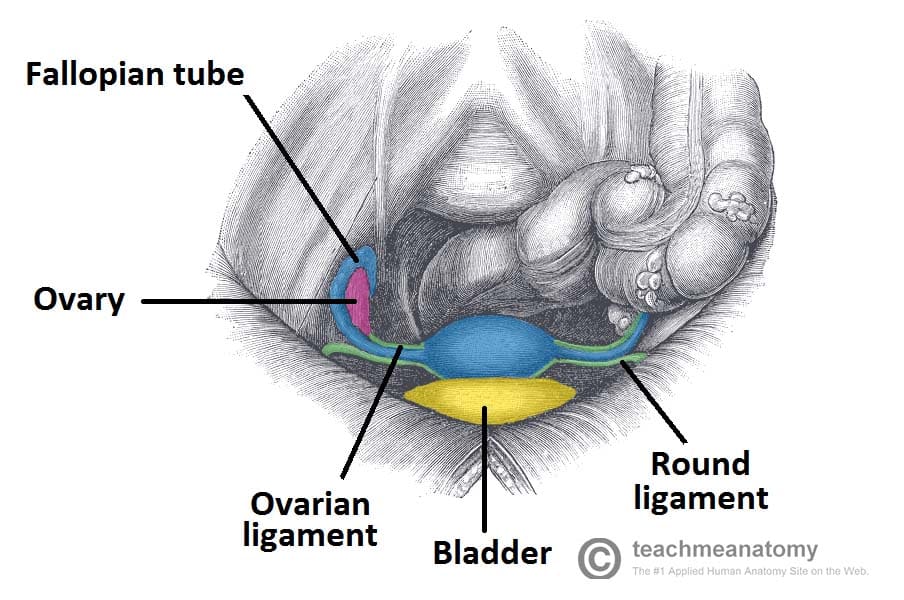
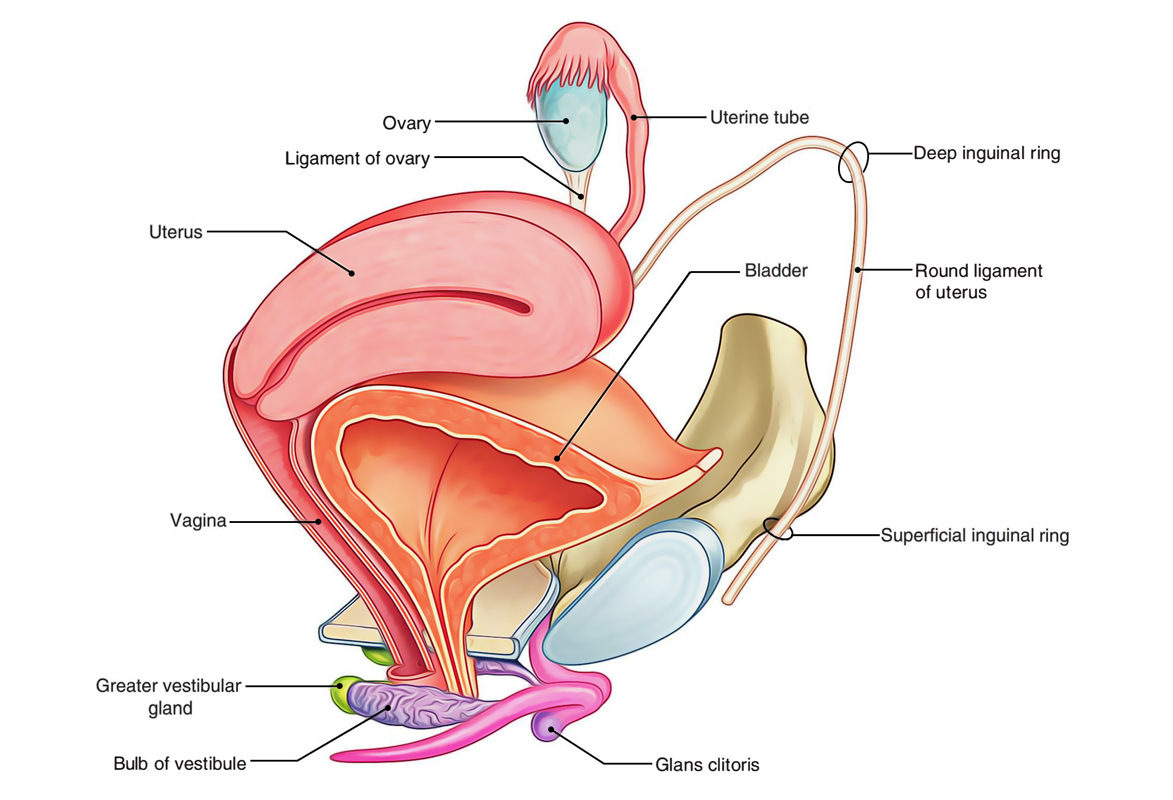
The ovarian ligament extends from the medial side of an ovary to the uter ine wall and the broad ligament is a fold of the peri toneum that covers the ovaries. They produce the ova eggs that when fertilized will develop into a fetus.
They also generate the female sex hormones estrogen and progesterone.

Ovary anatomy. They are paired organs located on either side of the uterus within the broad ligament below the uterine fallopian tubes. They lie within the ovarian fossa on the posterior wall of the true pelvis. On the concave surface of the ovary is the ovulation fossa where the oocyte is expelled from the ovary.
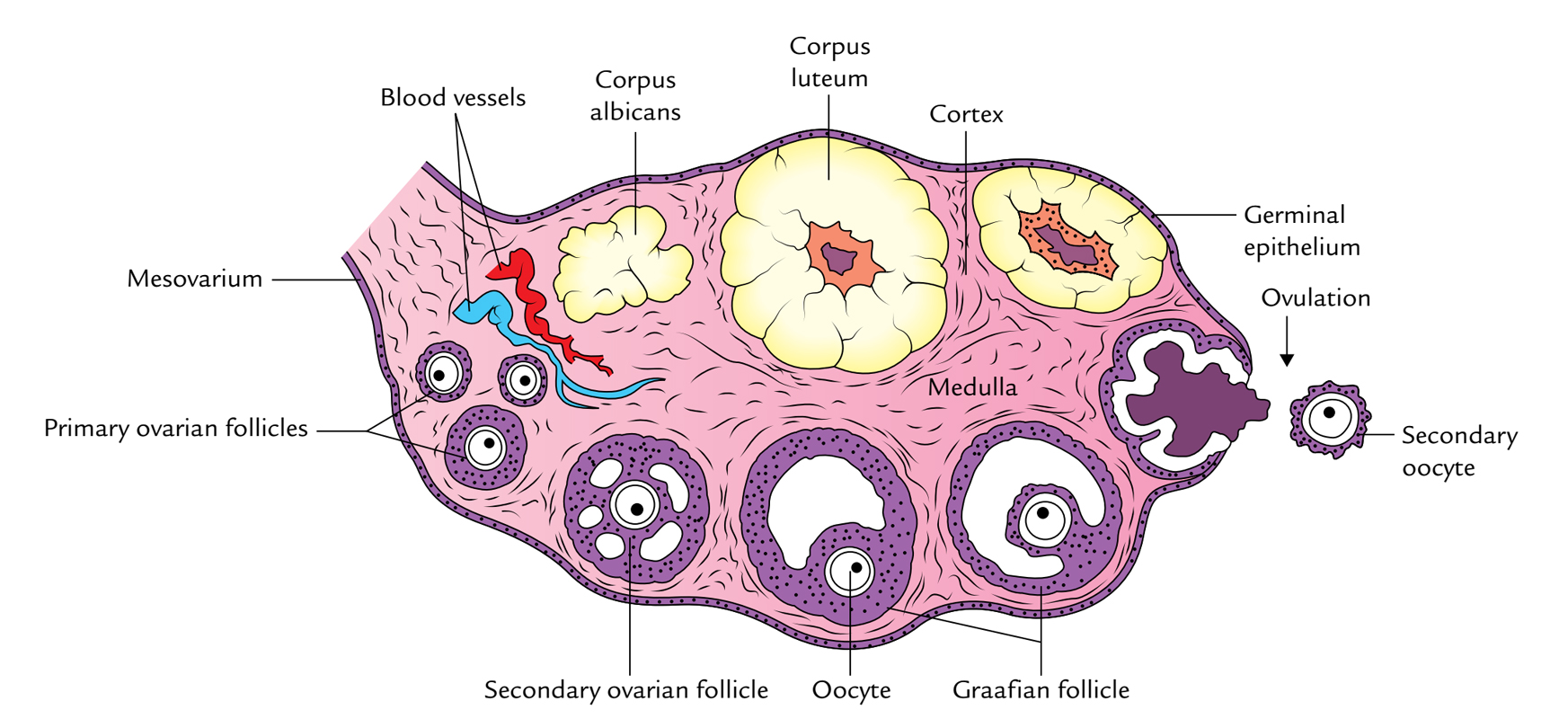
Neurovascular structures enter the hilum of the ovary via the mesovarium. The inner layer cortex contains the follicles. These ligaments help keep the ovaries in place.
When released this travels down the fallopian tube into the uterus where it may become fertilized by a sperm. Located laterally to the left and right of the uterus and inferior to the fallopian tubes the ovaries are connected to the uterus via the ovarian ligaments. The ovaries are the female pelvic reproductive organs that house the ova and are also responsible for the production of sex hormones.
Ovary anatomy the ovaries are female reproductive organs that are akin to the testes in men. Given the anatomy and location of the ovaries it is easy to imagine the processes of ovulation and reproductionwhen luteinizing hormone levels are high enough to trigger ovulation one of the ovaries releases an egg from its follicle and it is carried into the fallopian tube. The ovaries are a pair of almond shaped glands that produce ova and the female sex hormones.
However unlike the testes the ovaries stop in the pelvis. The ovaries are paired female gonads of the reproductive and endocrine systems. The ovaries are paired oval organs attached to the posterior surface of the broad ligament of the uterus by the mesovarium a fold of peritoneum continuous with the outer surface of the ovaries.
The structures found within the ovary are undergoing constant changes throughout the oestrus cycle from the follicles containing oocytes. The outer layer of the ovary is the medulla contains the blood vessels and nerves. The filly is born with all the oocytes eggs in the ovary.
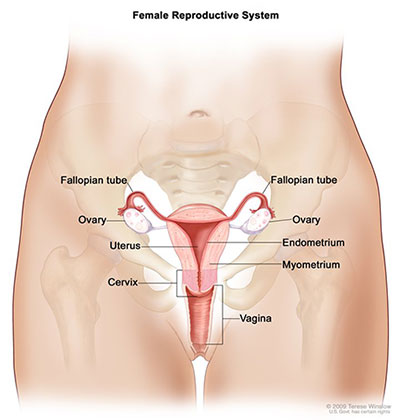
The ovaries are a pair of oval structures about 15 inches 4 cm long on either side of the uterus in the pelvic cavity fig. The ovary is the female gonad homologous to the male testes. The ovary is an organ found in the female reproductive system that produces an ovum.
There is an ovary from latin ovarium meaning egg nut found on each side of the body. Journey of an egg from the ovaries. Gross anatomy the ovaries are firm and ovoid in shape and measure approximately 15 30.
It is usually a paired organ in domestic species but in the bird only the left ovary is present.
 Easy Notes On Ovaries Learn In Just 4 Minutes Earth S Lab
Easy Notes On Ovaries Learn In Just 4 Minutes Earth S Lab
 Follicles Of The Ovary Learning Objectives Reproductive
Follicles Of The Ovary Learning Objectives Reproductive
 Ovary Diagram Anatomy Ovarian Follicle Corpus Luteum Anatomy
Ovary Diagram Anatomy Ovarian Follicle Corpus Luteum Anatomy
/the-steps-of-ovulation--a-primordial-follicle-grows-and-matures--before-being-released-by-the-ovary-into-the-fallopian-tube--141483857-5a39652a0d327a0037fa0016.jpg) Understanding What The Ovaries Do
Understanding What The Ovaries Do
 Anatomy Uterus Ovary Vagina Fallopian Tubes Ovarian
Anatomy Uterus Ovary Vagina Fallopian Tubes Ovarian
 Ovary Animal And Human Britannica
Ovary Animal And Human Britannica
 The Ovaries Structure Ligaments Vascular Supply Function
The Ovaries Structure Ligaments Vascular Supply Function
 Seer Training Salpingo Ovarian Peritoneal Functional Anatomy
Seer Training Salpingo Ovarian Peritoneal Functional Anatomy
 Vector Isolated Illustration Of Female Reproductive System Anatomy
Vector Isolated Illustration Of Female Reproductive System Anatomy
Week 10 Female Reproductive System Anatomy Phase 1
 Easy Notes On Ovaries Learn In Just 4 Minutes Earth S Lab
Easy Notes On Ovaries Learn In Just 4 Minutes Earth S Lab
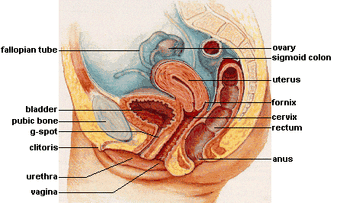 Ovaries Psychology Wiki Fandom
Ovaries Psychology Wiki Fandom
 Female Reproductive System Human Anatomy Uterus And Ovaries
Female Reproductive System Human Anatomy Uterus And Ovaries
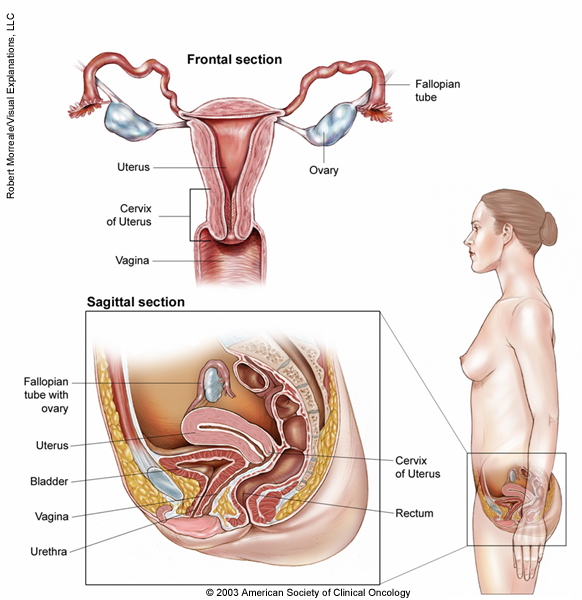 Ovarian Fallopian Tube And Peritoneal Cancer Medical
Ovarian Fallopian Tube And Peritoneal Cancer Medical
/male_female_gonads-58811e985f9b58bdb3e3dfe9.jpg) Male And Female Gonads Testes And Ovaries
Male And Female Gonads Testes And Ovaries
 Female Uterus Ovary Anatomical Model Anatomy Cross Section Nv Lifelike Anatomy Education Props Enlarged Edition Reproductive System
Female Uterus Ovary Anatomical Model Anatomy Cross Section Nv Lifelike Anatomy Education Props Enlarged Edition Reproductive System
 About Ovarian Cancer Spectrum Health
About Ovarian Cancer Spectrum Health
 The Female Reproductive System Boundless Anatomy And
The Female Reproductive System Boundless Anatomy And
 Anatomy Of An Ovarian Cancer Nature
Anatomy Of An Ovarian Cancer Nature
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/12472/Female_pelvis_superior_view__1_.png) Ovaries Anatomy And Embryology Kenhub
Ovaries Anatomy And Embryology Kenhub
Ovaries Anatomy And Physiology
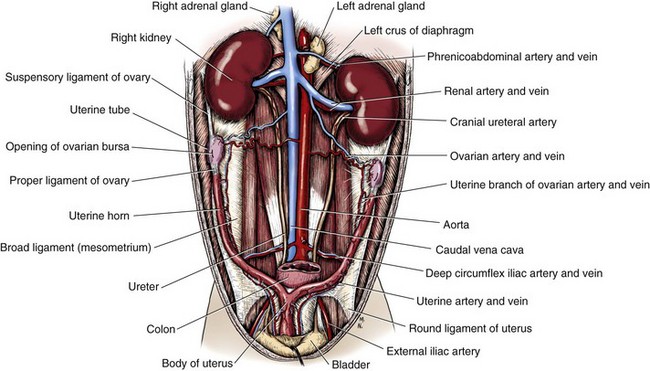 Ovaries And Uterus Veterian Key
Ovaries And Uterus Veterian Key
 Ovary Frontal Anatomy Physiology 2402 With Nioupin At
Ovary Frontal Anatomy Physiology 2402 With Nioupin At





Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar