In swimming and sessile forms however the foot is greatly reduced or greatly modified. 5body monomeric and highly variable in form may possess a dorsal or lateral shells of protein and calcareous spicules.
 Ucsc Biology 150 Mollusca Gastropoda
Ucsc Biology 150 Mollusca Gastropoda
4body possesses a through gut with mouth and anus.
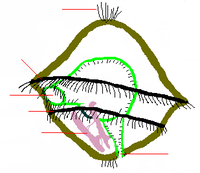
Mollusca anatomy. The shells of molluscs are formed of calcium carbonate 95 and organic components 1. Oysters clams scallops and yes snails squid and octopods. Molluscs have a huge range of shapes and sizes even with a single group like the gastropods.
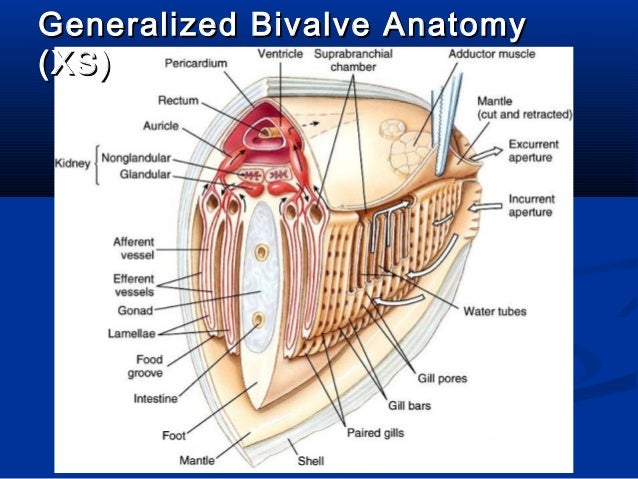
It has three layers and protects the main organs of the mollusk. This is what is examined in this section. Phylum mollusca class bivalvia.
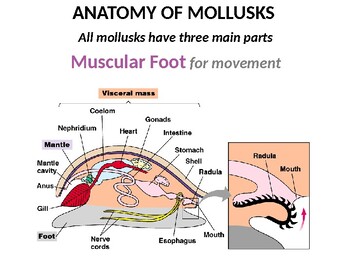
The three most universal features defining modern molluscs are a mantle with a significant cavity used for breathing and excretion the presence of a radula except for bivalves and the structure of the nervous system. 2body has more than two cell layers tissues and organs. Locomotion the foot is the organ of locomotion in land gastropods.
The foot although the basic form of the foot is a flat broadly tapered muscular organ which is highly. The edge of the mantle secretes a shell of calcium carbonate chitin and conchiolin. In limpets the foot is modified into a sucker which helps in anchoring the animal to hard surfaces.
This category has the following 5 subcategories out of 5 total. Other than these common elements molluscs express great morphological diversity. Characteristics of mollusca 1bilaterally symmetrical.
The foot in the gastropods. The phylum mollusca consists of over 100000 marine freshwater and terrestrial species. Anatomy of molluscs.
Shell many molluscs have shells. The feet of the molluscs carry out different functions in different classes. Most are familiar to you as food sources.
Mollusca anatomy function with some nematodes mantle cavity respitory systems open circulatory system developed eyes bilatteral head and food body wall forms mantle and mantle cavity. Some also serve as intermediate hosts for parasitic trematodes and others eg snails can be major agricultural pests. Coelem protect important organs.
They however also have many features in common. External and internal anatomy of a freshwater mussel. Jump to navigation jump to search.
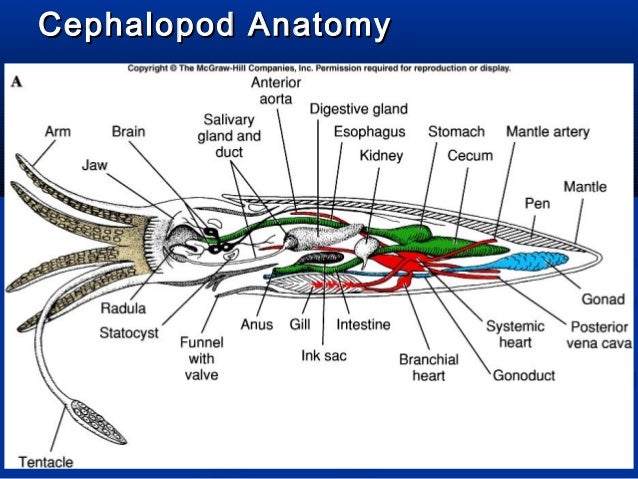
Wikimedia commons has media related to mollusca anatomy. B bivalve anatomy 16 p c cephalopod zootomy 41 p g gastropod anatomy. Bivalves are easily distinguished from other molluscs by the presence of two shells or valves.
Calcareous casing produced by the mantle.
 Ppt Molluscs Powerpoint Presentation Id 2254407
Ppt Molluscs Powerpoint Presentation Id 2254407
Fresh Water Mussel Collection Introduction Anatomy
 The Evolution Of Molluscs Wanninger 2019 Biological
The Evolution Of Molluscs Wanninger 2019 Biological
 Mollusca Anatomy Function With Some Nematodes Flashcards
Mollusca Anatomy Function With Some Nematodes Flashcards
 Snail Anatomy Snail Snail Farming Animals Information
Snail Anatomy Snail Snail Farming Animals Information
 Catalogue Of Organisms Anatomy Of Mollusca A Case Of
Catalogue Of Organisms Anatomy Of Mollusca A Case Of
 Catalogue Of Organisms Anatomy Of Mollusca A Case Of
Catalogue Of Organisms Anatomy Of Mollusca A Case Of
 Vintage Rollable Wall Chart Anatomy Of Mollusca Building Plan Animal World
Vintage Rollable Wall Chart Anatomy Of Mollusca Building Plan Animal World
Eukry Pp14 Molluscs Flashcards Quizlet
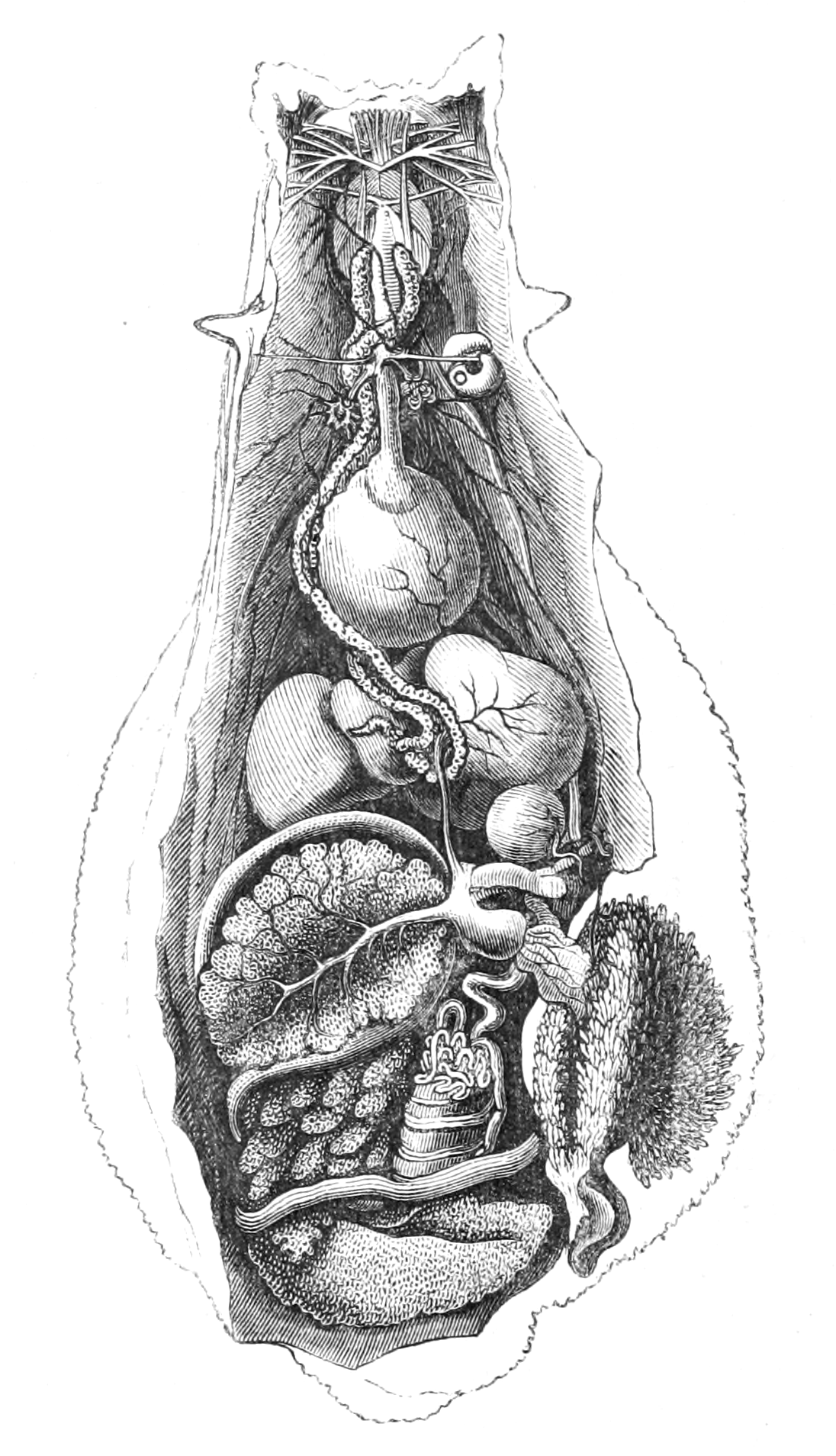 File Natural History Mollusca Sea Hare Anatomy Png
File Natural History Mollusca Sea Hare Anatomy Png
 Anatomy Of A Mollusc Monterey Bay Aquarium Marine Biology
Anatomy Of A Mollusc Monterey Bay Aquarium Marine Biology
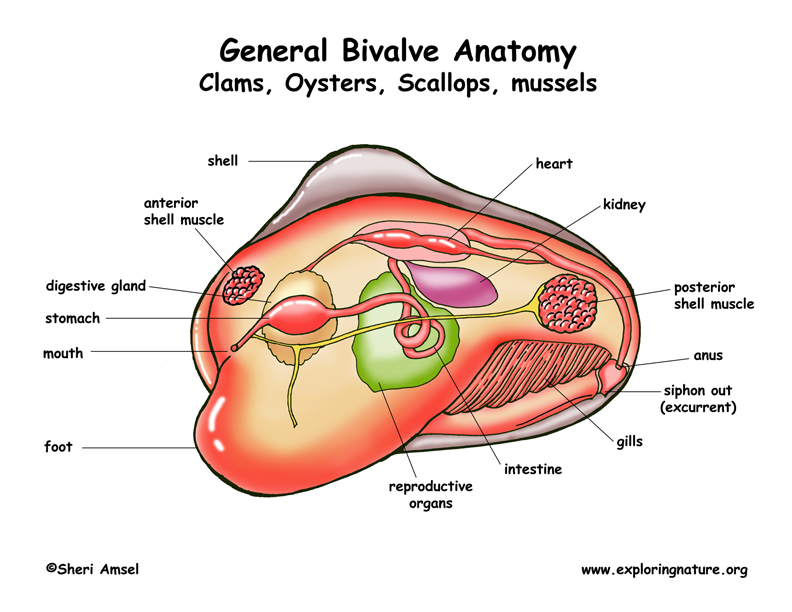 Phylum Mollusca Gastropods Bivalves Cephalopods
Phylum Mollusca Gastropods Bivalves Cephalopods
 Bivalve Anatomy Freshwater Mussel
Bivalve Anatomy Freshwater Mussel
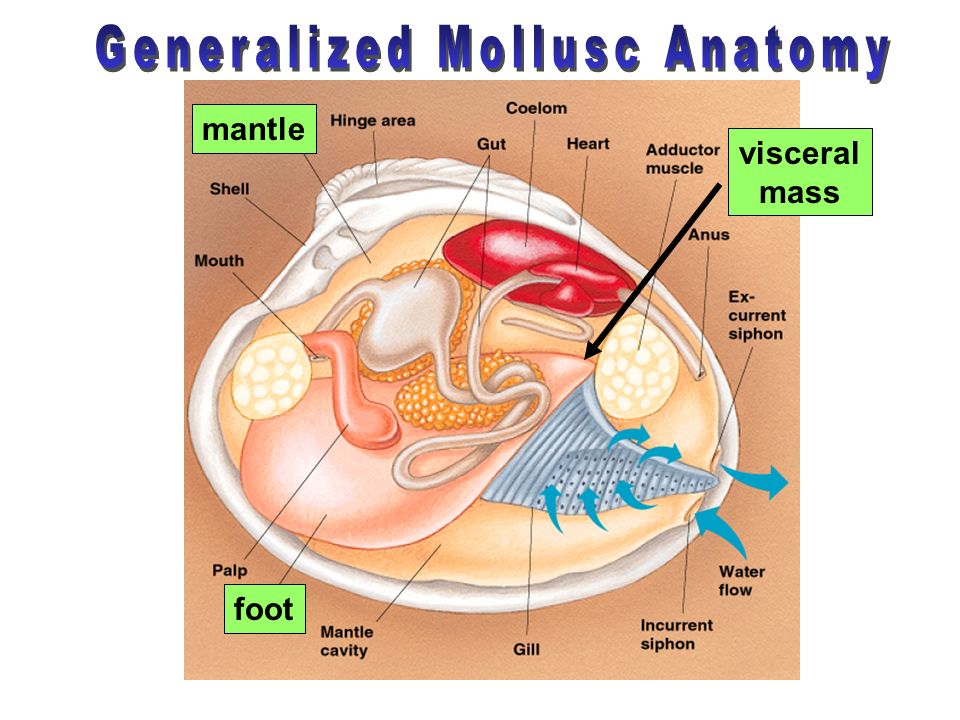 Mollusks Ppt Video Online Download
Mollusks Ppt Video Online Download
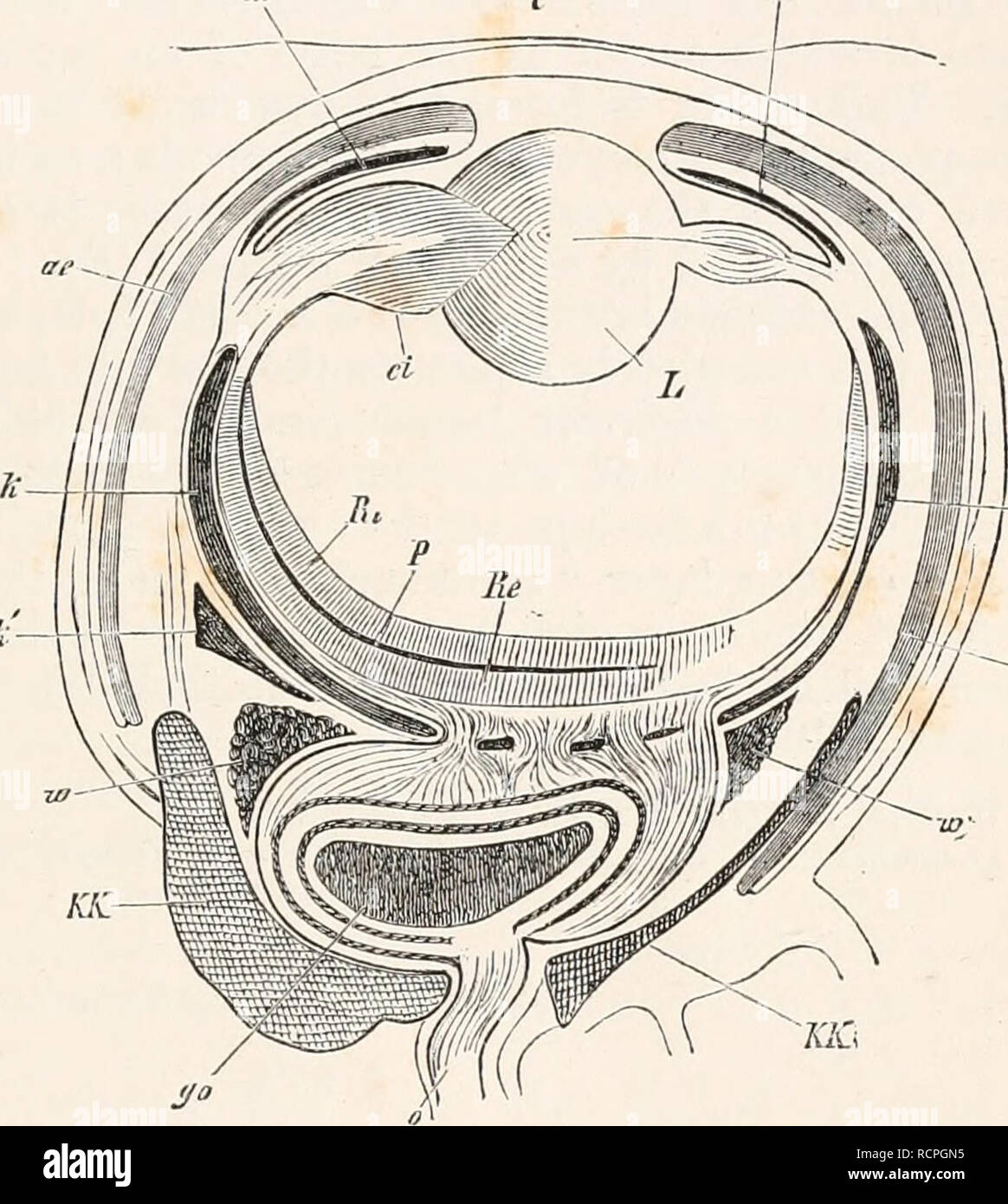 Elements Of Comparative Anatomy Anatomy Comparative
Elements Of Comparative Anatomy Anatomy Comparative
The Hatchery Culture Of Bivalves A Practical Manual
 Animal Phyla Mollusca Arthropoda Easy Peasy All In One
Animal Phyla Mollusca Arthropoda Easy Peasy All In One


Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar