Firm rubbery tissue that cushions bones at joints. Cartilage is a resilient and smooth elastic tissue a rubber like padding that covers and protects the ends of long bones at the joints and is a structural component of the rib cage the ear the nose the bronchial tubes the intervertebral discs and many other body components.
While more rigid and less flexible than muscle cartilage is not as stiff as bone.
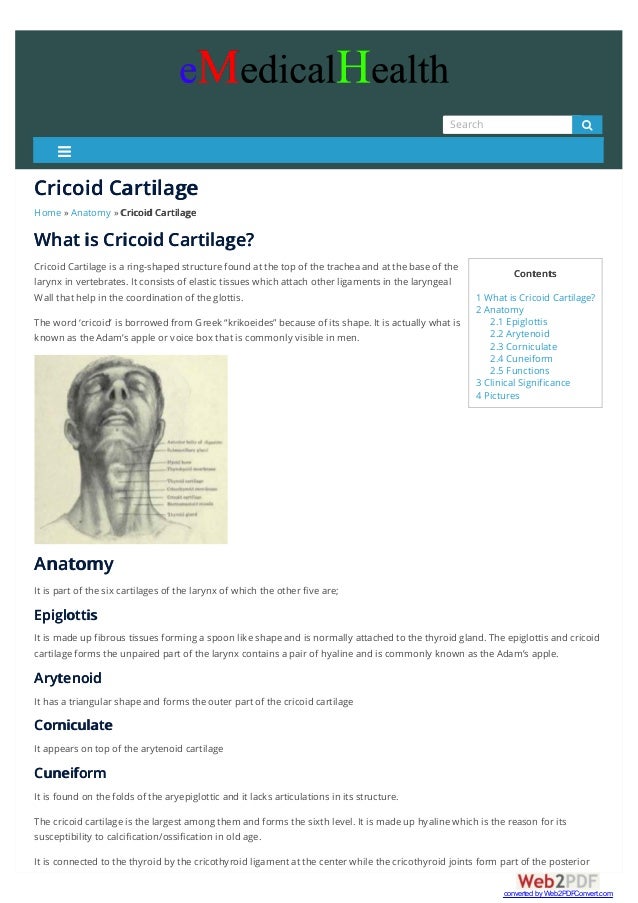
Cartilage anatomy definition. Cricoid cartilage a ringlike cartilage forming the lower and back part of the larynx. Jump to navigation jump to search. Cartilage is the only component of the skeletons of certain primitive vertebrates including lampreys and sharks.
Another integral type of connective tissue is cartilage. It is composed of a cartilage connective tissue forming the skeleton of mammalian embryos before bone formation begins and persisting in parts of the human skeleton into adulthood. Connective tissue is essential for our bodies to function properly.
Cartilage definition a firm elastic flexible type of connective tissue of a translucent whitish or yellowish color. A flexible kind of cartilage makes up other parts of the body such as the larynx and the outside parts of the ears. Cricoid cartilage a ringlike cartilage forming the lower and back part of the larynx.
With a pliable structure composed primarily of water this tissue type is also extremely tough. A flexible kind of cartilage makes up other parts of the body such as the larynx and the outside parts of the ears. Costal cartilage a bar of hyaline cartilage that attaches a rib to the sternum in the case of true ribs or to the immediately above rib in the case of the upper false ribs.
A strong flexible connective tissue that is found in various parts of the body including the joints the outer ear and the larynx. Cartilage is a robust and viscoelastic connective tissue that can be found in joints between bones the rib cage intervertebral discs the ear and the nose. Cartilage is found throughout the human body in areas such as the joints nose airway intervertebral discs of the spine and the ear.
Cartilage is a semi rigid but flexible avascular connective tissue found at various sites within the body. Costal cartilage a bar of hyaline cartilage that attaches a rib to the sternum in the case of true ribs or to the immediately above rib in the case of the upper false ribs. In the early development of most vertebrates the skeleton forms as cartilage before most of it hardens into bone.
Diarthrodial cartilage articular cartilage. Bone connective tissue provides structure and support adipose or fat connective tissue insulates and provides energy and blood connective tissue distributes oxygen to our tissues and removes carbon dioxide.
 Larynx Voice Box Definition Function Anatomy And Diagram
Larynx Voice Box Definition Function Anatomy And Diagram
 Hyaline Cartilage Definition Of Hyaline Cartilage By
Hyaline Cartilage Definition Of Hyaline Cartilage By
 Articular Cartilage Lesions Of The Knee Physiopedia
Articular Cartilage Lesions Of The Knee Physiopedia
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/skeletal_sys-5bd5e9fac9e77c00267ae289.jpg) Skeletal System Function And Components
Skeletal System Function And Components
 Hyaline Cartilage Definition Function Quiz Biology
Hyaline Cartilage Definition Function Quiz Biology
 Cartilage Definition Function And Types Biology Dictionary
Cartilage Definition Function And Types Biology Dictionary
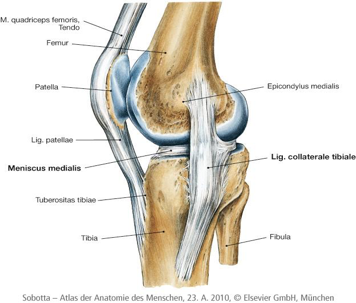
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/vector-illustration-of-a-meniscus-tear-and-surgery-871162428-03ac23d73f854954a8082f2ae3ce9219.jpg) Meniscus Vs Cartilage Tear Of The Knee
Meniscus Vs Cartilage Tear Of The Knee
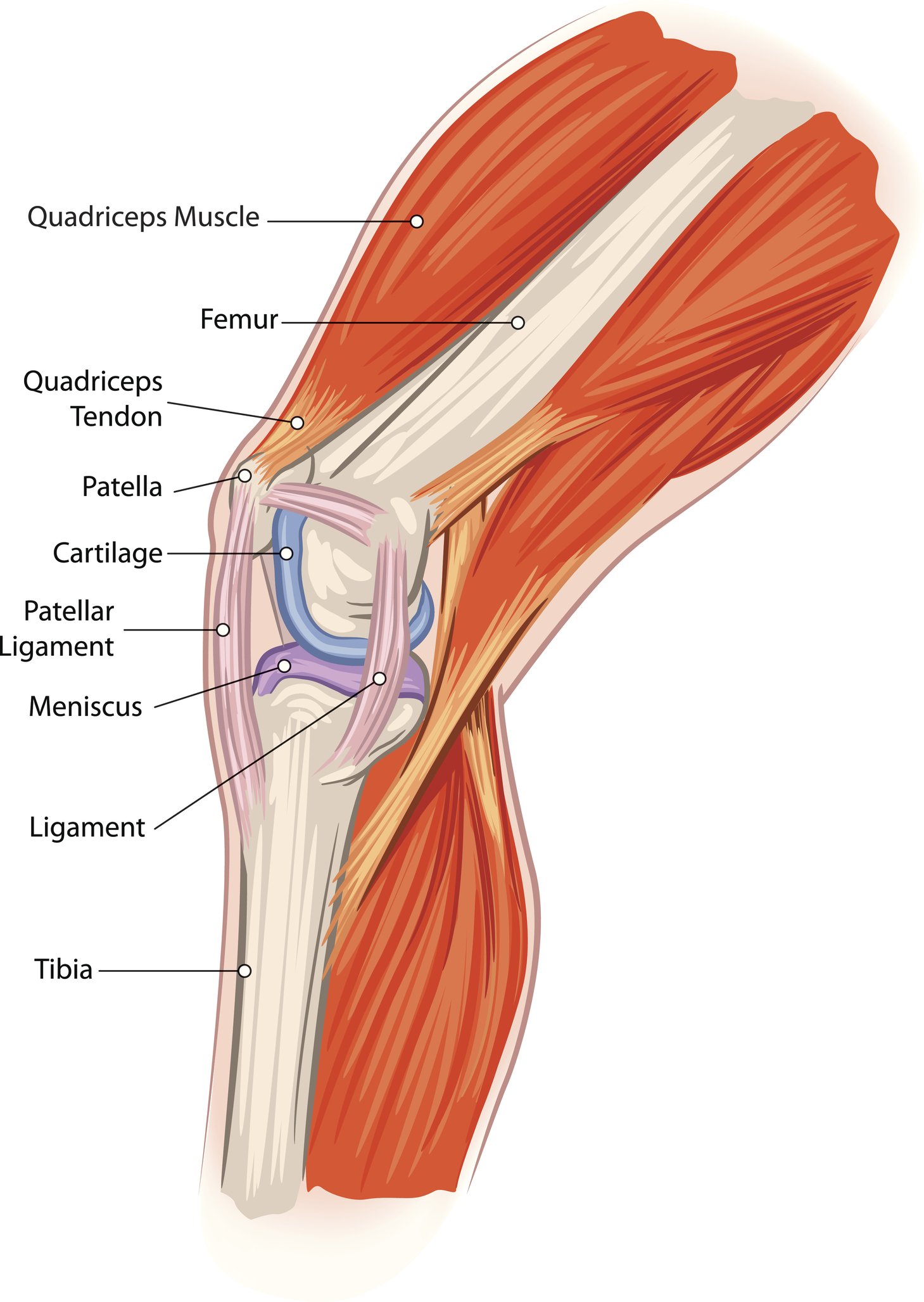
Functional Anatomy Of The Knee Movement And Stability
Osteochondritis Dissecans Orthoinfo Aaos

 Cartilage Definition Function And Types Biology Dictionary
Cartilage Definition Function And Types Biology Dictionary
 What Is Cartilage Definition Types Function Video
What Is Cartilage Definition Types Function Video
 What Is Cartilage Definition Types Function Video
What Is Cartilage Definition Types Function Video
 Patellar Fractures Broken Kneecap Orthoinfo Aaos
Patellar Fractures Broken Kneecap Orthoinfo Aaos

 A P 1 Skeletal System Anatomy Physiology 121 With Dr
A P 1 Skeletal System Anatomy Physiology 121 With Dr
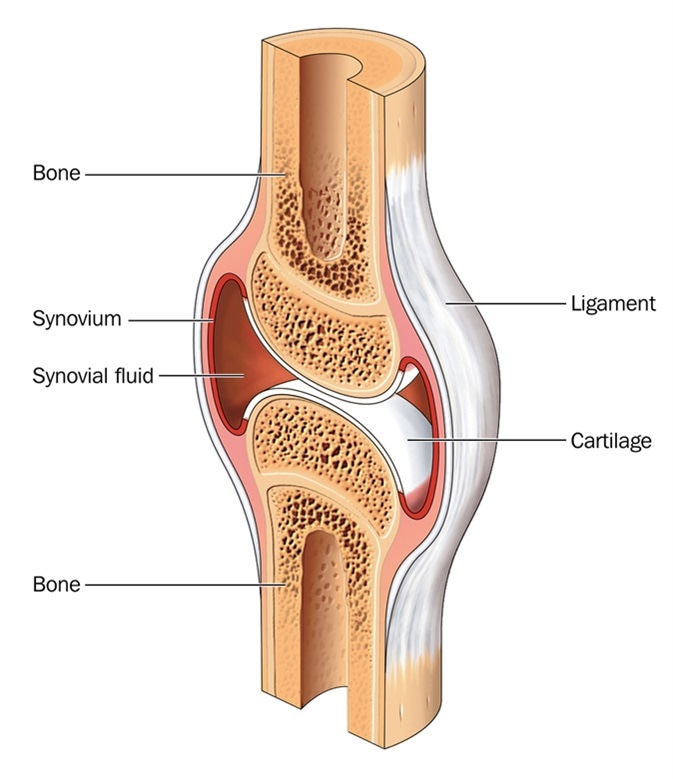
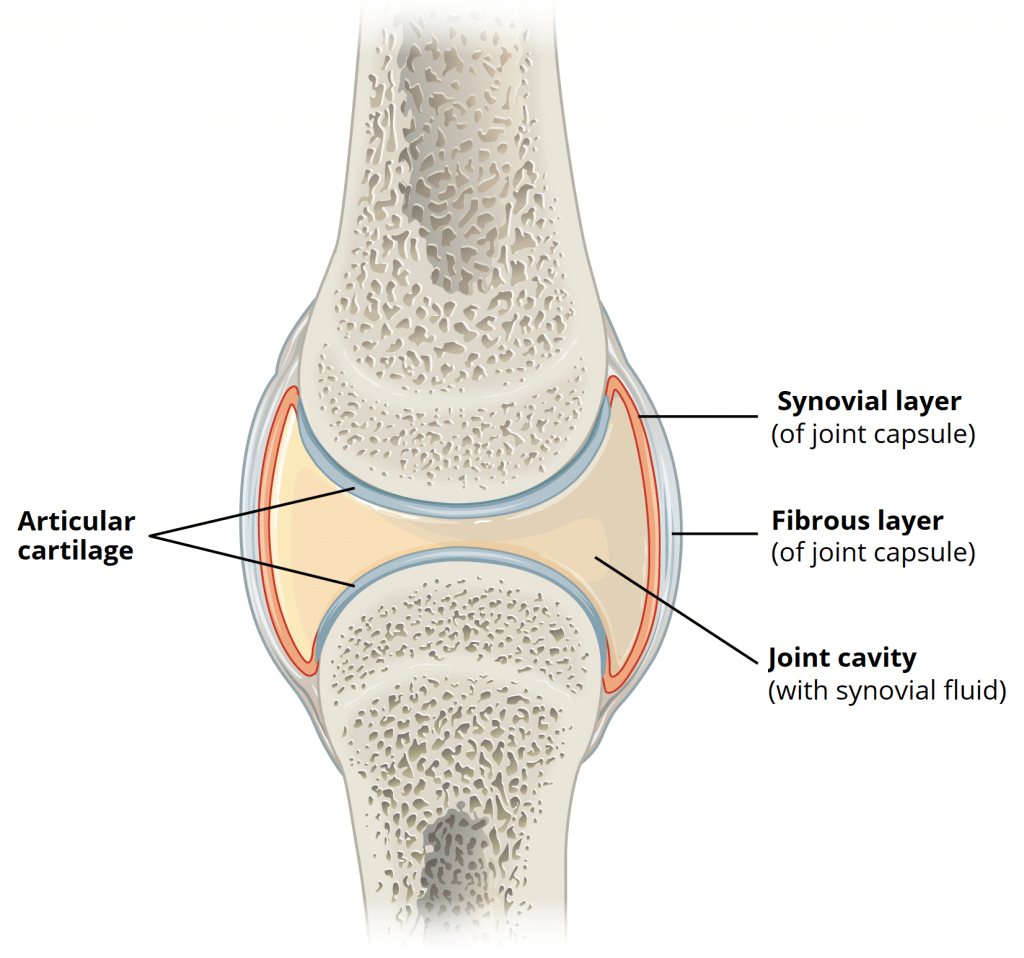 Structures Of A Synovial Joint Capsule Ligaments
Structures Of A Synovial Joint Capsule Ligaments
 Anatomy Bones And Cartilage At University Of Dundee Studyblue
Anatomy Bones And Cartilage At University Of Dundee Studyblue
 Picture Of The Ear Ear Conditions And Treatments
Picture Of The Ear Ear Conditions And Treatments
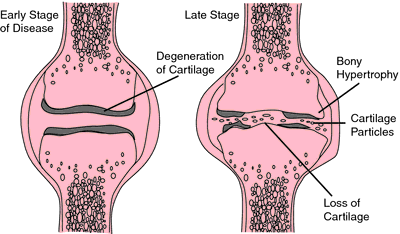
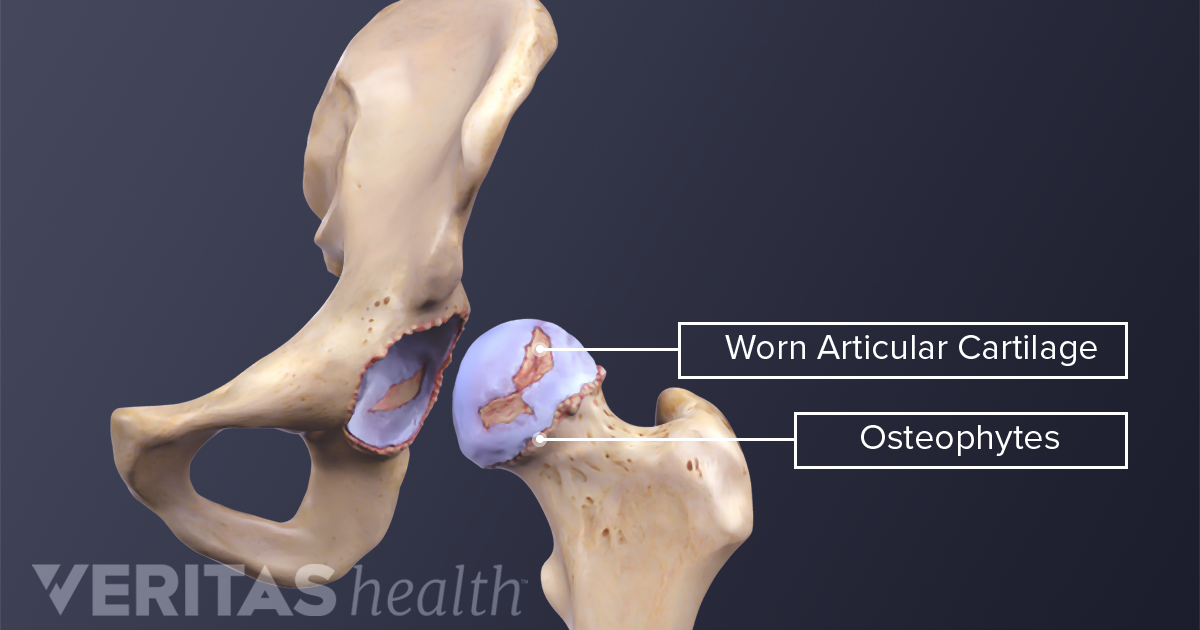
 Osteoarthritis Definition Of Osteoarthritis By Medical
Osteoarthritis Definition Of Osteoarthritis By Medical
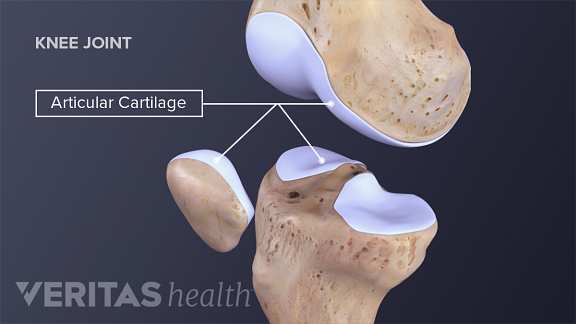
 Articular Cartilage Definition And Function Biology
Articular Cartilage Definition And Function Biology
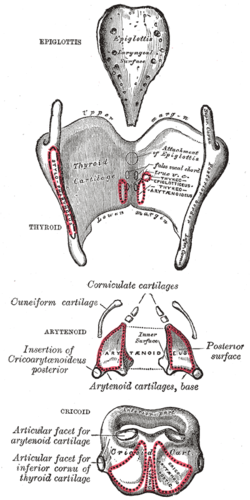
 Cricoid Cartilage Functions Definition Fracture Anatomy
Cricoid Cartilage Functions Definition Fracture Anatomy
 Cartilage Boundless Anatomy And Physiology
Cartilage Boundless Anatomy And Physiology
 Difference Between Bones And Cartilage With Comparison
Difference Between Bones And Cartilage With Comparison



Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar