Another example is the radiocarpal joint of the wrist between the shallow depression at the distal end of the radius bone and the rounded scaphoid lunate and triquetrum carpal bones. A syndesmosis is similar to a suture complete with the fibrous connective tissue but it is more flexible.
Topic 3 Anatomy And Physiology Of The Joints Anp1106
The intricate movements of a human such as those performed in dance and athletics are accomplished by using a wide variety of joints.

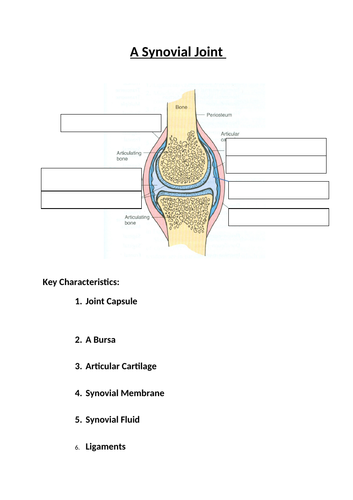
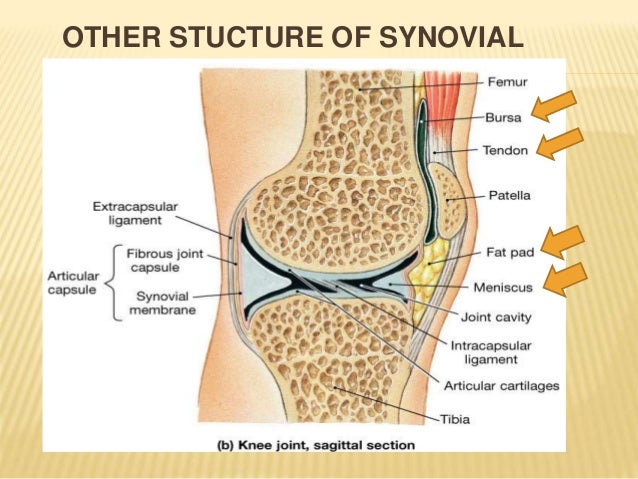
Anatomy and physiology of joints. Cells at the center of this interzone region undergo cell death to form the joint cavity while surrounding mesenchyme cells will form the articular capsule and supporting ligaments. The knuckle metacarpophalangeal joints of the hand between the distal end of a metacarpal bone and the proximal phalanx bone are condyloid joints. Articulating joints are separated by a fluid filled joint cavity which is bounded by a synovial membrane.
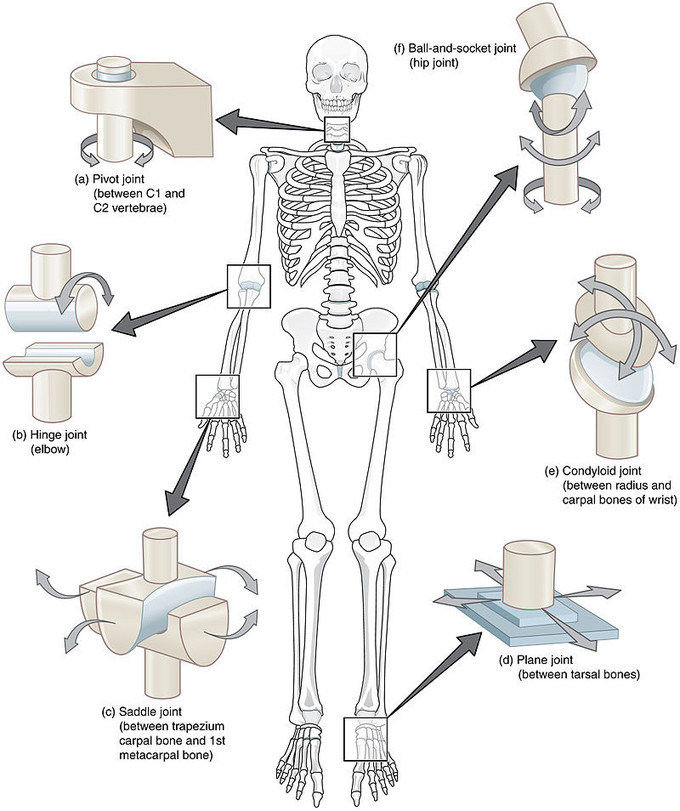
In fact the mobility of a joint is often inversely proportional to its stability. An axis in anatomy is described as the movements in reference to the three anatomical planes. At these joints the rounded head of one bone the ball fits into the concave articulation the socket of the adjacent bone see figure 3f.
There are two types of slightly movable joints amphiarthrosis. It can be unsupported membrane may pouch allowing remote access resting on an outer fibrous capsule or separated from the capsule by pads of fat. An inflammatory disease caused by spirochete bacteria transmitted by the bite of ticks that live on mice and deer.
Most diarthrotic joints are found in the appendicular skeleton and thus give the limbs a wide range of motion. These joints are divided into three categories based on the number of axes of motion provided by each. Though joints enable the skeleton to be dynamic they also play an important role in stability and protection.
Thus diarthroses are classified as uniaxial for movement in one plane biaxial for movement in two planes or multiaxial joints for movement in all three anatomical planes. The synovial joints will form between the adjacent cartilage models in an area called the joint interzone. The hip joint and the glenohumeral shoulder joint are the only ball and socket joints of the body.
Anatomy and physiology joints. An axis in anatomy is described as the movements in reference to the three anatomical planes. The joint with the greatest range of motion is the ball and socket joint.
It often results in joint pain and arthritis especially in the knees and is characterized by a skin rash flu like symptoms and foggy thinking. Such a joint is useful if the body needs to link two bones but allow a little flexibility. Transverse frontal and sagittal.
A synovial membrane is a pink connective tissue sheet that is vascular and sensitive. Transverse frontal and sagittal.
 Chapter 8 Human Anatomy Physiology Joints Anatomy
Chapter 8 Human Anatomy Physiology Joints Anatomy
Overview Of Joint Anatomy And Physiology A Basis For
 Chapter 8 Joints Of The Skeletal System
Chapter 8 Joints Of The Skeletal System
 Joints And Articulations Honors Anatomy Physiology Ms
Joints And Articulations Honors Anatomy Physiology Ms
 Human Anatomy Physiology Lab Activity Analysis Of Joint Movement W Answer Key
Human Anatomy Physiology Lab Activity Analysis Of Joint Movement W Answer Key
 Types Of Joints In The Human Body Anatomy Examples Kenhub
Types Of Joints In The Human Body Anatomy Examples Kenhub
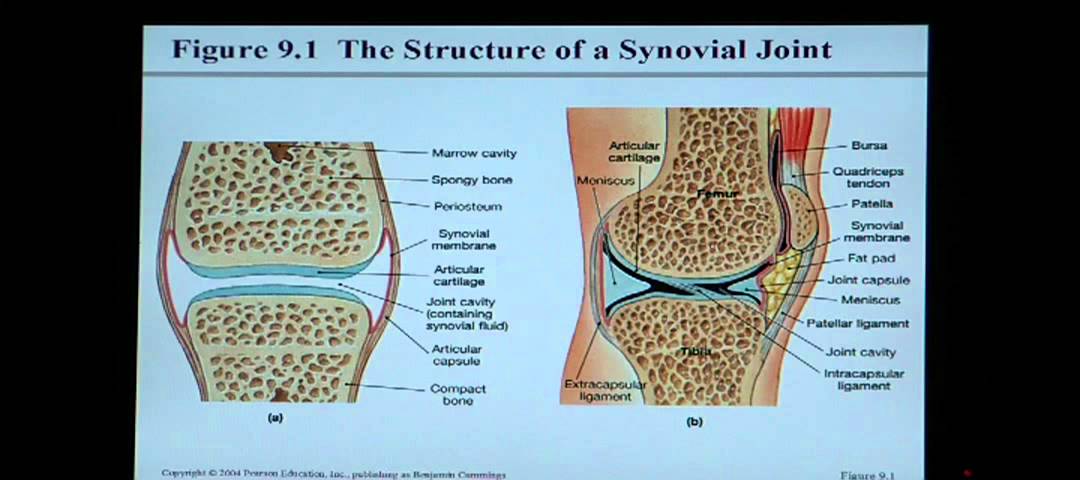 Anatomy And Physiology Help Chapter 9 Articulations
Anatomy And Physiology Help Chapter 9 Articulations

 Total Knee Replacement Orthoinfo Aaos
Total Knee Replacement Orthoinfo Aaos
Anatomy Gross Anatomy Physiology Cells Cytology Cell
 Summary Joints Ch8 Pdf Shs111 Uow Studocu
Summary Joints Ch8 Pdf Shs111 Uow Studocu
Anatomy Gross Anatomy Physiology Cells Cytology Cell
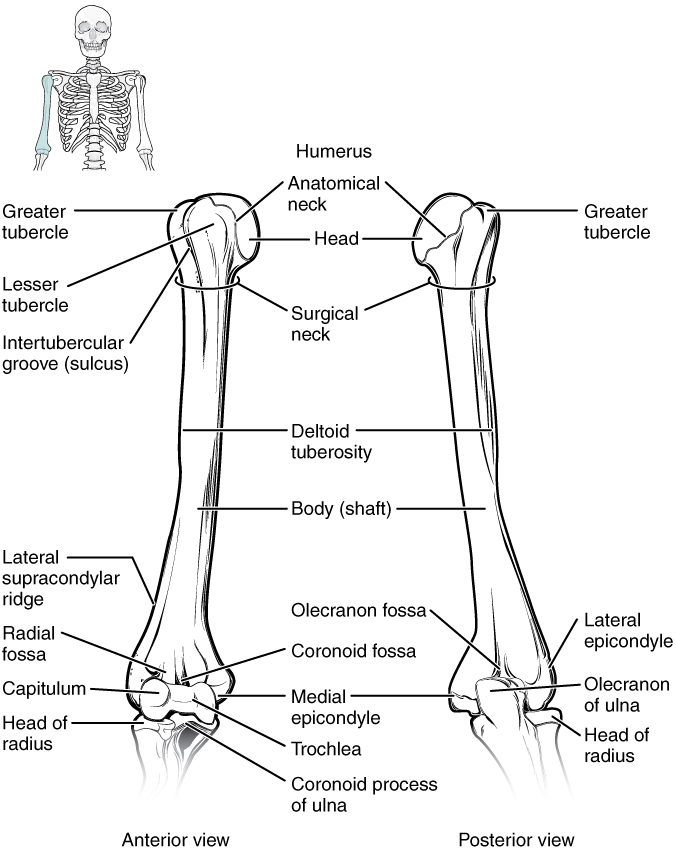 8 2 Bones Of The Upper Limb Anatomy And Physiology
8 2 Bones Of The Upper Limb Anatomy And Physiology
Abstract Of A Paper On The Anatomy And Physiology Of Joints
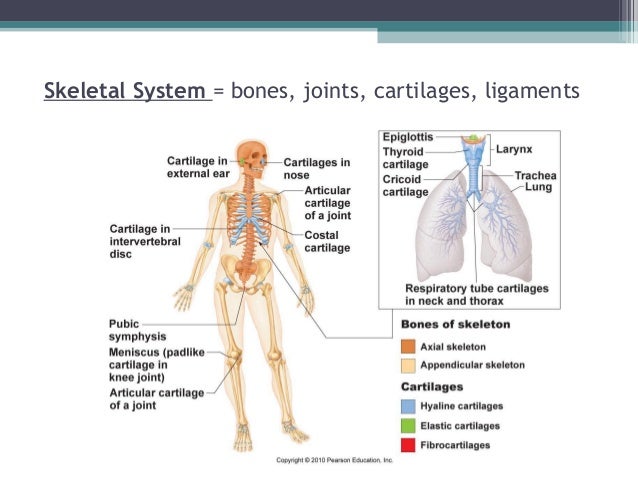 Anatomy Physiology Lecture Notes Skeletal System
Anatomy Physiology Lecture Notes Skeletal System
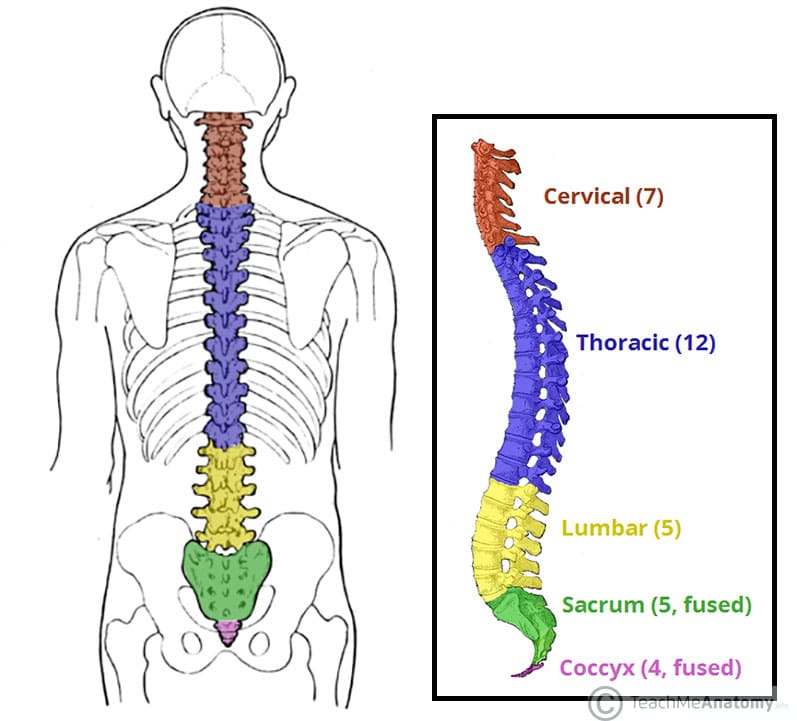 The Vertebral Column Joints Vertebrae Vertebral Structure
The Vertebral Column Joints Vertebrae Vertebral Structure
 Skeletal System Skeleton Bones Joints Cartilage
Skeletal System Skeleton Bones Joints Cartilage
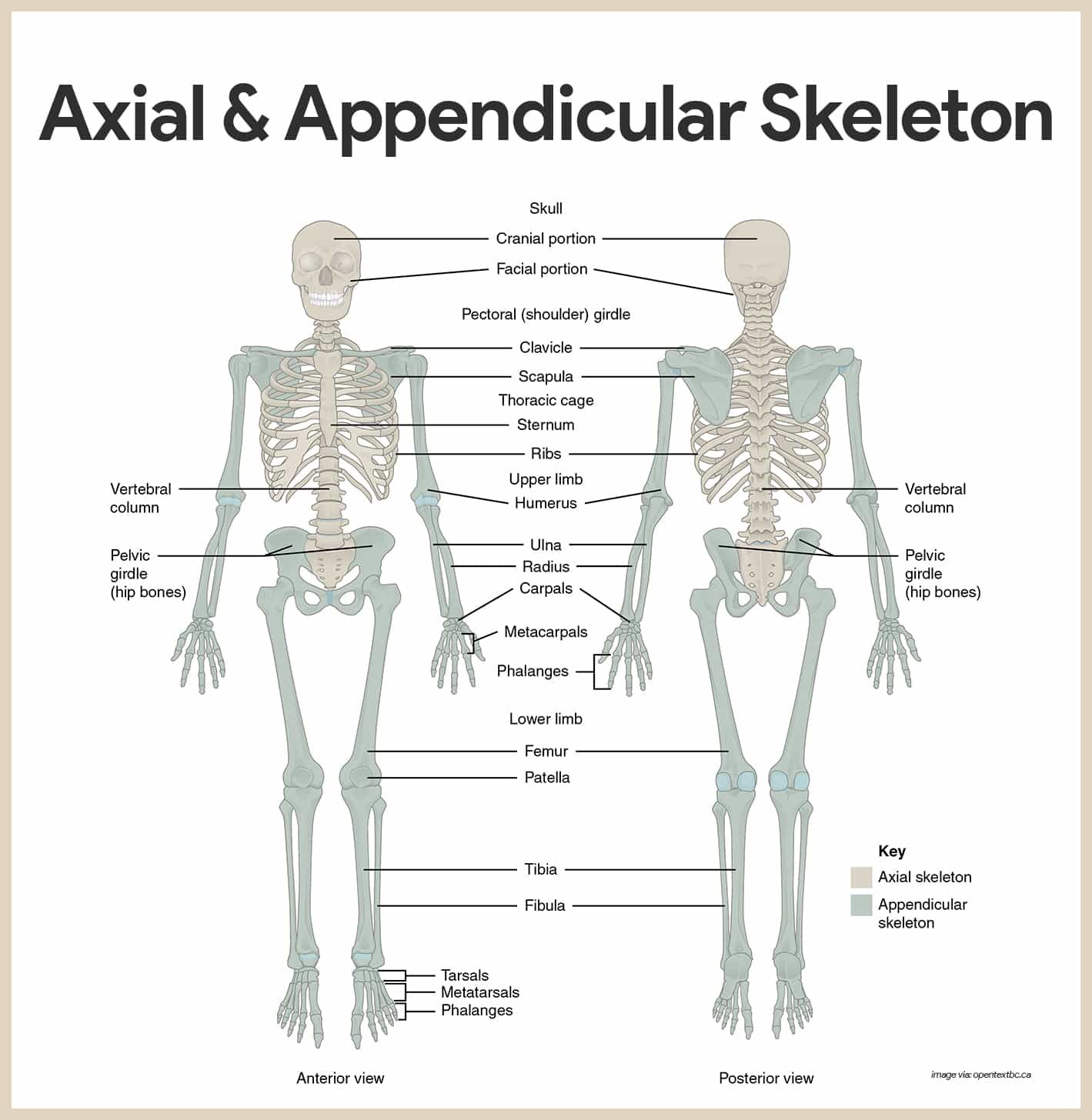 Skeletal System Anatomy And Physiology Nurseslabs
Skeletal System Anatomy And Physiology Nurseslabs
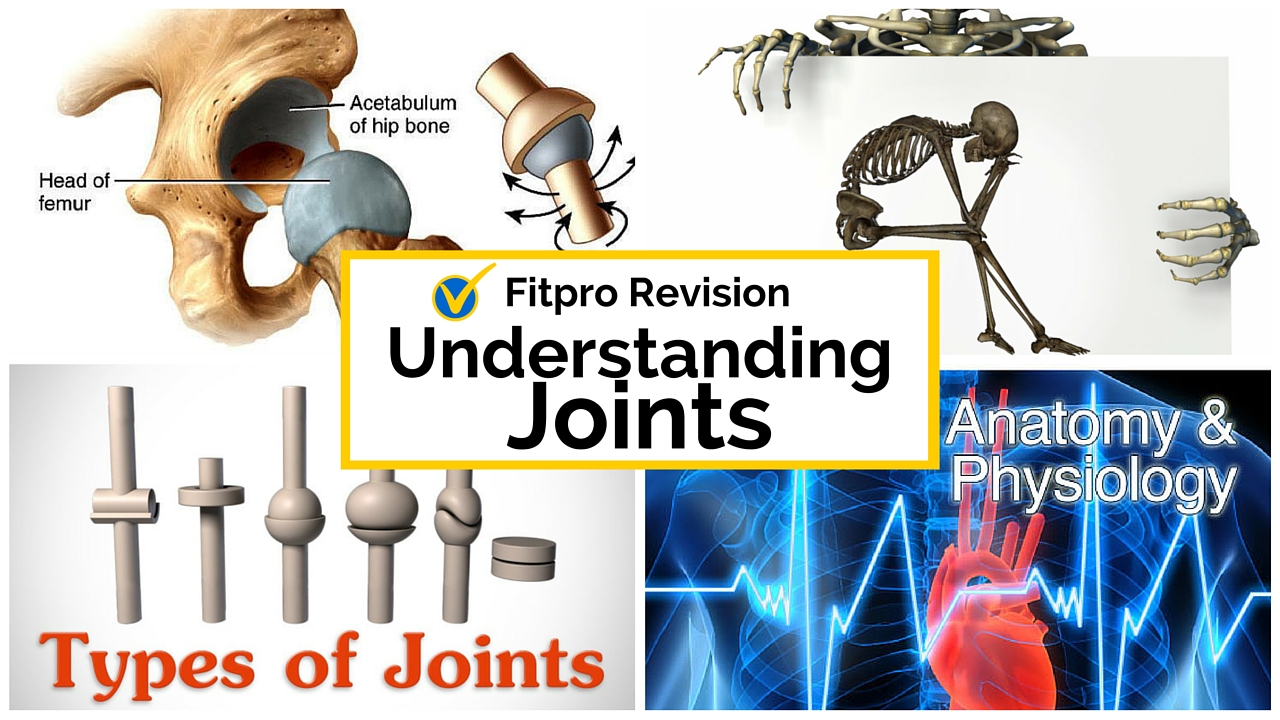 3 Facts To Ace Your Anatomy And Physiology Test Joints
3 Facts To Ace Your Anatomy And Physiology Test Joints
 Bones Skeletal System Human Anatomy Isolated Anatomical Structure
Bones Skeletal System Human Anatomy Isolated Anatomical Structure
 Amazon Com Gifts Delight Laminated 17x13 Poster Anatomy Of
Amazon Com Gifts Delight Laminated 17x13 Poster Anatomy Of
 The Physiology Of The Joints 6ed Vol 1 The Upper Limb
The Physiology Of The Joints 6ed Vol 1 The Upper Limb
Anatomy Of Selected Synovial Joints Anatomy And Physiology
 Joints Lecture Outline Ppt Download
Joints Lecture Outline Ppt Download
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-687795661-969f111662dc4df7a9c3d78c17045ea6.jpg) Anatomy And Physiology Of The Ankle For Sports Medicine
Anatomy And Physiology Of The Ankle For Sports Medicine

Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar