The pancreas is a tubuloalveolar gland and has exocrine and endocrine tissues. Consequently the physiology of the pancreas can be considered in the.
 The Pancreas And Its Functions Columbia University
The Pancreas And Its Functions Columbia University
Anatomy pancreas is an organ situated in the upper part of ones abdomen.
Anatomy and physiology of the pancreas. Anatomy and physiology of the pancreas. Although it is primarily an exocrine gland secreting a variety of digestive enzymes the pancreas has an endocrine function. Anatomy of the pancreas the pancreas is an elongated tapered organ located across the back of the belly behind the stomach.
The pancreas has both exocrine and endocrine functions. The pancreas is a long slender organ most of which is located posterior to the bottom half of the stomach figure 1718. The pancreas is a long slender organ most of which is located posterior to the bottom half of the stomach figure 1791.
Although it is primarily an exocrine gland secreting a variety of digestive enzymes the pancreas also has endocrine cells. It may occur suddenly in a severe form as in acute pancreatitis or may continue as a slow long drawn illness as in chronic pancreatitis. The portion of the pancreas that lies anterior to the aorta is somewhat thinner than the adjacent portions of the head and body of the pancreas.
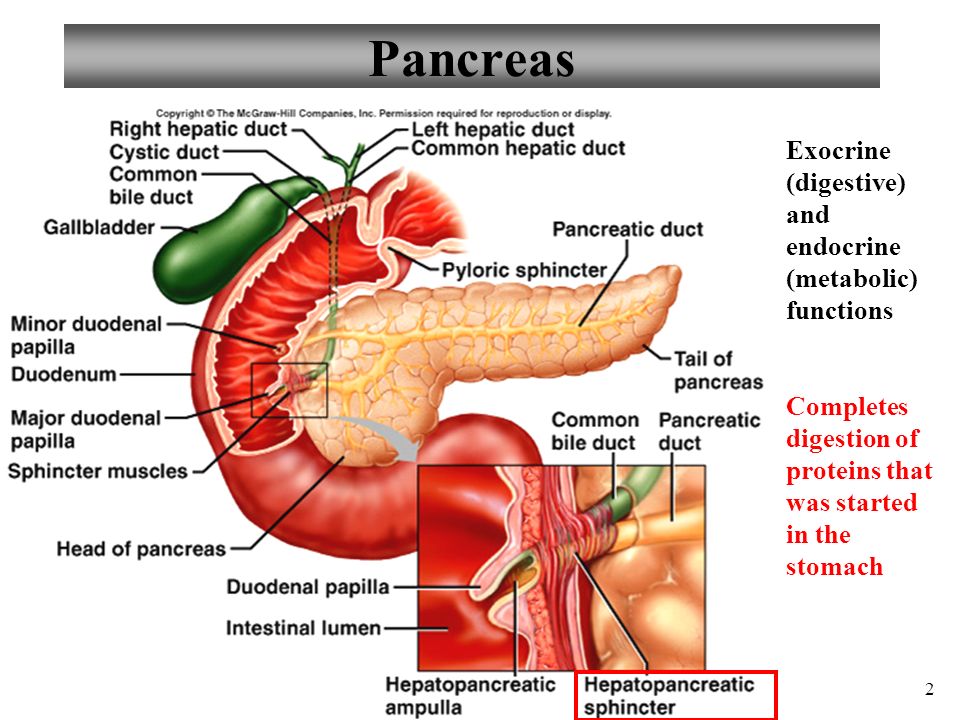
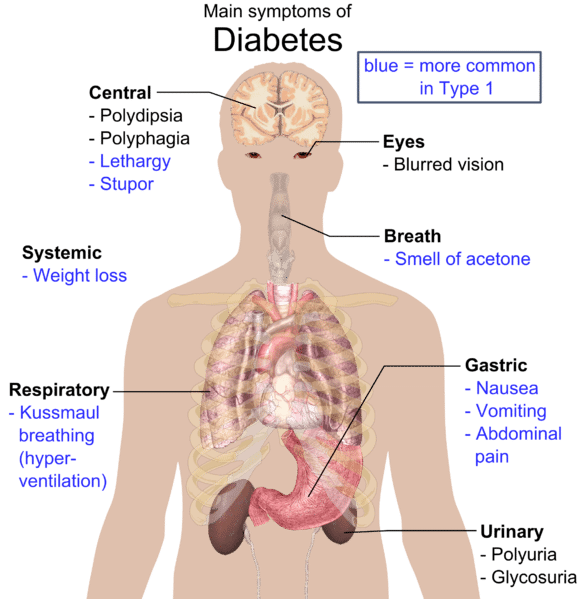
Now when we study the digestive system we see that the pancreas is a vital digestive organ. Exocrine glands secrete substances outside the body or into the gut while endocrine glands secrete substances into the blood. The pancreas secretes digestive juices through the pancreatic duct making it an exocrine gland.
The pancreas is located in the craniodorsal part of the abdomen in close association. Pancreas anatomy physiology introduction. Pancreatitis is an inflammation of the pancreas.
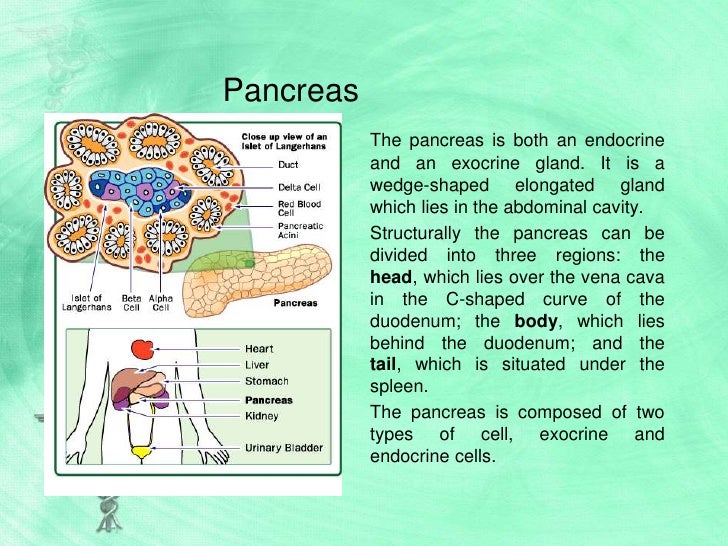
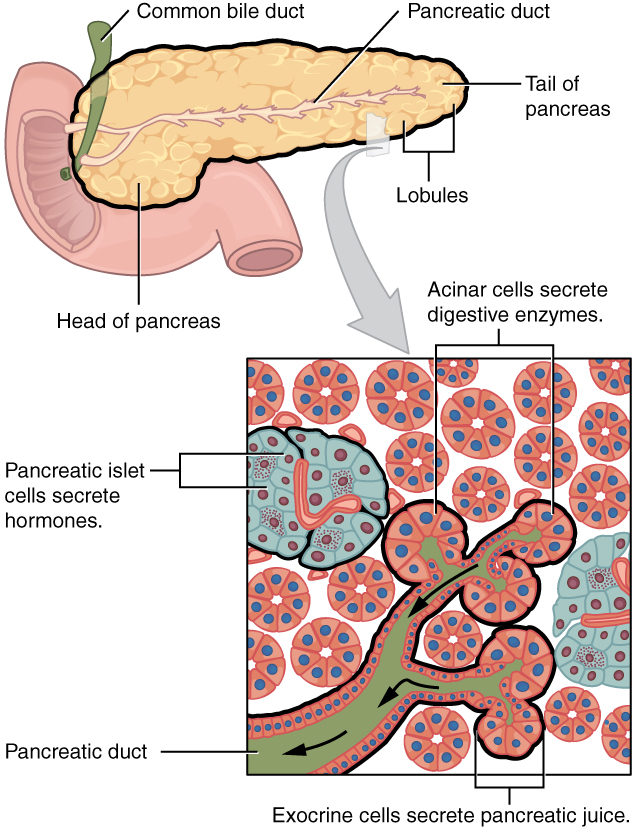
Delta cells which produce somatostatin. Beta cells which produce insulin. The body of the pancreas lies posterior to the distal portion of the stomach between the tail and the neck and is unlabeled in this drawing.
Pancreatic juice discharges into the duodenum through. The pancreatic islet cell types include alpha cells which produce glucagon. The right side of the organcalled the headis the widest part of the organ and lies in the curve of the duodenum the first division of the small intestine.
And pp cells which produce pancreatic polypeptide.
 Anatomy Amp Physiology Of The Pancreas Dm
Anatomy Amp Physiology Of The Pancreas Dm
 The Role And Anatomy Of The Pancreas
The Role And Anatomy Of The Pancreas
 Anatomy And Physiology Part 4 Pancreas And Pancreatic
Anatomy And Physiology Part 4 Pancreas And Pancreatic
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/11887/pancreas-in-situ_english.jpg) Pancreas Anatomy Functions Blood Supply Innervation Kenhub
Pancreas Anatomy Functions Blood Supply Innervation Kenhub

 Abdomen Anatomy Definition Function Muscles Biology
Abdomen Anatomy Definition Function Muscles Biology
 Understanding Pancreas Digestive Health Baseline Of Health
Understanding Pancreas Digestive Health Baseline Of Health
Acute Pancreatitis Armando Hasudungan
 23 6 Accessory Organs In Digestion The Liver Pancreas And
23 6 Accessory Organs In Digestion The Liver Pancreas And
 The Digestive System Ross And Wilson Anatomy And
The Digestive System Ross And Wilson Anatomy And
Digestive System Physiology Of The Pancreas Liver And T
Project Open Anatomy Learning Materials Tool2 Anatomytool
 All About Pancreas Anatomy Physiology Surgery
All About Pancreas Anatomy Physiology Surgery
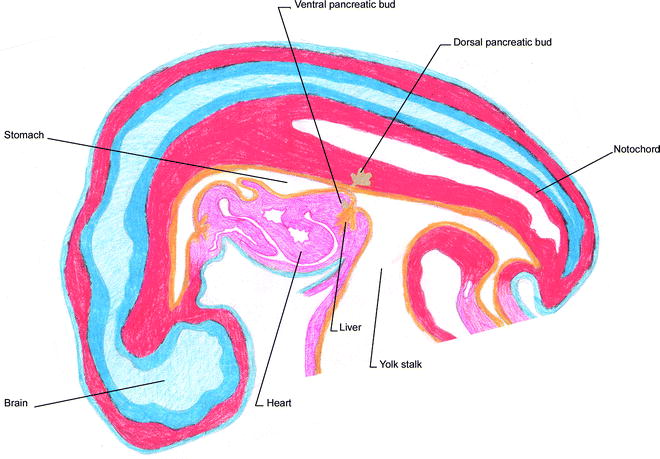 Pancreas Embryology Anatomy And Physiology Springerlink
Pancreas Embryology Anatomy And Physiology Springerlink
 The Cyclopaedia Of Anatomy And Physiology Anatomy
The Cyclopaedia Of Anatomy And Physiology Anatomy
 Pancreas Functions And Disorders
Pancreas Functions And Disorders
 Pancreas Clinical Anatomy And Physiology
Pancreas Clinical Anatomy And Physiology
Anatomy And Physiology Ii Pancreas Spleen Duodenum Model
 Endocrine Pancreas Insulin Glucagon
Endocrine Pancreas Insulin Glucagon
Losing A Grip On The Notion Of B Cell Specificity For Immune
 Pancreatitis Anatomy Physiology 101 With Dhere At Emory
Pancreatitis Anatomy Physiology 101 With Dhere At Emory
 Pancreas Gland Endocrine System
Pancreas Gland Endocrine System
 The Cyclopaedia Of Anatomy And Physiology Anatomy
The Cyclopaedia Of Anatomy And Physiology Anatomy

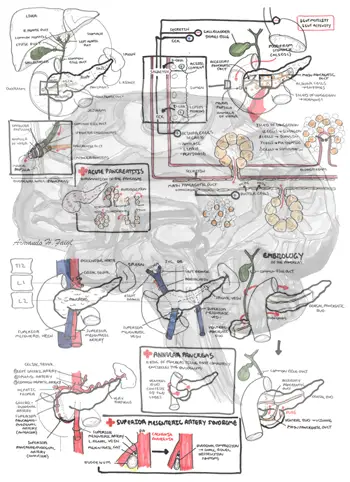 Pancreas Anatomy And Physiology
Pancreas Anatomy And Physiology
5 Pancreas Extracted From Anatomy And Physiology Classes
Digestive System Anatomy Of The Pancreas Liver And The
 Anatomy And Physiology Chapter 14 Liver Pancreas And
Anatomy And Physiology Chapter 14 Liver Pancreas And
 Pancreas Anatomy Physiology Wikivet English
Pancreas Anatomy Physiology Wikivet English



Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar