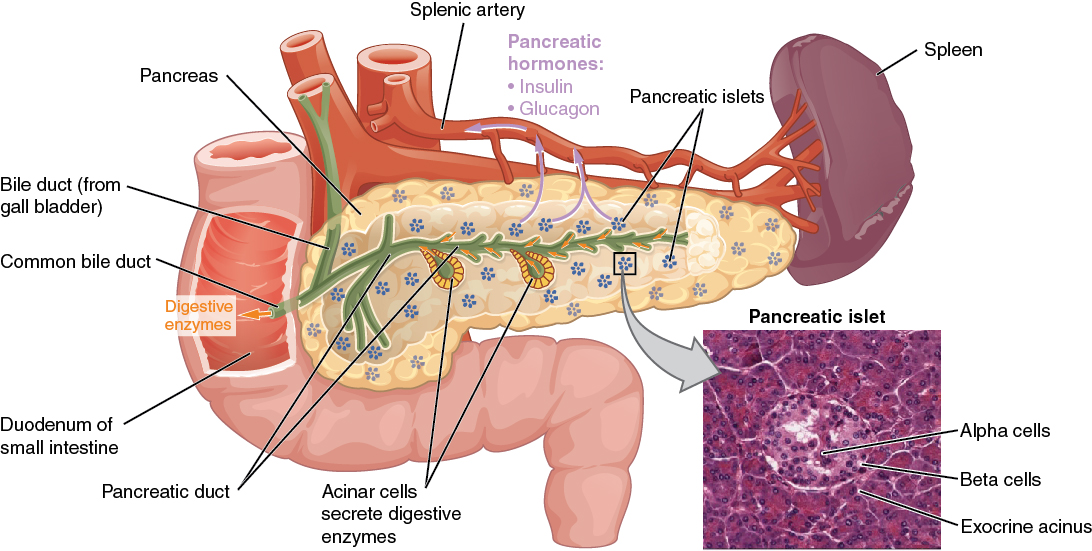
Beta cells which produce insulin. Anatomy of the pancreas the pancreas is an elongated tapered organ located across the back of the belly behind the stomach.
Pancreas Anatomy And Physiology
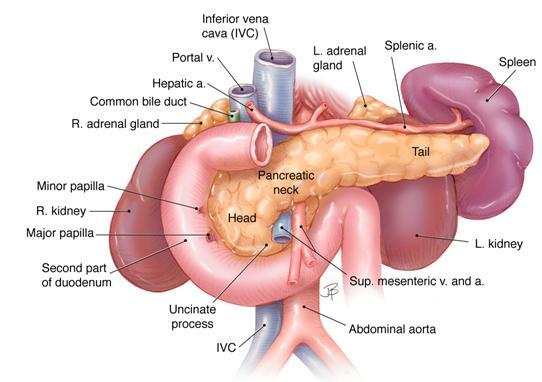
The body of the pancreas lies posterior to the distal portion of the stomach between the tail and the neck and is unlabeled in this drawing.
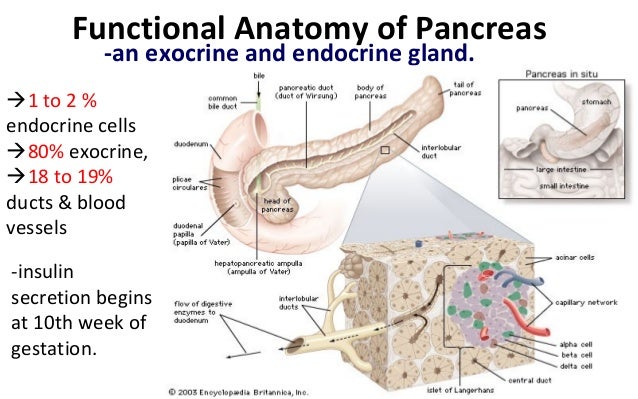
Anatomy and physiology of pancreas. The pancreas is one of those dual citizenship organs acting as both an endocrine organ and as an accessory organ of the digestive system see the digestive system. Pancreatic juice discharges into the duodenum through. The pancreas has both exocrine and endocrine functions.
The pancreas is a long slender organ most of which is located posterior to the bottom half of the stomach figure 1791. Pancreatitis is an inflammation of the pancreas. Your pancreas is about six inches long and sits deep in your abdomen partly behind your.
Delta cells which produce somatostatin. It may occur suddenly in a severe form as in acute pancreatitis or may continue as a slow long drawn illness as in chronic pancreatitis. The right side of the organcalled the headis the widest part of the organ and lies in the curve of the duodenum the first division of the small intestine.
The digestive enzymes produced by the exocrine pancreas 99 percent of the organ are by definition picked up by ducts near the pancreatic acini which ultimately empty into the small intestine. Anatomy pancreas is an organ situated in the upper part of ones abdomen. The pancreas is located in the craniodorsal part of the abdomen in close association.
Anatomy and physiology of the pancreas. The pancreas is a tubuloalveolar gland and has exocrine and endocrine tissues. Pancreas anatomy physiology introduction.
And pp cells which produce pancreatic polypeptide. The portion of the pancreas that lies anterior to the aorta is somewhat thinner than the adjacent portions of the head and body of the pancreas. The pancreatic islet cell types include alpha cells which produce glucagon.
Although it is primarily an exocrine gland secreting a variety of digestive enzymes the pancreas also has endocrine cells. In fact both your digestive system and endocrine system count on the pancreas to carry out vital functions.
 The Role And Anatomy Of The Pancreas
The Role And Anatomy Of The Pancreas
 The Cyclopaedia Of Anatomy And Physiology Anatomy
The Cyclopaedia Of Anatomy And Physiology Anatomy
 Gastrointestinal Tract 3 The Duodenum Liver And Pancreas
Gastrointestinal Tract 3 The Duodenum Liver And Pancreas
 Anatomy And Histology Of The Pancreas Pancreapedia
Anatomy And Histology Of The Pancreas Pancreapedia
 Pancreatitis Anatomy Physiology 101 With Dhere At Emory
Pancreatitis Anatomy Physiology 101 With Dhere At Emory
 Pancreas Clinical Anatomy And Physiology
Pancreas Clinical Anatomy And Physiology
 17 9 The Endocrine Pancreas Anatomy And Physiology
17 9 The Endocrine Pancreas Anatomy And Physiology
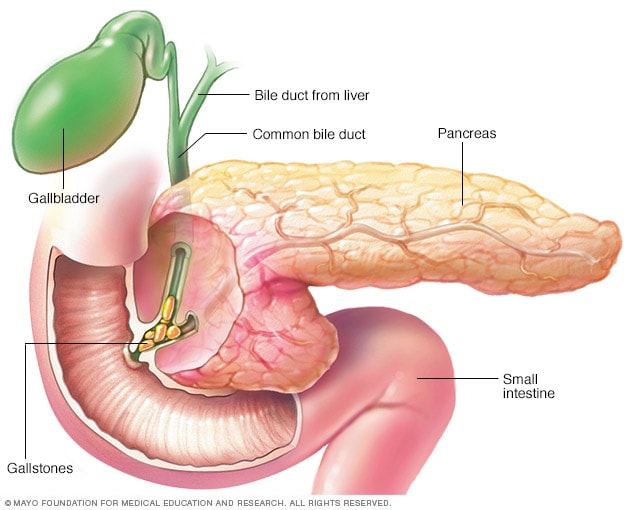 Pancreatitis Caused By Gallstones Mayo Clinic
Pancreatitis Caused By Gallstones Mayo Clinic
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/12288/anatomy-pancreatic-duct-system_english.jpg) Pancreas Histology Exocrine Endocrine Parts Function
Pancreas Histology Exocrine Endocrine Parts Function
 The Pancreas Boundless Anatomy And Physiology
The Pancreas Boundless Anatomy And Physiology
 Physiology Of The Pancreas Anatomy Medicine Com
Physiology Of The Pancreas Anatomy Medicine Com
Anatomy And Physiology Of The Pancreas Dm Authorstream
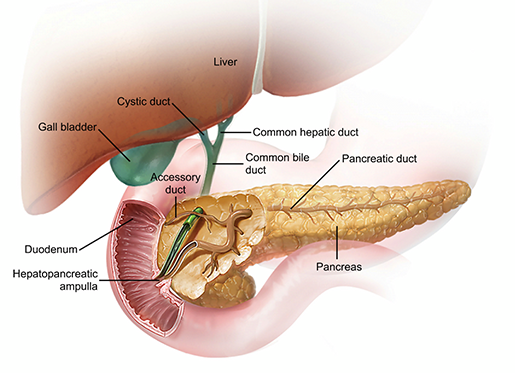 The Precious Pancreas Insulin Glucagon And Digestive Juices
The Precious Pancreas Insulin Glucagon And Digestive Juices
 An Overview Of The Pancreas Understanding Insulin And Diabetes
An Overview Of The Pancreas Understanding Insulin And Diabetes
 Anatomy And Histology Of The Pancreas Pancreapedia
Anatomy And Histology Of The Pancreas Pancreapedia
 Anatomy And Histology Of The Pancreas Pancreapedia
Anatomy And Histology Of The Pancreas Pancreapedia
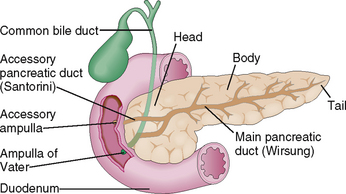 The Exocrine Pancreas Basicmedical Key
The Exocrine Pancreas Basicmedical Key
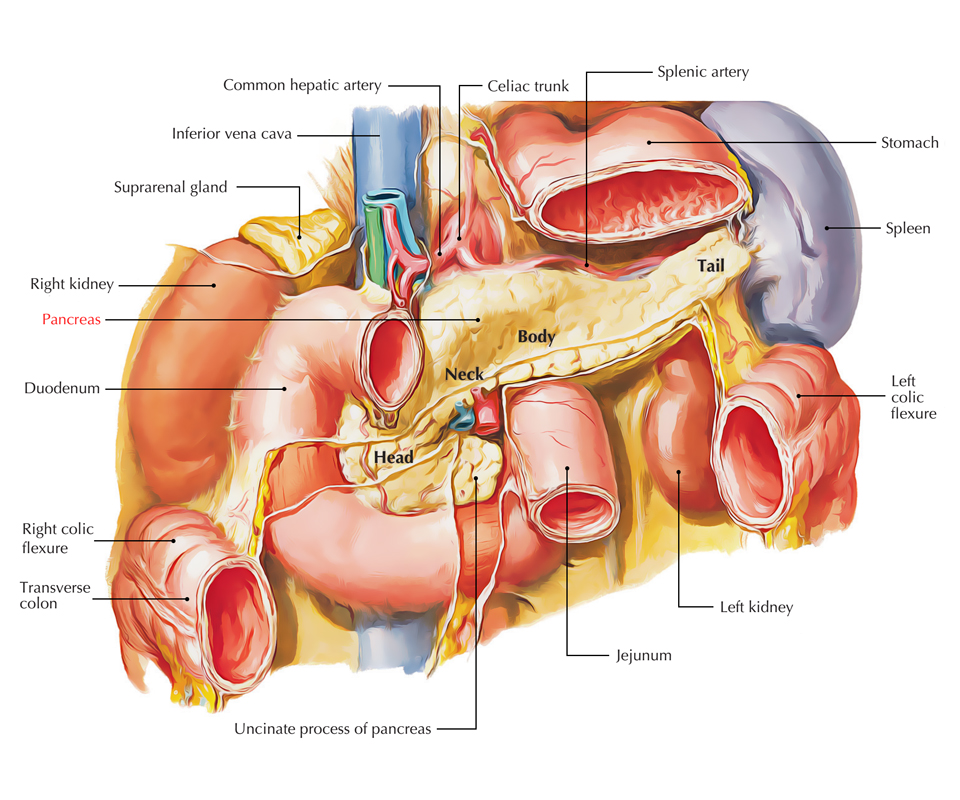 Easy Notes On Pancreas Learn In Just 4 Minutes Earth S Lab
Easy Notes On Pancreas Learn In Just 4 Minutes Earth S Lab
 Chapter 23 Digestive System Lectures 9 10 Part 4 Pancreas
Chapter 23 Digestive System Lectures 9 10 Part 4 Pancreas
Anatomy And Physiology Ii Pancreas Spleen Duodenum Model


 Physiology Of Thyroid And Pancreas Pptx
Physiology Of Thyroid And Pancreas Pptx
 Pathology Of The Pancreas Pathology A Modern Case Study
Pathology Of The Pancreas Pathology A Modern Case Study
 Pancreas Cool Stuff Pancreas Health Gastroenterology
Pancreas Cool Stuff Pancreas Health Gastroenterology

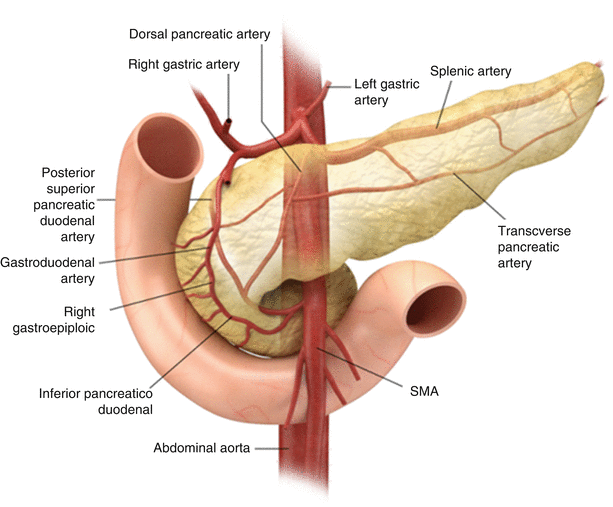
Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar