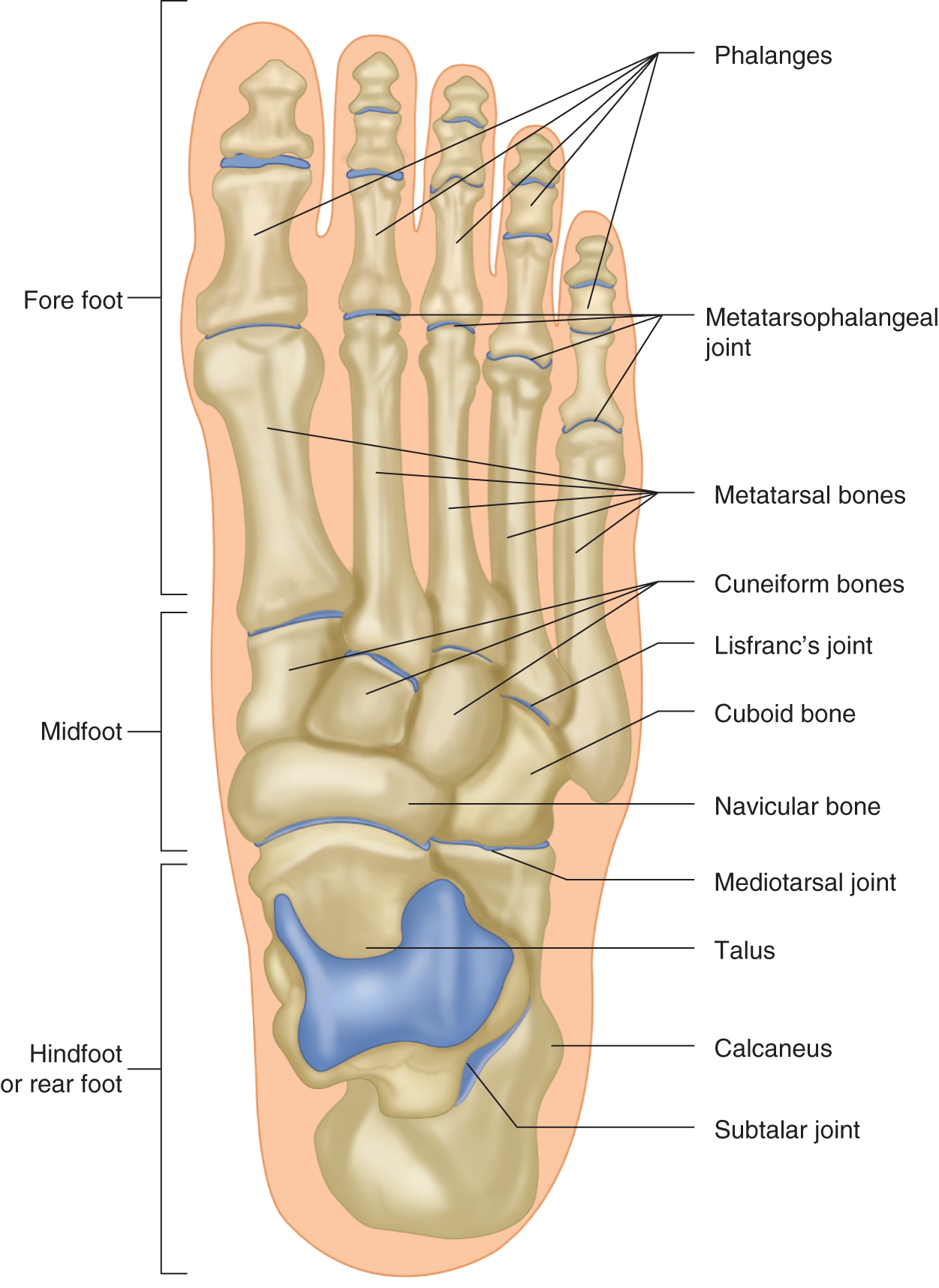
Foot anatomy the foot contains 26 bones 33 joints and over 100 tendons muscles and ligaments. Joints of the foot the intertarsal joints are between the tarsal bones.
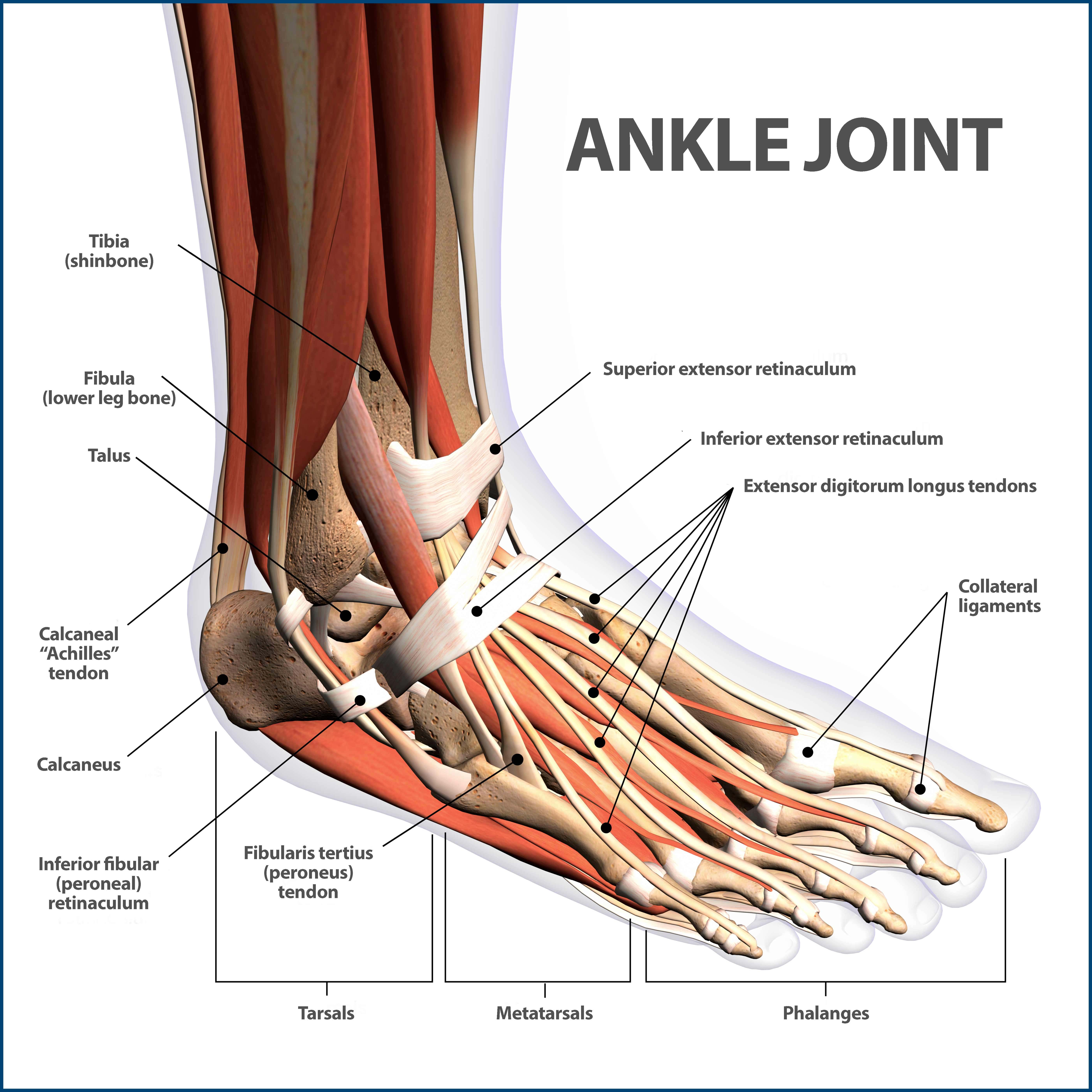 Ankle Fractures Broken Ankle Florida Orthopaedic Institute
Ankle Fractures Broken Ankle Florida Orthopaedic Institute
It consists of 28 bones which can be divided functionally into three groups referred to as the tarsus metatarsus and phalanges.
Foot joint anatomy. The foot contains a number of joints but two important joints are the subtalar and transverse tarsal joints. The feet are divided into three sections. This may sound like overkill for a flat structure that supports your weight but you may not realize how much work your foot does.
During the gait cycle the foot can pronate in many different ways based on rearfoot and forefoot function. The bones of the feet are. Its a synovial joint and its stabilized by medial lateral and interosseous talocalcaneal ligaments.
Calcaneus the largest bone of the foot which lies beneath the talus to form the heel bone. The midfoot is a pyramid like collection of bones that form the. Foot bones the hindfoot.
Metatarsophalangeal joints mtp are the joints between the heads of metatarsals. The ankle joint is both a synovial joint and a hinge joint. Tarsometatarsal joints are the articulations between the tarsals and metatarsals.
Talus the bone on top of the foot that forms a joint with the two bones of the lower leg. The hindfoot comprises of the ankle joint found at the bottom of the leg and is where the end. Plantar aponeurosis is primary structure of loadforce transfer between hindfoot and forefoot.
Allows for supple foot to accommodate ground just after heel strike. Eversion of subtalar joint unlocks the transverse tarsal joint. Inversion of subtalar joint locks the transverse tarsal joint.
These two joints allow you to invert and evert the foot. Allows for a stable hindfootmidfoot for toe off. The forefoot contains the five toes phalanges and the five longer bones metatarsals.
Pronation of the foot refers to how the body distributes weight as it cycles through the gait. The foot is the region of the body distal to the leg that is involved in weight bearing and locomotion. Joints and ligaments of the foot.
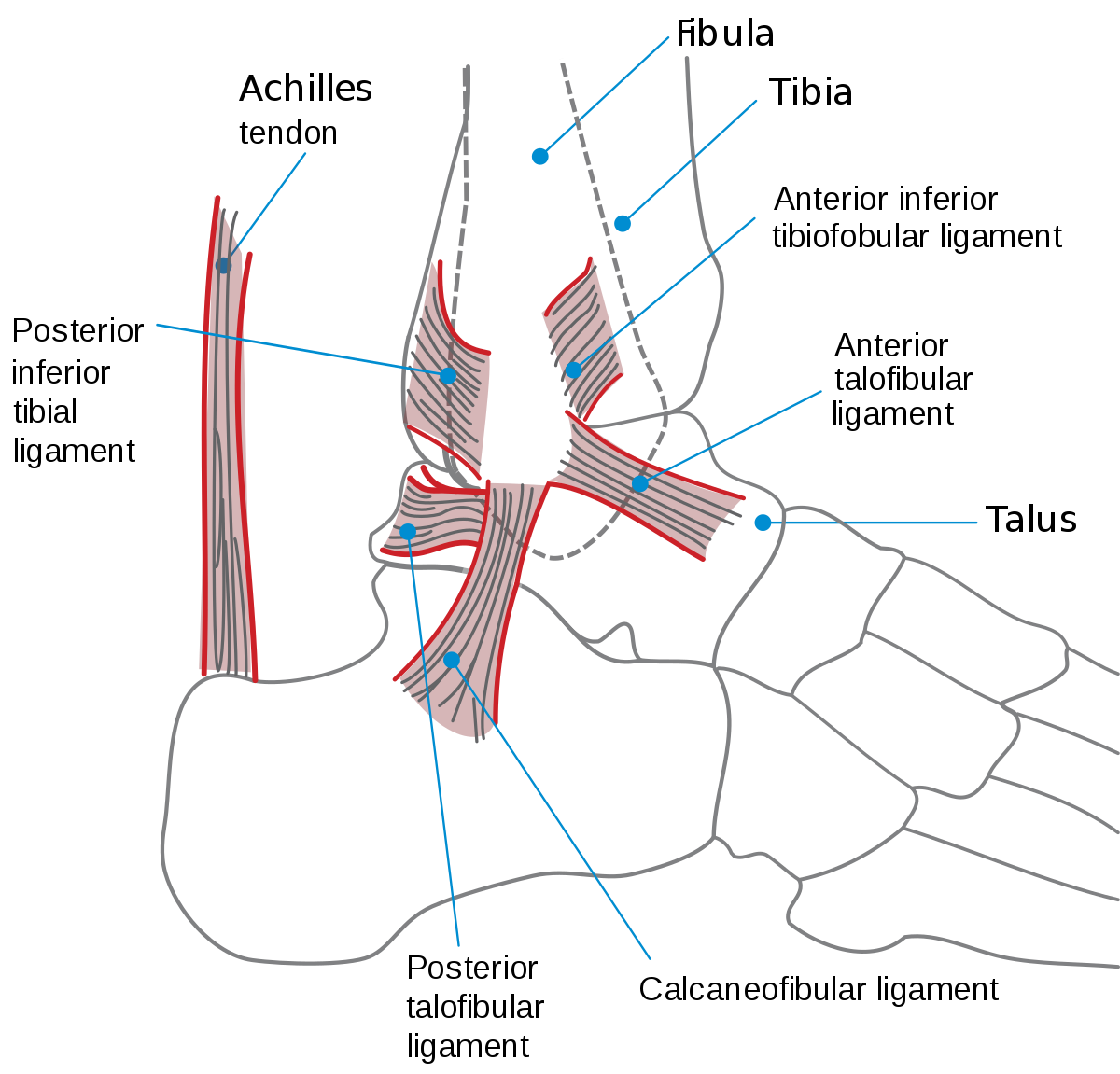
The five bones of the midfoot are what make up our foot arches. This joint is the posterior joint formed between the talus and the calcaneus. The ankle joint or tibiotalar joint is formed where the top of the talus the uppermost bone in the foot and the tibia shin bone and fibula meet.
Hinge joints typically allow for only one direction of motion much like a door hinge. Interphalangeal joints are between the phalanges of the. The foot and toe joints.
Tarsals five irregularly shaped bones of the midfoot that form the foots arch. In anatomy pronation is a rotational movement of the forearm at the radioulnar joint or foot at the subtalar and talocalcaneonavicular joints. There are nineteen bones in the forefoot.
Anatomy Of The Foot And Ankle Orthopaedia
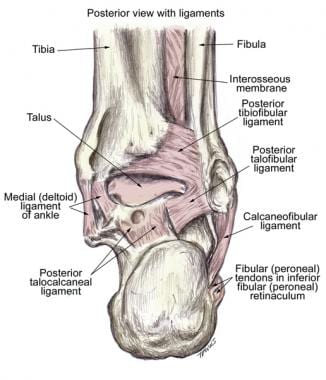 Ankle Joint Anatomy Overview Lateral Ligament Anatomy And
Ankle Joint Anatomy Overview Lateral Ligament Anatomy And
 The Foot Advanced Anatomy 2nd Ed
The Foot Advanced Anatomy 2nd Ed
Foot Anatomy For Runners Timeoutdoors
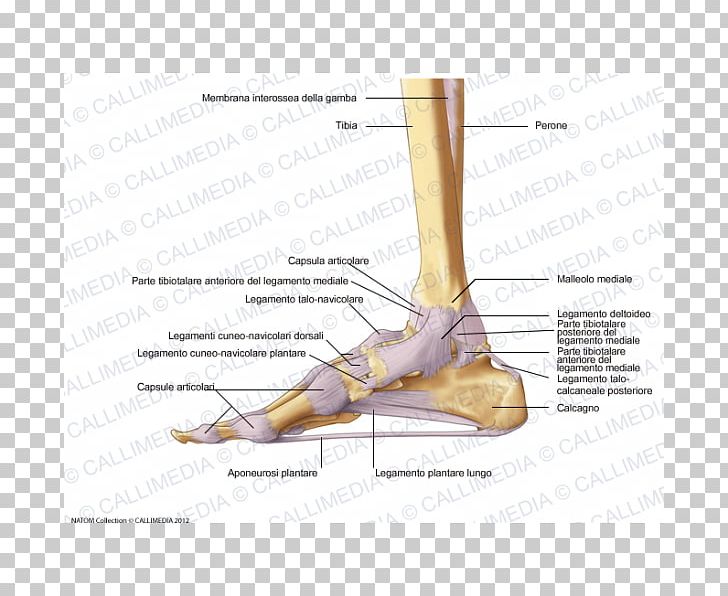 Foot Joint Capsule Deltoid Ligament Png Clipart Anatomical
Foot Joint Capsule Deltoid Ligament Png Clipart Anatomical
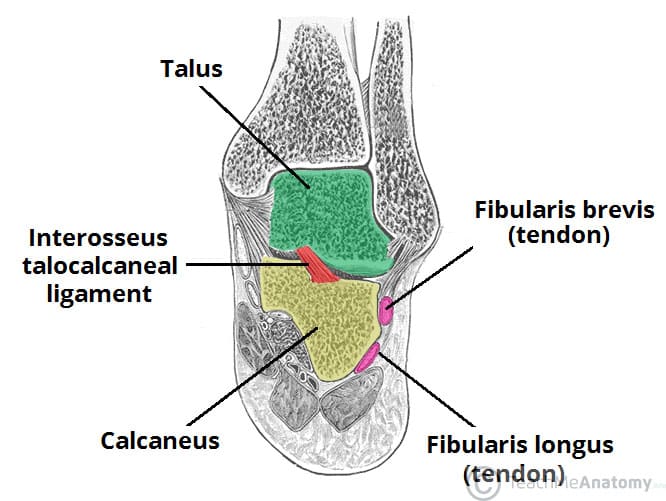 The Subtalar Joint Ligaments Neurovascular Teachmeanatomy
The Subtalar Joint Ligaments Neurovascular Teachmeanatomy
 1000 Foot Muscle Stock Images Photos Vectors Shutterstock
1000 Foot Muscle Stock Images Photos Vectors Shutterstock
Rheumatoid Arthritis Of The Foot And Ankle Orthoinfo Aaos
Lisfranc Midfoot Injury Orthoinfo Aaos
 Blood Supply To The Foot Foot Ankle Orthobullets
Blood Supply To The Foot Foot Ankle Orthobullets
 Tarsometatarsal Joint Anatomy Figure Courtesy Of Mmg Via
Tarsometatarsal Joint Anatomy Figure Courtesy Of Mmg Via
 General International Association For Dance Medicine Science
General International Association For Dance Medicine Science
 Foot Vertebrate Anatomy Britannica
Foot Vertebrate Anatomy Britannica
Anatomy Of The Foot And Ankle Orthopaedia
Tarsal Coalition Orthoinfo Aaos
 Foot And Ankle Anatomy Allen Tx Foot Doctor
Foot And Ankle Anatomy Allen Tx Foot Doctor
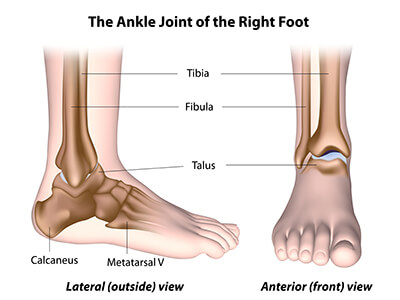 Foot Ankle Preservation Baltimore Md Towson Orthopaedics
Foot Ankle Preservation Baltimore Md Towson Orthopaedics
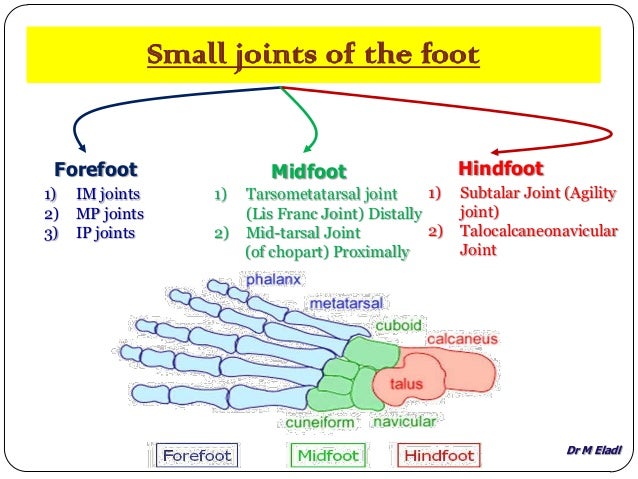 Anatomy Of Small Joints Of The Foot
Anatomy Of Small Joints Of The Foot
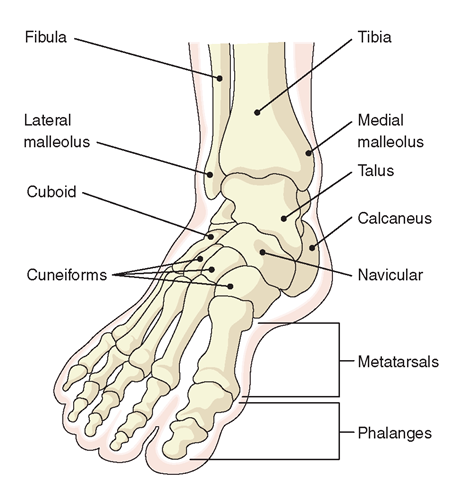 Foot Bones Foot Pain Anatomy Info
Foot Bones Foot Pain Anatomy Info





Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar