The anatomy of a tadpole is a tail a mouth and some gills until it begins to turn into a frog. Tube leading to the stomach tongue.
Tube leading to the lungs esophagus.
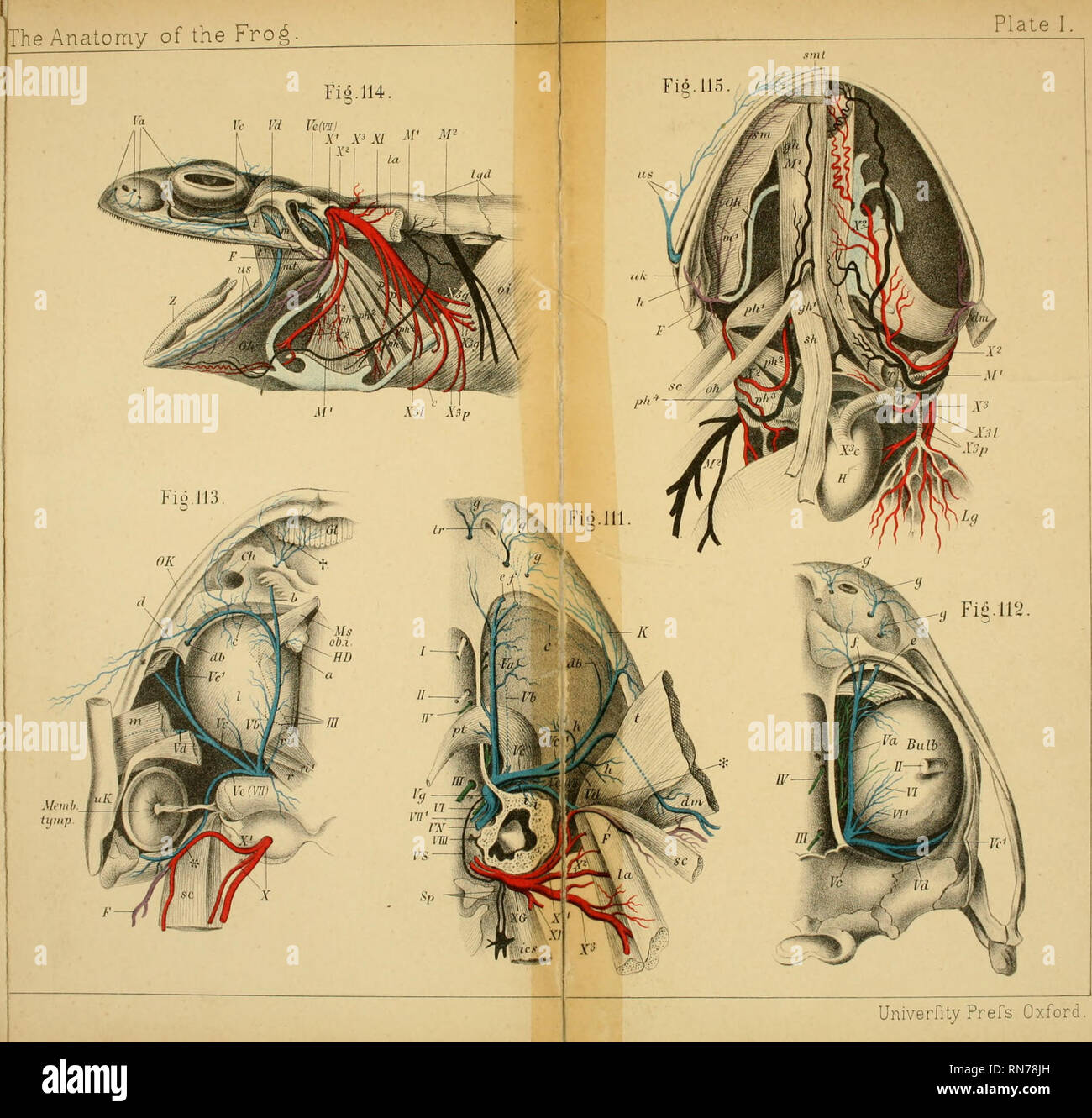
Frogs anatomy. They also have a highly developed sense of sight and smell. Anatomy of the frog. They use their keen sense of smell to detect chemical signals that help them identify potential food.
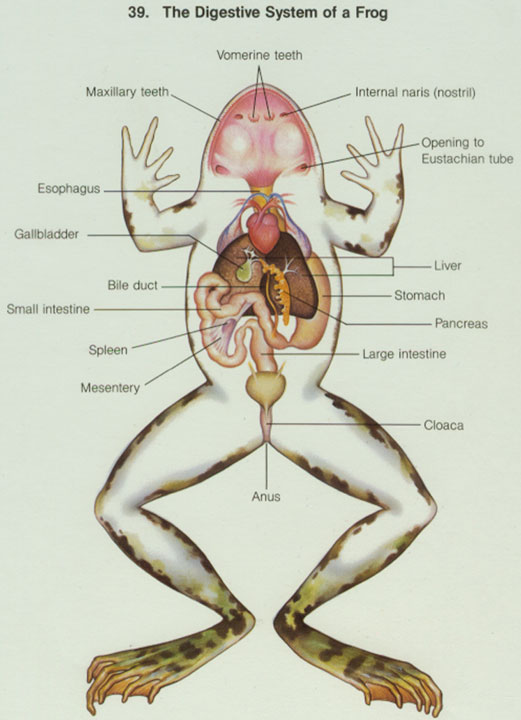
Functions of the internal anatomy of a frog. Both man and the frog have the same kinds of organs and systems of organs. Large intestine posterior organ of the digestive system which stores undigested food.
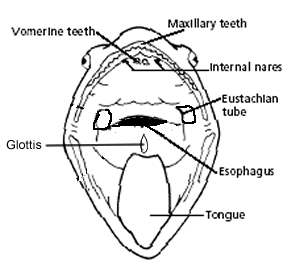
Equalize pressure in inner ear glottis. Frogs live on land most of the time but they are amphibians because they are born in the water because the female frogs lay their eggs under water and they start their life as tadpoles which have gills and can only live under water. Frog anatomy and dissection.
Body anatomy of a frog inside the body cavity of a frog there are many organ systems present such as the circulatory system digestive system respiratory system nervous system excretory system and reproductive system. Used for holding prey located around the edge of the mouth internal nares nostrils breathing connect to lungs eustachian tubes. Frogs can detect predators and prey using their large eyes that protrude from their head.
Frogs are used for dissections in high school and university anatomy classes often first being injected with coloured substances to enhance contrasts among the biological systems. Liver secretes bile and processes digested food molecules urinary bladder the organ that collects and stores urine until released. As in other higher vertebrates the frog body may be divided into a head a short neck and a trunk see vertebrates.
All the organs and organ systems are well developed with specific functions. This practice is declining due to animal welfare concerns and digital frogs are now available for virtual dissection. Frogs have two forelimbs in the front or anterior end and two powerful hind limbs in the rear or posterior for swimming.
The webbing creates resistance in the water allowing frogs to be agile swimmers. The frogs anatomy however is much simpler. Each forelimb has four toes but the hind limbs have five toes with webbing in between.
Let us know more about these organ systems. The body structure or anatomy of the frog is very similar to the anatomy of man. Fat bodies masses of fat in the body cavities of frogs.
 Diagram Of Frog Anatomy Huge Color Image
Diagram Of Frog Anatomy Huge Color Image
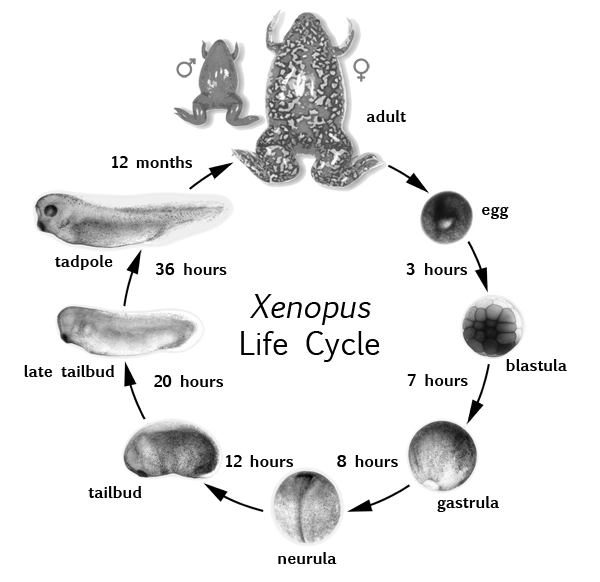 Introduction To Xenopus Xenbase A Xenopus Laevis And
Introduction To Xenopus Xenbase A Xenopus Laevis And
Copy Of Frog Dissection Lessons Tes Teach
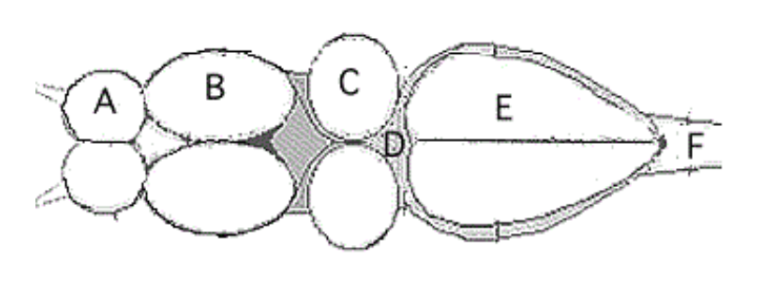 Study And Removal Of The Frog S Brain Biology Libretexts
Study And Removal Of The Frog S Brain Biology Libretexts
 Amazon Com The Frog S Anatomy Graphic Illustration T Shirt
Amazon Com The Frog S Anatomy Graphic Illustration T Shirt
Red Eyed Tree Frog Printout Enchanted Learning Software
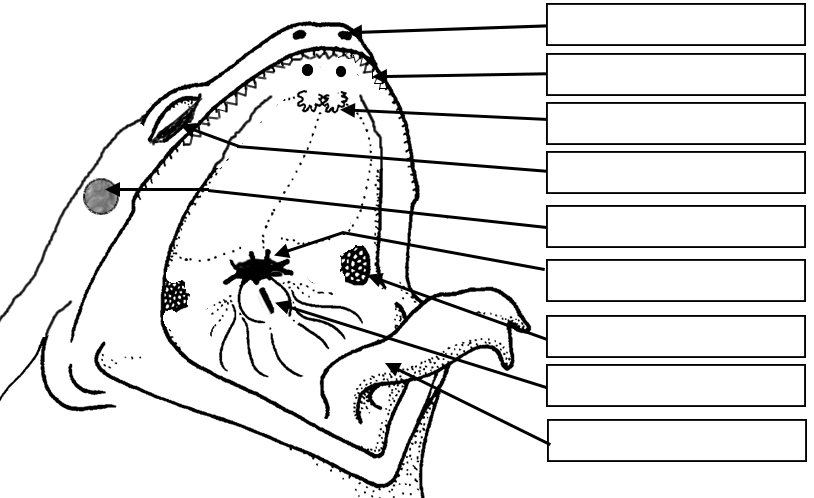 Frog Dissection External Anatomy
Frog Dissection External Anatomy
 The Frog S Anatomy Illustration Poster
The Frog S Anatomy Illustration Poster
 Frog And Human Anatomy Comparison Ms Pearrow S 7th Grade
Frog And Human Anatomy Comparison Ms Pearrow S 7th Grade
 Internal Anatomy Of A Frog Purposegames
Internal Anatomy Of A Frog Purposegames
Geography Of Frogs Frogs Anatomy
 The Anatomy Of The Insect Eating Slimy Frog
The Anatomy Of The Insect Eating Slimy Frog
 The Frog S Anatomy Camper Mug White
The Frog S Anatomy Camper Mug White
 The Anatomy Of The Frog Frogs Anatomy Amphibians
The Anatomy Of The Frog Frogs Anatomy Amphibians
Class 11 Zoology Chapter Morphology Anatomy Of Earthworm
 Frog Diagram Anatomy Contact Sheri Amsel For Prior Written
Frog Diagram Anatomy Contact Sheri Amsel For Prior Written
 How To Draw Frogs And Toads John Muir Laws
How To Draw Frogs And Toads John Muir Laws
 Frogs And Toads Color Vision Found To Function In Near
Frogs And Toads Color Vision Found To Function In Near
Frog Dissection Lessons Tes Teach
 3d Frog Anatomy Software Biosphera Org
3d Frog Anatomy Software Biosphera Org
 Amazon Com Frog Dissection Model Animal Dissecting Kits
Amazon Com Frog Dissection Model Animal Dissecting Kits
 Comparative Anatomy Dog Vs Frog By Nirjhar Deb Infographic
Comparative Anatomy Dog Vs Frog By Nirjhar Deb Infographic




Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar