The brachial veins are the largest in size and are situated either side of the brachial artery. 2 the subclavian vein occasionally rises in the neck to a level with the third part of the subclavian artery and occasionally passes with this vessel behind the scalenus anterior.
 Venous Lymphatic Drainage Of Upper Limb
Venous Lymphatic Drainage Of Upper Limb
Chronic upper extremity venous disease.

Venous anatomy upper extremity. Technique and normal anatomy the venous anatomy of the neck thoracic inlet and arm is illustrated in figure 1. The diagnosis of chronic venous disease is considerably more challenging than acute venous disease because enlarged thrombusfilled veins are not present. The deep venous system of the upper limb is situated underneath the deep fascia.
In green you can see arising laterally from the dorsal venous network is the cephalic vein and from the medial aspect of the dorsal venous network weve got the basillic vein which ive highlighted in purple. Upper limb dvt ultrasound normal anatomy basic deep venous anatomy of the arm. The routine examination includes interrogation of the inter nal jugular brachiocephalic subclavian axillary brachial and basilic veins of the symptomatic upper extremity.
Vena comitantes and superficial veins. Dorsal digital veins dorsal metacarpal veins palmar digital veins intercapitular veins dorsal venous network palmar venous network cephalic vein basilic vein median antebrachial vein. In the hand forearm and upper arm the superficial system functions as the principal means for venous drainage.
The hand is a very mobile part of the upper limb and we perform very specialised tasks with it every day key adaptations can be seen in the specialised structures of the hand. This vein as well as the deep veins act as counterparts to the arteries supplying the arm by bringing deoxygenated blood back to the heart. Evaluation of the cephalic vein.
The superficial venous system of the upper limb essentially consists of two main veins which arise from the dorsal venous network. Veins for the upper extremity direct blood flow from the hand wrist forearm upper arm and shoulder to the ipsilateral central thorax veins and ultimately the superior vena cava. The superficial veins of the upper extremity are the digital metacarpal cephalic basilic median.
In the upper extremity the deep veins share the name of the artery they accompany. Chronic venous disease may affect the upper extremity after an acute thrombotic event of any cause or in any patient with longterm catheterization. It is formed by paired veins which accompany and lie either side of an artery.
Basic superficial venous anatomy of the arm. Veins of the upper extremities are grouped into deep veins which are accompanying veins of arteries from which they derive their names latin.
 Cardiovascular System Of The Arm And Hand
Cardiovascular System Of The Arm And Hand
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/7442/WKoUybPwsfA4Pe1075q5lw_b1gZoVsy7X_Vena_mediana_cubiti_1.png) Veins Of The Upper Limb Anatomy Kenhub
Veins Of The Upper Limb Anatomy Kenhub
Emdocs Net Emergency Medicine Educationcore Em
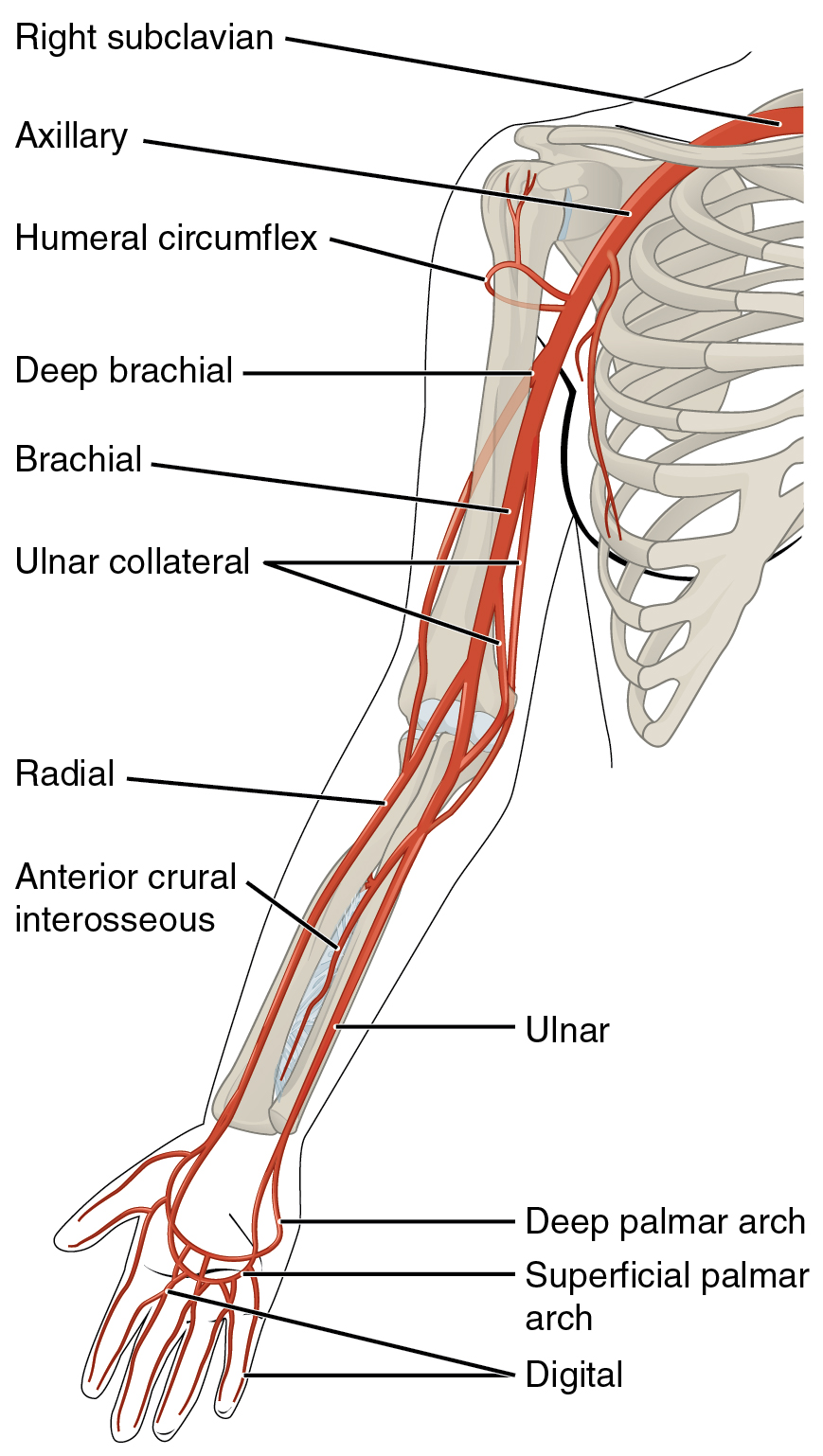 20 5 Circulatory Pathways Anatomy And Physiology
20 5 Circulatory Pathways Anatomy And Physiology
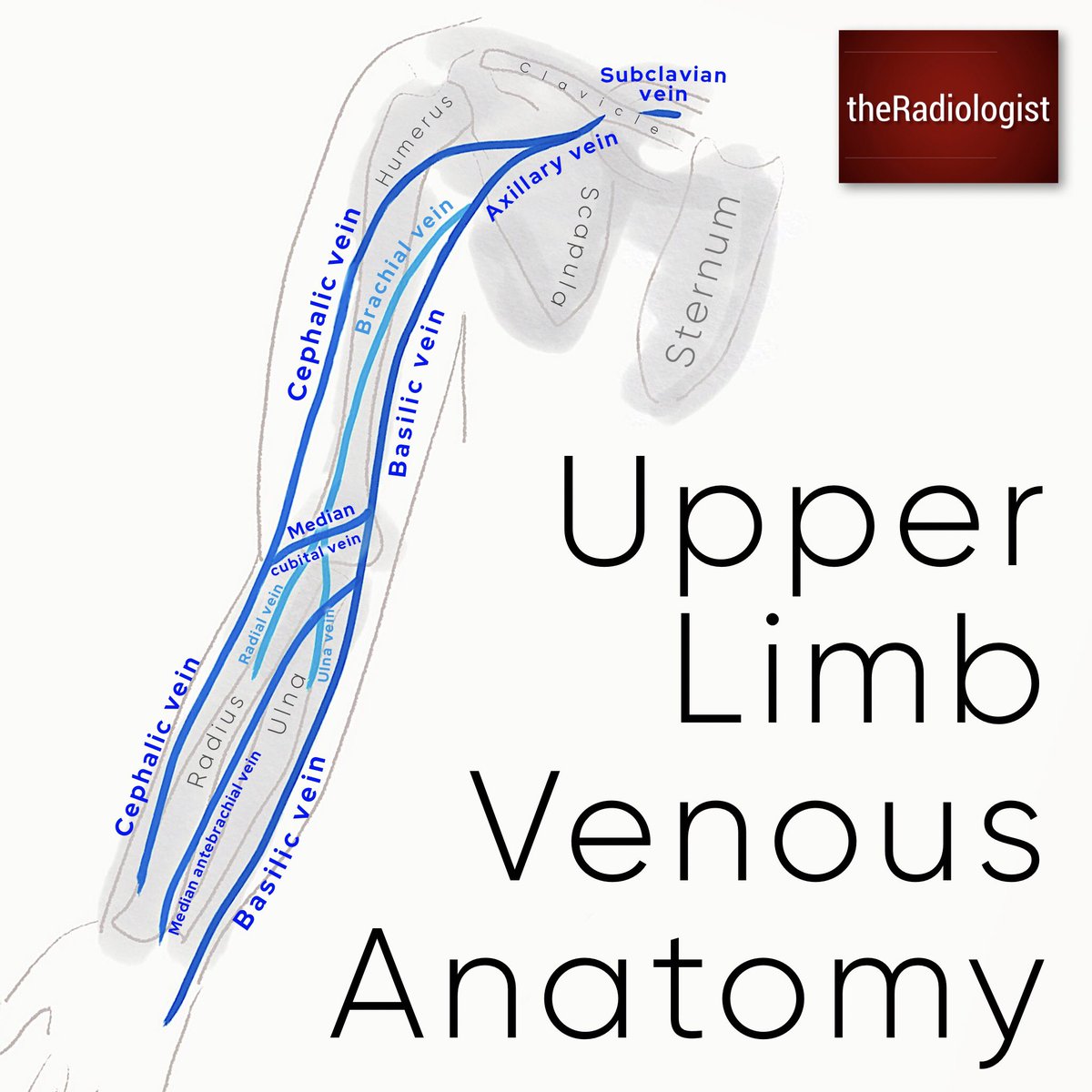 Theradiologist On Twitter Diagram Simplified Diagram Of
Theradiologist On Twitter Diagram Simplified Diagram Of
:watermark(/images/watermark_5000_10percent.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/atlas_overview_image/771/PoKFfwUGXrJ4sytwNutLA_upper-arm-nerves-vessels_english.jpg) Upper Limb Arteries Veins And Nerves Kenhub
Upper Limb Arteries Veins And Nerves Kenhub
 Clinical Education Intravenous Therapy Skills
Clinical Education Intravenous Therapy Skills
 Chapter 33 Venous And Intraosseous Access In Adults
Chapter 33 Venous And Intraosseous Access In Adults
 Figure 6 From Emergency Department Diagnosis Of Upper
Figure 6 From Emergency Department Diagnosis Of Upper
 Sonographic Evaluation Of Upper Extremity Deep Venous
Sonographic Evaluation Of Upper Extremity Deep Venous
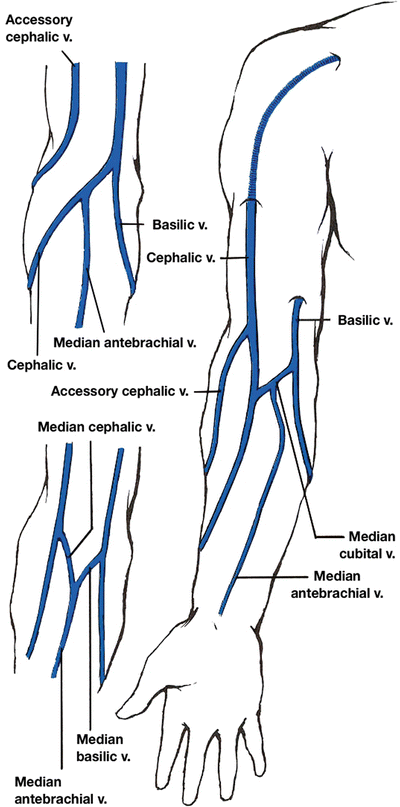 Vascular Anatomy Of The Upper Limbs Springerlink
Vascular Anatomy Of The Upper Limbs Springerlink
:watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/cephalic-vein-2/eLJ5jKP7qJXngpaABmDZpQ_V._cephalica_02.png) Veins Of The Upper Limb Anatomy Kenhub
Veins Of The Upper Limb Anatomy Kenhub
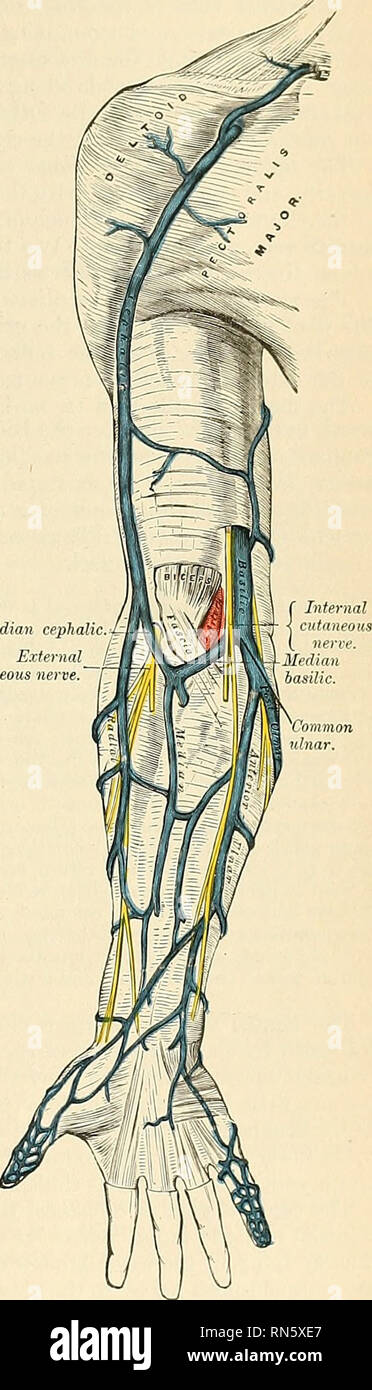 Anatomy Descriptive And Applied Anatomy The Superficial
Anatomy Descriptive And Applied Anatomy The Superficial
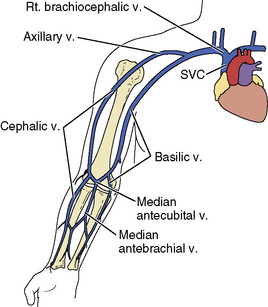 Interventions For Failing Hemodialysis Access Thoracic Key
Interventions For Failing Hemodialysis Access Thoracic Key
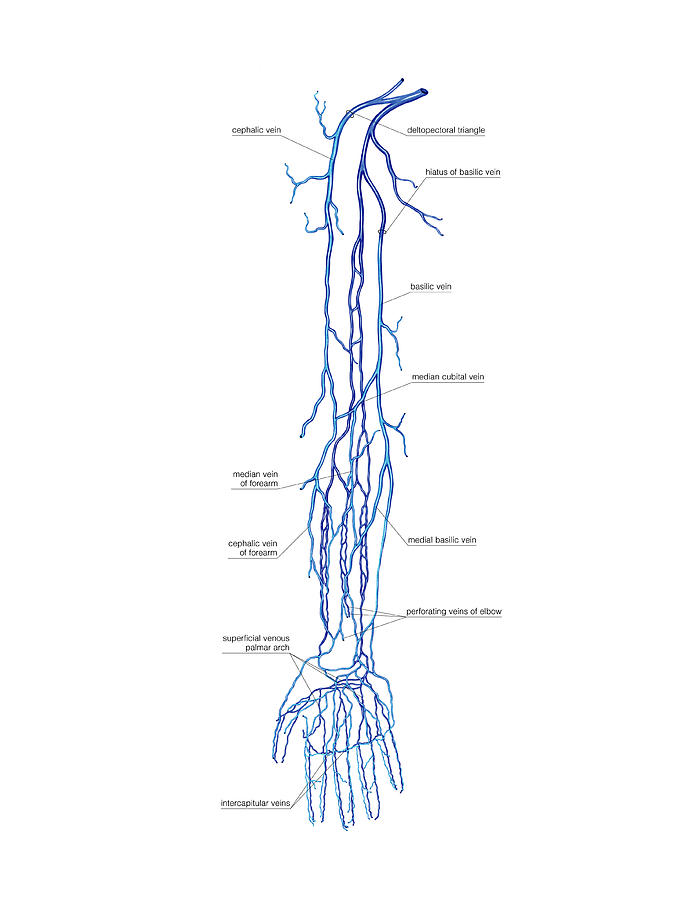 Venous System Of The Upper Limb
Venous System Of The Upper Limb
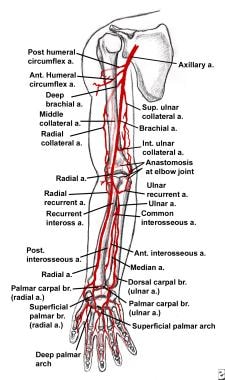 Vascular Upper Extremity Injury Background History Of The
Vascular Upper Extremity Injury Background History Of The
 Arm Dvt Normal Ultrasoundpaedia
Arm Dvt Normal Ultrasoundpaedia
 Venous Anatomy And Upper Extremity
Venous Anatomy And Upper Extremity
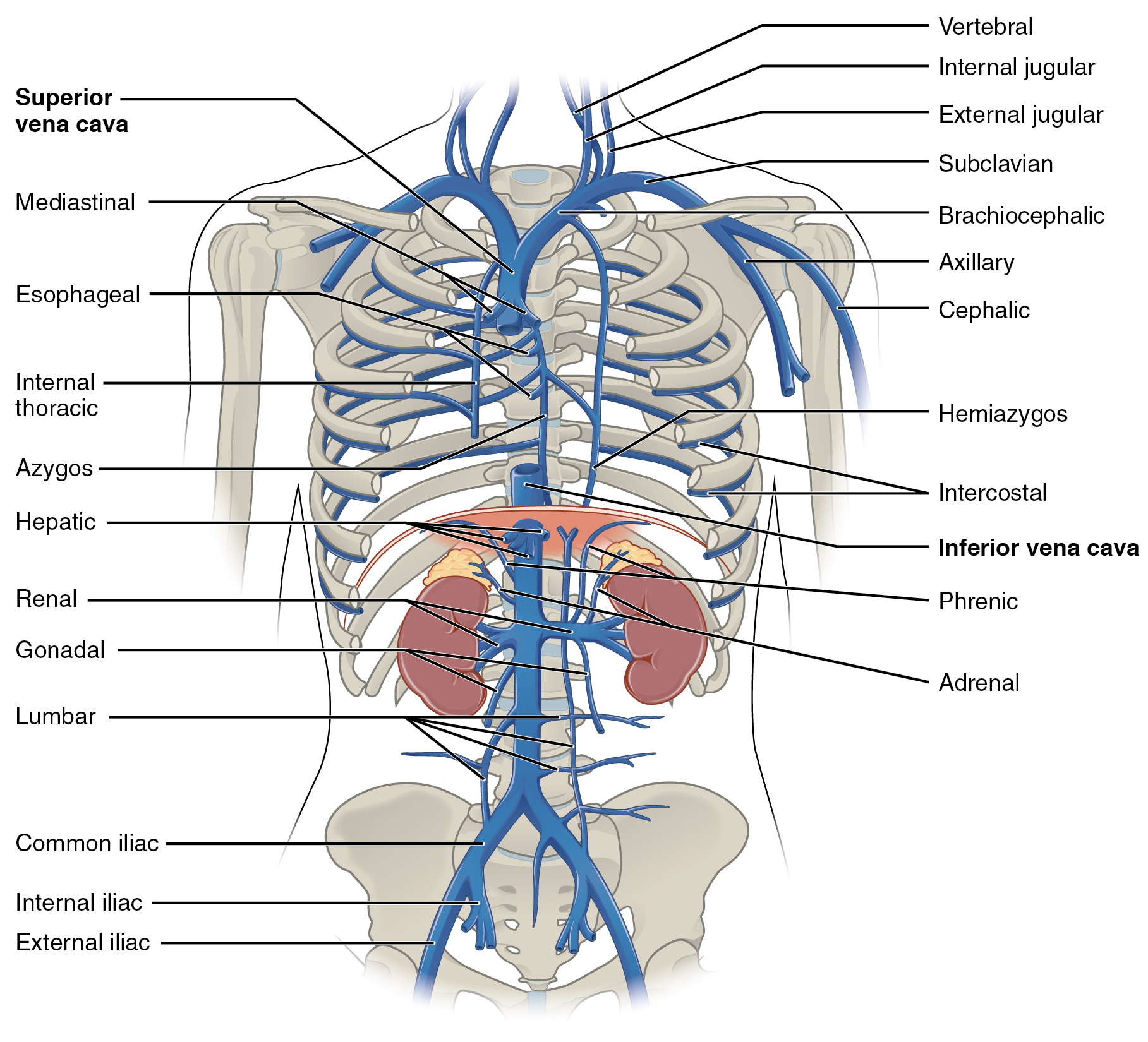 20 5 Circulatory Pathways Anatomy And Physiology
20 5 Circulatory Pathways Anatomy And Physiology
 Upper Limb Veins Illustrations Radiology Case
Upper Limb Veins Illustrations Radiology Case
 The Veins Of The Upper Extremity And Thorax Human Anatomy
The Veins Of The Upper Extremity And Thorax Human Anatomy



Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar