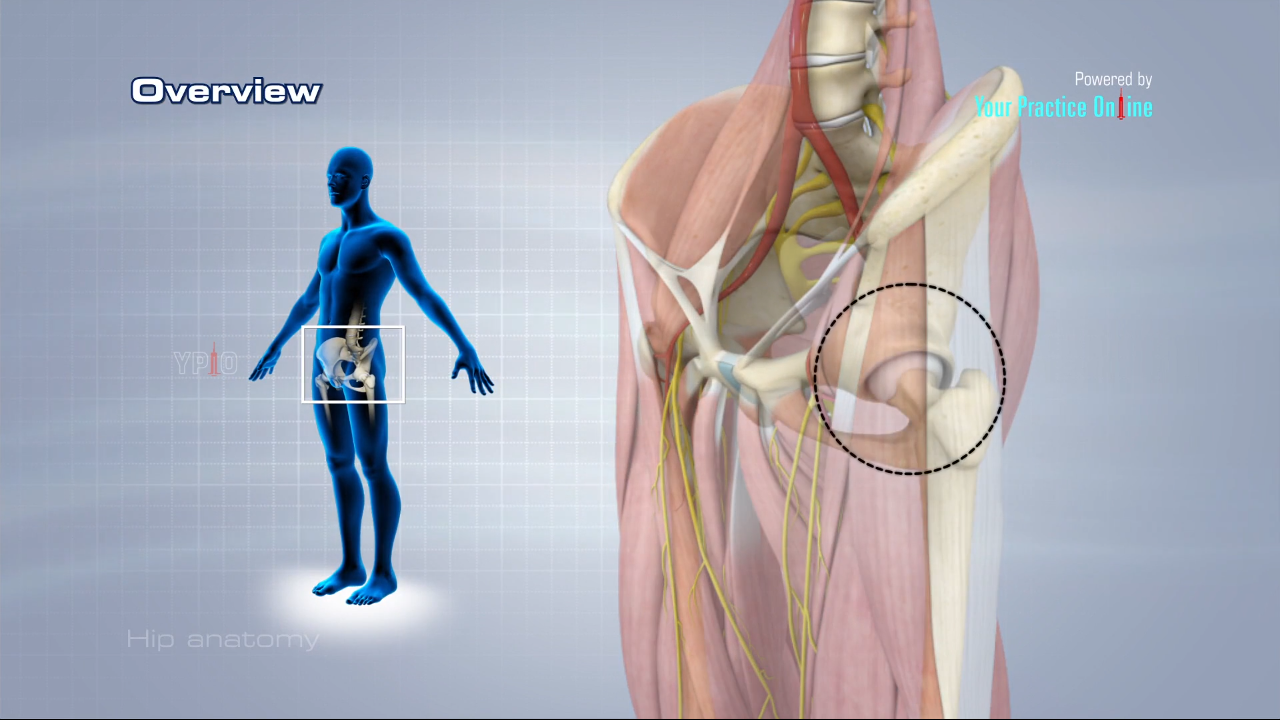
And synovial membrane and fluid which encapsulates the hip joint and lubricates it respectively. Hip anatomy function and common problems.
 Lower Anatomy Hip Ligament Diagram Quizlet
Lower Anatomy Hip Ligament Diagram Quizlet
The only intracapsular ligament is the ligament of head of femur.
Hip anatomy ligaments. Hip problems occur when any one of these components starts to degenerate or is in some way compromised or irritated. The iliofemoral ligament is the strongest ligament in the body and checks extension adduction superior fibers and abduction inferior fibers. The thigh bone or femur and the pelvis join to form the hip joint.
Hip joint capsule attaches anteriorly to the along the intertrochanteric crest. It attaches to the anatomical structures known as the acetabular labrum the transverse acetabular ligament and the intertrochanteric line of the femur. It keeps the hip from hyper extension.
The most notable ligaments in the hip joint are. Since the cartilage is smooth and slippery the bones move against each other easily and without pain. The hip joint is the largest weight bearing joint in the human body.
The extracapsular ligaments are the iliofemoral ischiofemoral and pubofemoral ligaments attached to the bones of the pelvis the ilium ischium and pubis respectively. They can be divided into two groups intracapsular and extracapsular. It is also referred to as a ball and socket joint and is surrounded by muscles ligaments and tendons.
Three ligaments iliofemoral ligament y ligament of bigelow strongest ligament. Ligaments joint capsule. The hip joint is reinforced by four ligaments of which three are extracapsular and one intracapsular.
Take a hip test. It is a relatively small structure which runs from the acetabular fossa to the fovea of the femur. Large ligaments tendons and muscles around the hip joint called the joint capsule hold the bones ball and socket in place and keep it from dislocating.
Iliofemoral ligament which connects the pelvis to the femur at the front of the joint. The hip joint is encircled with ligaments to provide stability to the hip by forming a dense and fibrous structure around the joint capsule. Hip ligaments and tendons tough fibrous tissues that bind bones to bones and muscles to bones.
Pubofemoral ligament which attaches the most forward part of the pelvis known as the pubis to the femur. The capsule of the hip joint has been described as strong and fibrous but loose enough to accommodate a range of movements. In addition because this ligament limits hip extension it allows maintenance of the upright posture by reducing the need for muscle contractions.
Iliofemoral ligament this is a y shaped ligament that connects the pelvis to the femoral head at the front of the joint. The ligaments of the hip joint act to increase stability. Extends posteriorly only partially across the femoral neck basicervical and intertrochanteric regions are extracapsular.
Aiis to intertrochanteric line. The ligaments adjoining the hip joint include.
 Hip Joint Model With Ligaments
Hip Joint Model With Ligaments
Hip Anatomy Orthopedic Surgery Algonquin Il Barrington
Posterior Cruaciate Ligament Injury Hip And Knee Clinic
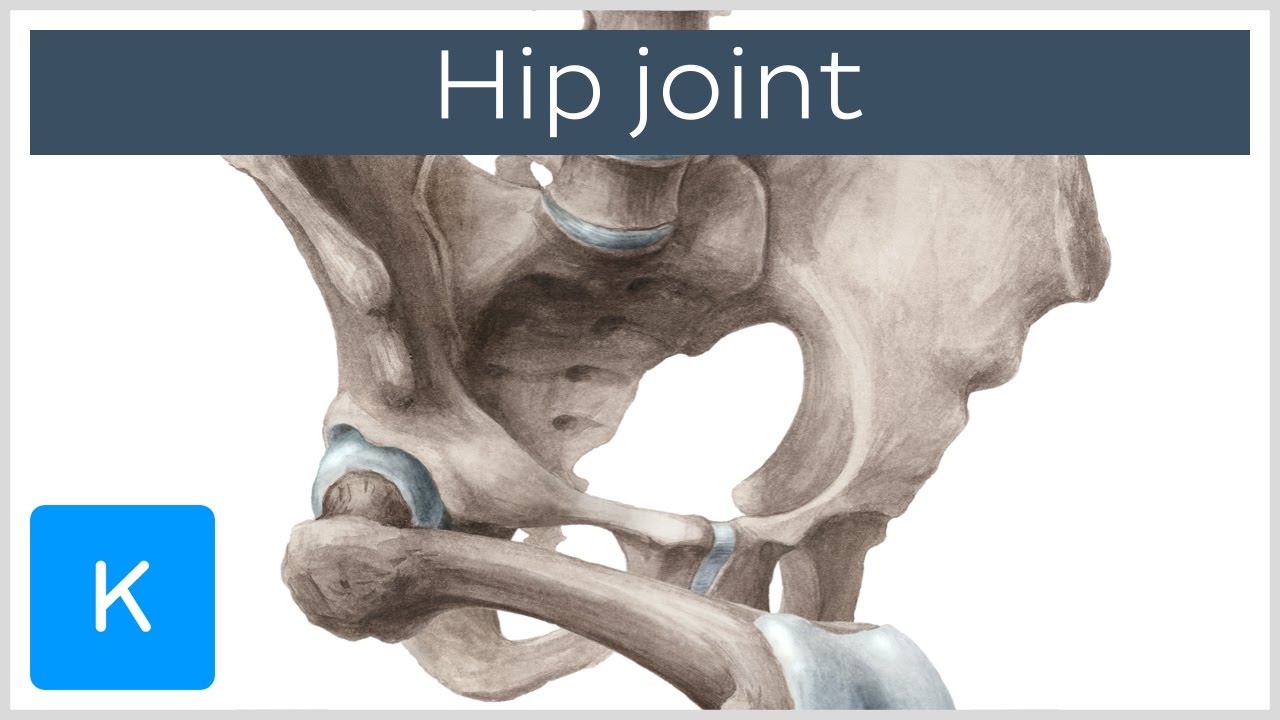 Hip Joint Bones Ligaments Blood Supply And Innervation Anatomy Kenhub
Hip Joint Bones Ligaments Blood Supply And Innervation Anatomy Kenhub
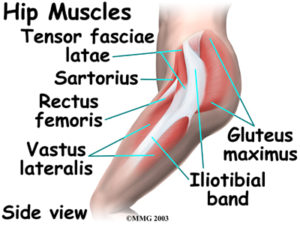 Ligaments Tendons And Muscles Of The Hip Joint Naples
Ligaments Tendons And Muscles Of The Hip Joint Naples
Ligaments Of The Lumbar Spine And Pelvis
 Hip Anatomy Hip Surgeon Columbia Sc Hip Treatment
Hip Anatomy Hip Surgeon Columbia Sc Hip Treatment
 Hip Anatomy Recon Orthobullets
Hip Anatomy Recon Orthobullets
 Anterior Aspect Of The Hip Ligaments Synovial Joint
Anterior Aspect Of The Hip Ligaments Synovial Joint
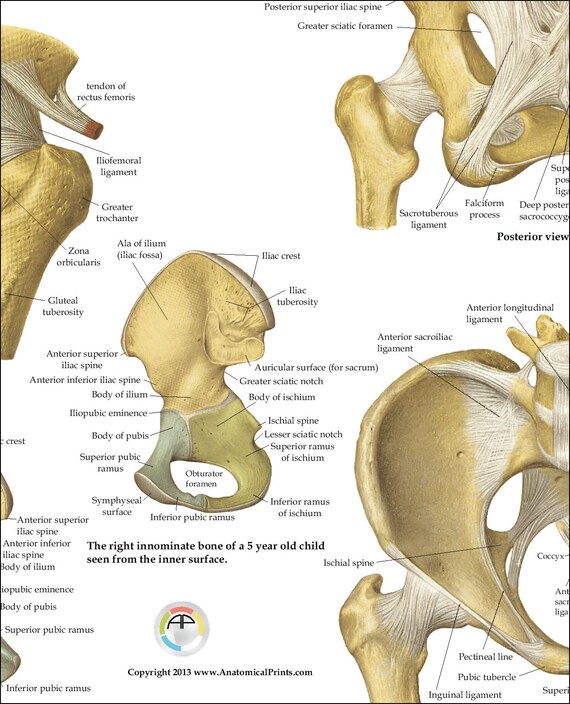 Human Ligaments And Bones Of The Hip And Pelvis Anatomy Poster 18 X 24 Medical Chart
Human Ligaments And Bones Of The Hip And Pelvis Anatomy Poster 18 X 24 Medical Chart
Total Hip Arthroplasty Morphopedics
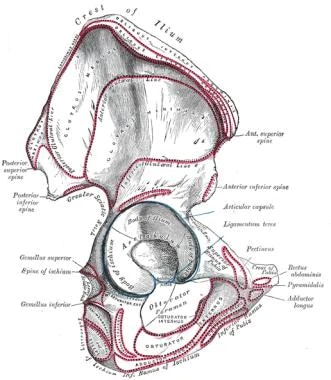 Hip Joint Anatomy Overview Gross Anatomy
Hip Joint Anatomy Overview Gross Anatomy

 Bones Ligaments Joints Atlas Of Anatomy
Bones Ligaments Joints Atlas Of Anatomy
 Joints Ligaments And Connective Tissues Advanced Anatomy
Joints Ligaments And Connective Tissues Advanced Anatomy
 Hip Anatomy Yoga Understanding The Hips For Yoga Jason
Hip Anatomy Yoga Understanding The Hips For Yoga Jason
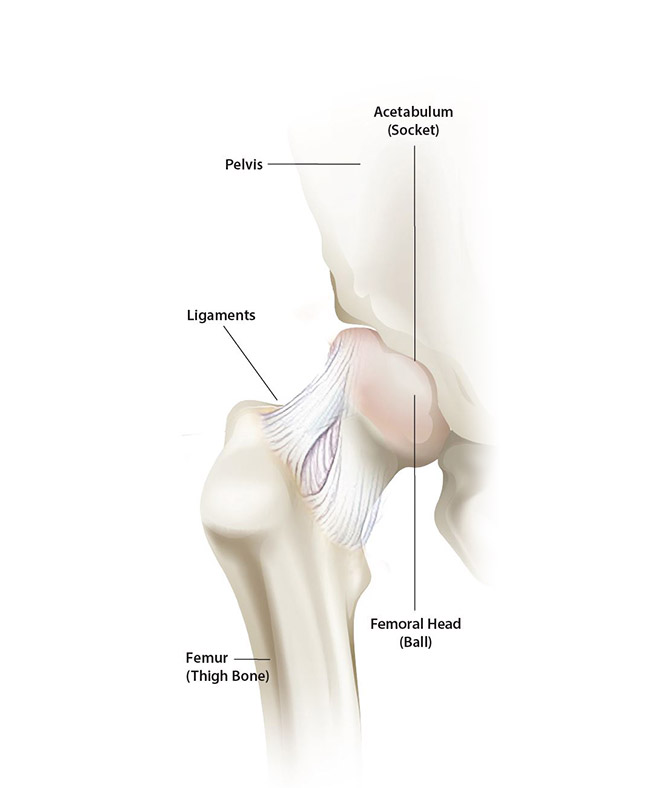 Understanding Total Hip Replacement Microport Orthopedics
Understanding Total Hip Replacement Microport Orthopedics
 Hip Joint Anatomy Hip Bones Ligaments Muscles
Hip Joint Anatomy Hip Bones Ligaments Muscles
 Acetabular Fractures Orthoinfo Aaos
Acetabular Fractures Orthoinfo Aaos
Hip Joint Treatment Sydney Hip Ligaments Treatment Sydney



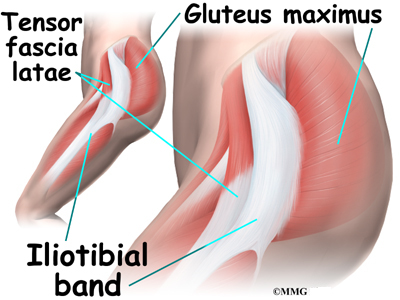

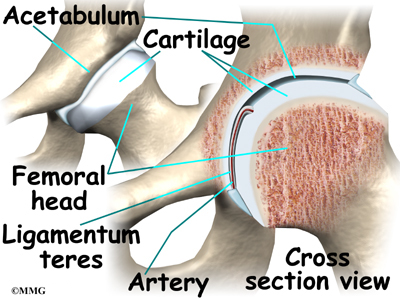
Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar