Polarity definition is the quality or condition inherent in a body that exhibits opposite properties or powers in opposite parts or directions or that exhibits contrasted properties or powers in contrasted parts or directions. Property of a molecule with oppositely charged ends.
Water is a polar molecule.
Polarity definition anatomy. Biology polarity is also an essential and common feature in organisms particularly at the cell level. Because of it water is able to dissolve many different substances. Pertaining to a compound exhibiting polarity or dipole moment that is a compound bearing a partial positive charge on one side and a partial negative charge on the other.
Na k atpase enzyme na k pump for instance is located on the basolateral membrane. Deeper layers are cuboidal or columnar active in mitosis. A fluid necessary for the life of most animals and plants a molecule 2 atoms of h and 1 atom of o.
Both membrane have different carrier proteins protein channels and pumps. The particular state of a part of a body or system that has polarityan electrode with positive polarity. Adjective general of or having one or more poles in a spherical body.
Polarity enables water to interact with various compounds. The polarity practitioner determines the energy imbalance in an individual and restores balance to the energy poles in the body with gentle techniques including gentle rocking stretching and touch. Chemistry polarity confers molecules and compounds distinctive features in terms of structure and chemical interaction with other molecules.
The condition of a body or system in which it has opposing physical properties at different points esp magnetic poles or electric charge. The condition of having poles. This assymmetry is called as polarity.
Mosbys dictionary of complementary and alternative medicine. The condition of having poles. Polar and nonpolar cov.
Basolateral membrane which sits on the basement membrane. Free surface cells are squamous m ay be dead m ay contain keratin protective protein 2. Epithelial cells have two kind of membranes.
Polarity polarity in chemical bonding the distribution of electrical charge over the atoms joined by the bond. Monomer of proteins a molecule that has both a hydrophilic region and a hydrophobi a type of organic compound that is composed of monosaccharides the core element of organic compounds. Monomer for proteins monomer nucleic acids monomer unit for carbohydrates.
Being in opposite extremes. Specifically while bonds between identical atoms as in h 2 are electrically uniform in the sense that both hydrogen atoms are electrically neutral bonds between atoms of different elements are electrically inequivalent.
Human Polarity A New Context For Human Origins And Behavior
 Neuronal Polarity An Evolutionary Perspective Journal Of
Neuronal Polarity An Evolutionary Perspective Journal Of
 Pyramidal Neuron Polarity Axis Is Defined At The Bipolar
Pyramidal Neuron Polarity Axis Is Defined At The Bipolar
 Wellness Institute Polarity Therapy A Comprehensive
Wellness Institute Polarity Therapy A Comprehensive
Planar Cell Polarity Genes Frizzled4 And Frizzled6 Exert
Spatial And Polarity Precision Of Concentric High Definition
Law Of Polarity Ascension Glossary
 Definition Of Polarity Therapy Polarity Center
Definition Of Polarity Therapy Polarity Center
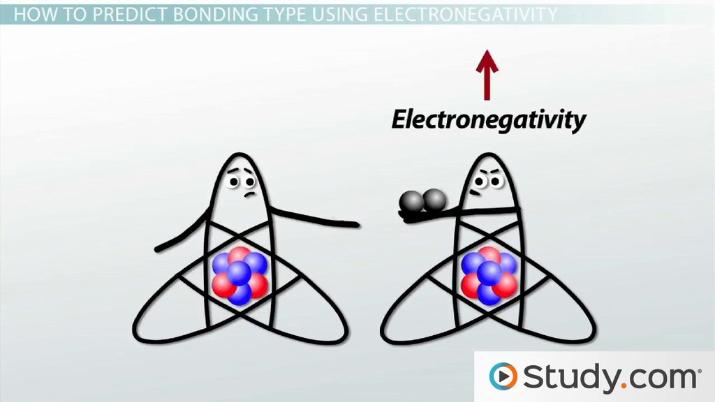 Polar And Nonpolar Covalent Bonds Definitions And Examples
Polar And Nonpolar Covalent Bonds Definitions And Examples
 Hale S Polarity Law Switching Of Polarities During Two
Hale S Polarity Law Switching Of Polarities During Two
Polarity Correction Divinity For Life
 Do Either Maleic Or Fumaric Acids Have Dipole Moments Which
Do Either Maleic Or Fumaric Acids Have Dipole Moments Which
 Introduction To Current Transformers Part 2 Ct Polarity
Introduction To Current Transformers Part 2 Ct Polarity
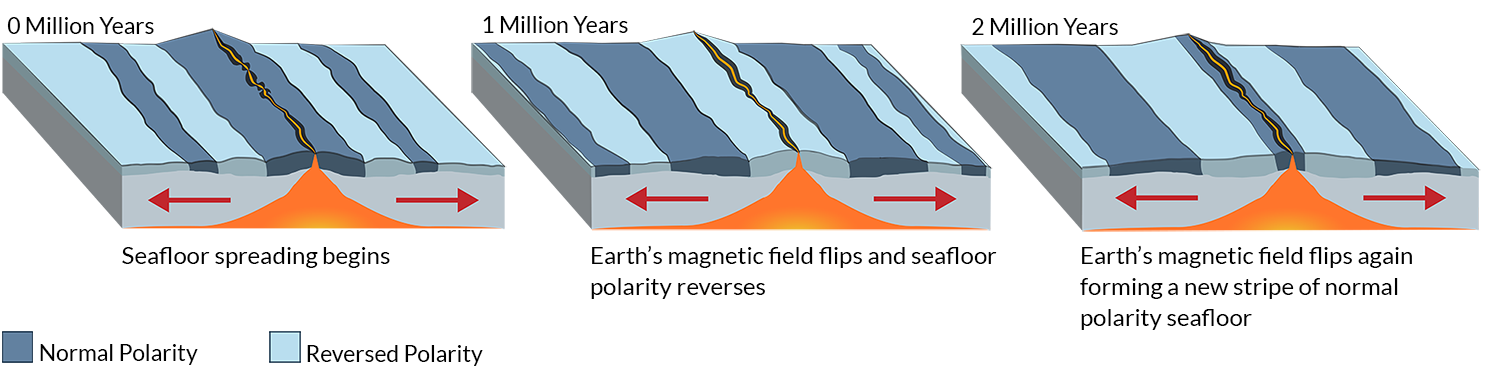 Magnetics Polarity Dive Discover
Magnetics Polarity Dive Discover
 17 Best Polarity Therapy Images In 2019 Therapy
17 Best Polarity Therapy Images In 2019 Therapy
 Polar Molecule Definition And Examples Biology Dictionary
Polar Molecule Definition And Examples Biology Dictionary
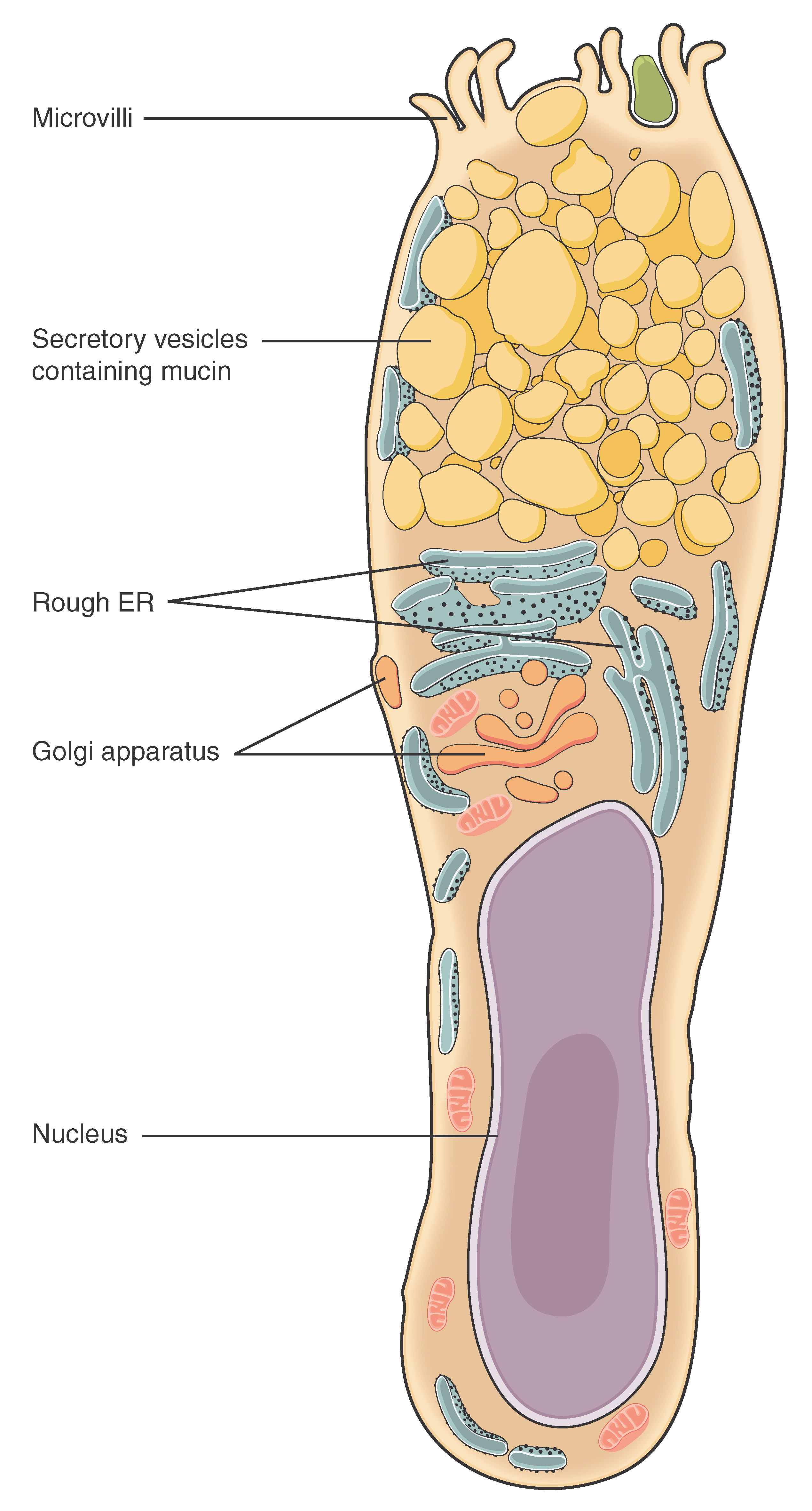 4 2 Epithelial Tissue Anatomy And Physiology
4 2 Epithelial Tissue Anatomy And Physiology
Human Polarity A New Context For Human Origins And Behavior
 Definition Of Polarity Therapy Polarity Center
Definition Of Polarity Therapy Polarity Center
 Polarity Download For Pc In Parts Wattpad
Polarity Download For Pc In Parts Wattpad
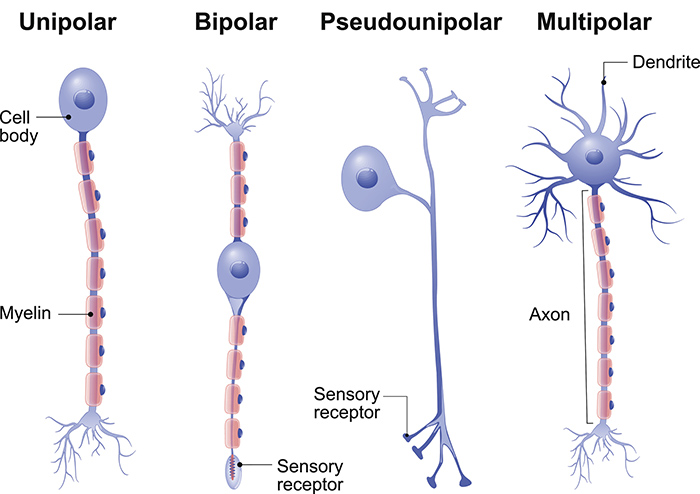 Types Of Neurons Queensland Brain Institute University
Types Of Neurons Queensland Brain Institute University
 Golden Ratio Spiral The Breath Of Brahma Polarity Therapy
Golden Ratio Spiral The Breath Of Brahma Polarity Therapy
 How Can I Calculate The Polarity Of A Compound Socratic
How Can I Calculate The Polarity Of A Compound Socratic
 Neuronal Polarity An Evolutionary Perspective Journal Of
Neuronal Polarity An Evolutionary Perspective Journal Of
 Definition Of Polarity Therapy Polarity Center
Definition Of Polarity Therapy Polarity Center
Sexual Polarity Essential Life Drives Attraction Between



Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar