Abnormalities in the metabolism of glucose and fat in diabetic dogs cause an accumulation of fat in the liver that may eventually result in liver dysfunction. Steroid hepatopathy is a condition in which there is excessive glycogen deposition in liver cells due to high circulating levels of steroids in the blood.
 Imaging Essentials Small Animal Abdominal Ultrasonography
Imaging Essentials Small Animal Abdominal Ultrasonography
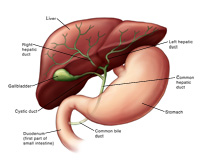
In dogs the livers left lobe medial sublobe quadrate lobe and right lobe medial sublobe encircle the gallbladder.

Liver anatomy dog. Other common symptoms of liver disease are gastrointestinal signs such as decreased appetite vomiting and diarrhea weight loss increased drinking and urination and changes in stool color. The rear legs of the dog begin with the femur bone which extends to a pair of bones known as the tibia and the fibula. Signs of liver disease in dogs.
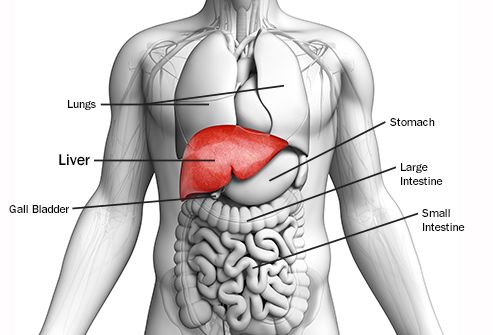
The liver is a multi lobed organ that is located at the most forward part of the abdomen. The caudate lobe extends dorsally and caudally ending with the renal fossa which contains the cranial pole of the right kidney. It is so far forward that it lays up against the diaphragm the muscle that aids in breathing in mammals birds and reptiles do not have a diaphragmthis autopsy picture of a cat shows the gallbladder in green with several lobes of the liver laying right up against the diaphragm towards the top of the.
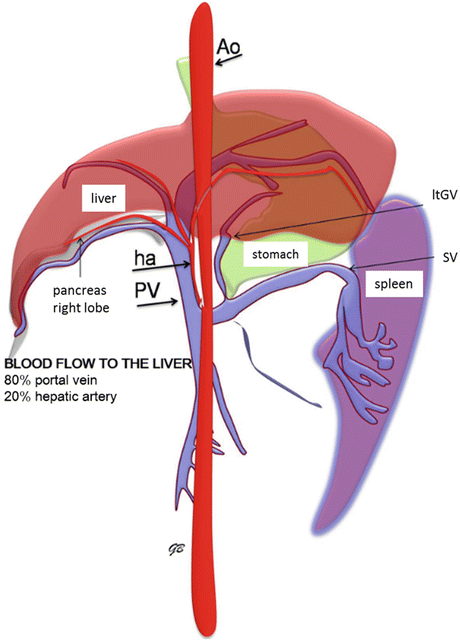
An enlarged caudate process contacts the right kidney. Alt ast ggt albumin and bilirubin are important values on the chemistry profile that are often abnormal in dogs that have liver disease. Complete obstruction of the hepatic artery is fatal.
Vomiting loss of appetite or diarrhea. Both the left and right lobes are subdivided. Liver disease in dogs is diagnosed through history physical examination complete blood count bile acid testing urinalysis radiographs x ray abdominal ultrasound and biopsy.
Dogs may develop fluid retention in the abdomen commonly referred to as ascites. It is less lobated. The liver is contained entirely within the rib cage to the right of the midline.
Canine liver and anatomy canine liver disease is among the top five leading causes of non accidental death in dogs and as such should be taken seriously. In experimental studies normal dogs tolerated acute removal of 65 to 70 of total liver volume but they did not tolerate 84 removal154 204 and approximately 28 of dogs survived at least 7 days after 80 hepatectomy. The liver is responsible for a number of essential bodily functions and if it is compromised in any way your dogs overall health is in jeopardy.
These further extend to the heel bone known as tarsus the paw bone known as metatarsus and the toe bone phalange. Fortunately the normal liver has an incredible regenerative capacity. The liver is almost entirely intra thoracic.
A liver sick dog may also present with.
:watermark(/images/watermark_only.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/ligamentum-coronarium-hepatis-2/WQJ8r8OfKhR7hbdhEEuctg_Coronary_ligament_of_liver.png) Liver Ligaments And Liver Anatomy Kenhub
Liver Ligaments And Liver Anatomy Kenhub
 Disorders Of The Liver And Gallbladder In Dogs Dog Owners
Disorders Of The Liver And Gallbladder In Dogs Dog Owners
 Dog Digestive Apparatus Veterinary Science Tv2001 With
Dog Digestive Apparatus Veterinary Science Tv2001 With
 Porta Hepatis An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Porta Hepatis An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

 Dog Prosection Demonstrating The Complex Anatomy Of The
Dog Prosection Demonstrating The Complex Anatomy Of The
 Pdf Comparative Study Of The Liver Anatomy In The Rat
Pdf Comparative Study Of The Liver Anatomy In The Rat
 Digestive System Anatomy And Physiology Liver Anatomy
Digestive System Anatomy And Physiology Liver Anatomy
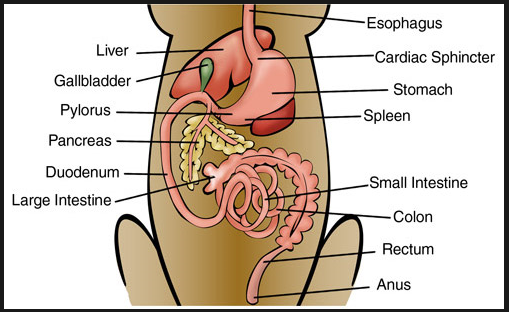 Canine Anatomy Learn About Animal Anatomy
Canine Anatomy Learn About Animal Anatomy
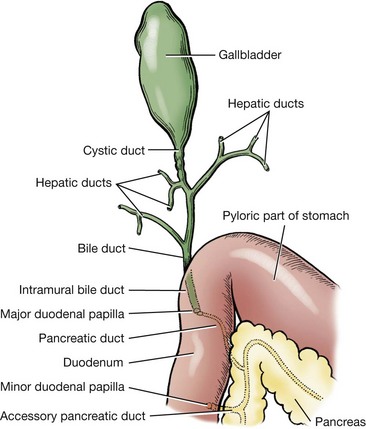 Liver And Biliary System Veterian Key
Liver And Biliary System Veterian Key
 Liver Lobes Anatomy Liver Anatomy Bile Duct Dog Anatomy
Liver Lobes Anatomy Liver Anatomy Bile Duct Dog Anatomy
 Figure 1 From Corrosion Cast Study Of The Canine Hepatic
Figure 1 From Corrosion Cast Study Of The Canine Hepatic
 Anatomy Of Domestic Dog And Cat Educational Chart Cool Wall Decor Art Print Poster 12x18
Anatomy Of Domestic Dog And Cat Educational Chart Cool Wall Decor Art Print Poster 12x18
 Liver Anatomy Pt 1 Proprofs Quiz
Liver Anatomy Pt 1 Proprofs Quiz
 Liver Anatomy Physiology Wikivet English
Liver Anatomy Physiology Wikivet English
 Vector Illustration Of Digestive System Of The Dog Anatomy
Vector Illustration Of Digestive System Of The Dog Anatomy
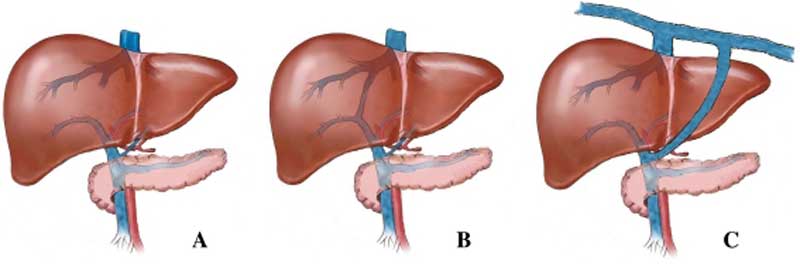 File Dog Liver Portosystemic Shunts Jpg Embryology
File Dog Liver Portosystemic Shunts Jpg Embryology
 Human Liver Anatomy Stock Vector Royalty Free 1067046614
Human Liver Anatomy Stock Vector Royalty Free 1067046614
Anatomy Of The Canine Digestive System Easyanatomy


Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar