skin type cells also known. The rectum follows the shape of the sacrum and ends in an expanded section called the rectal ampulla where feces are stored before their release via the anal canal.
It stores fecal matter produced in the colon until the body is ready to eliminate the waste through the process of defecation. The rectum is a part of the lower gastrointestinal tract. A muscular sheet called the pelvic diaphragm runs perpendicular to the juncture of the rectum and anal canal.
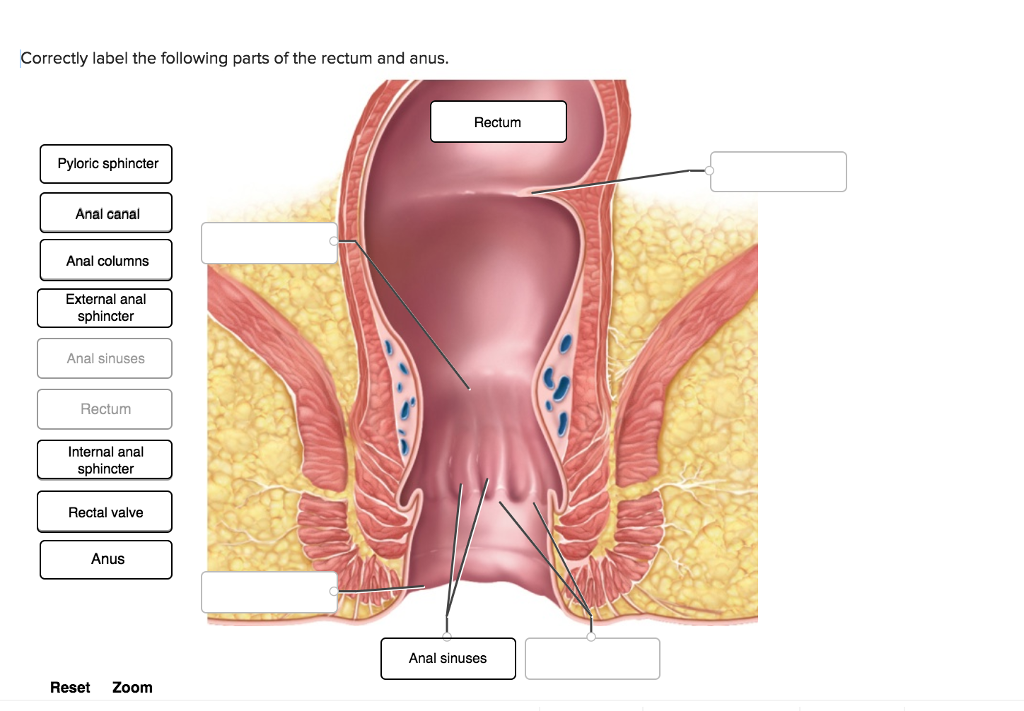 Solved Correctly Label The Following Parts Of The Rectum
Solved Correctly Label The Following Parts Of The Rectum
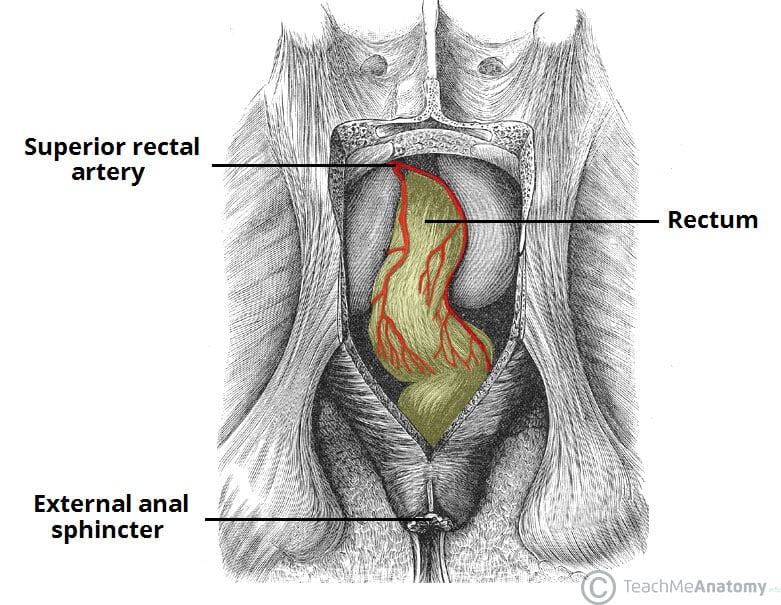 The Rectum Position Neurovascular Supply Teachmeanatomy
The Rectum Position Neurovascular Supply Teachmeanatomy
 Human Papilloma Virus And Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of The
Human Papilloma Virus And Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of The
 Anal Canal Anatomy Gross Anatomy Tissue Nerves And
Anal Canal Anatomy Gross Anatomy Tissue Nerves And
 Amazon Com Anatomy Anus Sphincter Muscle Print Sra3 12x18
Amazon Com Anatomy Anus Sphincter Muscle Print Sra3 12x18
 Anorectal Disorders Anatomy Of Anus And Rectum
Anorectal Disorders Anatomy Of Anus And Rectum
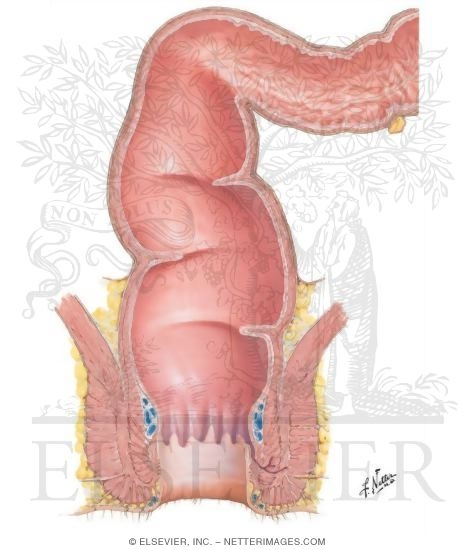 Rectum And Anal Canal Structure Of The Rectum And Anal Canal
Rectum And Anal Canal Structure Of The Rectum And Anal Canal
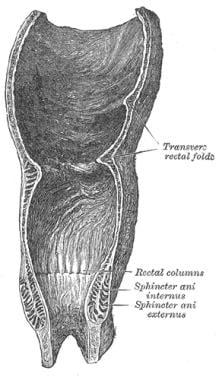 Anal Canal Anatomy Gross Anatomy Tissue Nerves And
Anal Canal Anatomy Gross Anatomy Tissue Nerves And

 Gastrointestinal Tract 5 The Anatomy And Functions Of The
Gastrointestinal Tract 5 The Anatomy And Functions Of The
 Anatomy Of The Anus Anal Cancer Information
Anatomy Of The Anus Anal Cancer Information
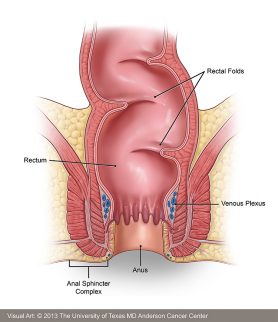 Anal Cancer Symptoms Diagnosis Treatment Md Anderson
Anal Cancer Symptoms Diagnosis Treatment Md Anderson
 Git Anatomy The Rectum And The Anal Canal
Git Anatomy The Rectum And The Anal Canal
 Why Does Anal Sphincter Muscle Damage Cause Faecal
Why Does Anal Sphincter Muscle Damage Cause Faecal
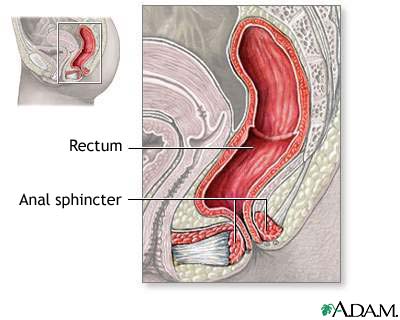 Anal Sphincter Anatomy Medlineplus Medical Encyclopedia Image
Anal Sphincter Anatomy Medlineplus Medical Encyclopedia Image
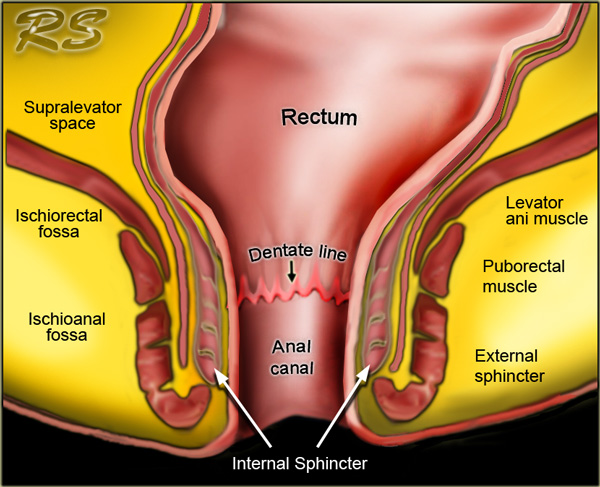 The Radiology Assistant Rectum Perianal Fistulas
The Radiology Assistant Rectum Perianal Fistulas
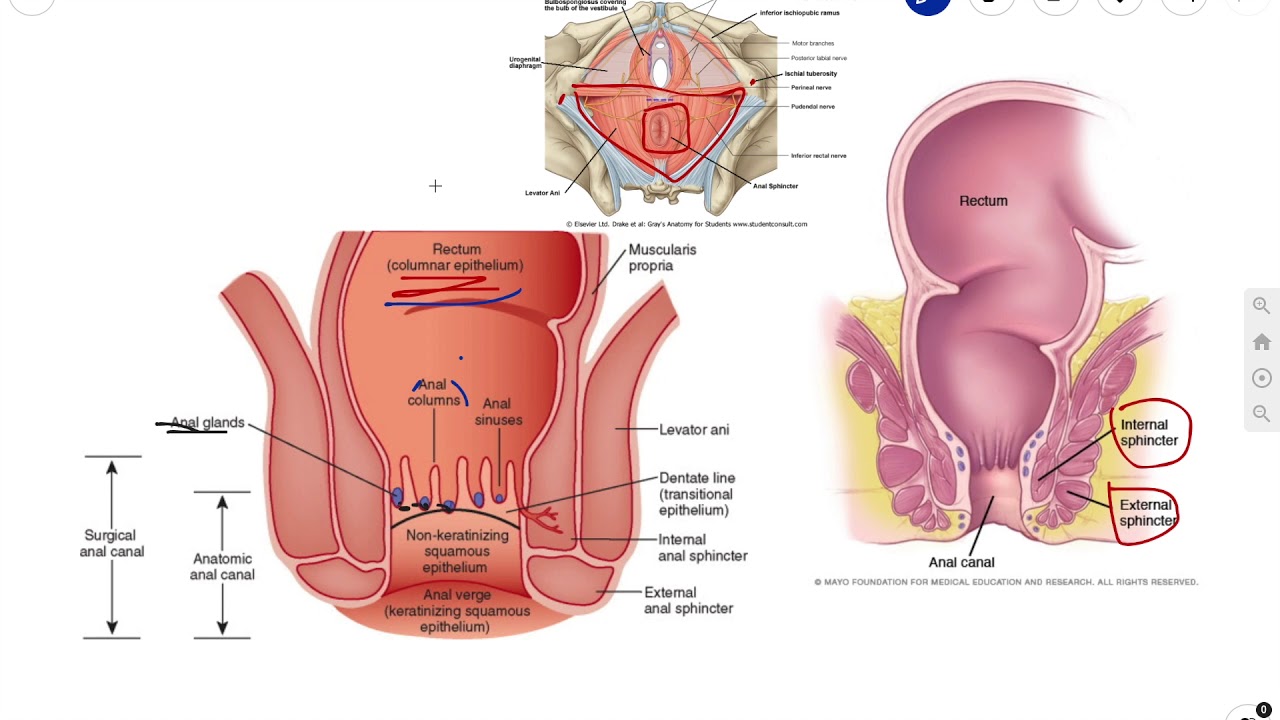 Internal Structure Of Anal Canal Anatomy
Internal Structure Of Anal Canal Anatomy
 Operative Anatomy Of The Colon Rectum And Anus Sciencedirect
Operative Anatomy Of The Colon Rectum And Anus Sciencedirect
 Amazon Com Ahawoso Mousepad Oblong 7 9x9 8 Anatomy
Amazon Com Ahawoso Mousepad Oblong 7 9x9 8 Anatomy
Digestive Diseases Rectal Colon Diseases Cleveland Clinic
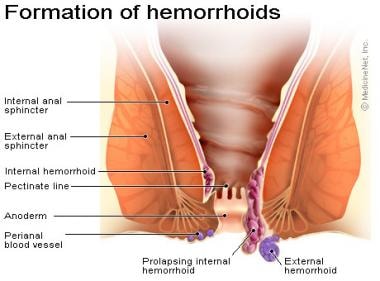 Hemorrhoids Background Anatomy Etiology And Pathophysiology
Hemorrhoids Background Anatomy Etiology And Pathophysiology



Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar